

Background: AVT05, a recombinant human IgG1қ monoclonal antibody (mAb), is a proposed biosimilar to golimumab.
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to investigate the pharmacokinetic (PK) similarity, safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity between AVT05 and US-licensed and EU-approved reference product (RP) golimumab (US-RP and EU-RP, respectively) in healthy adult participants.
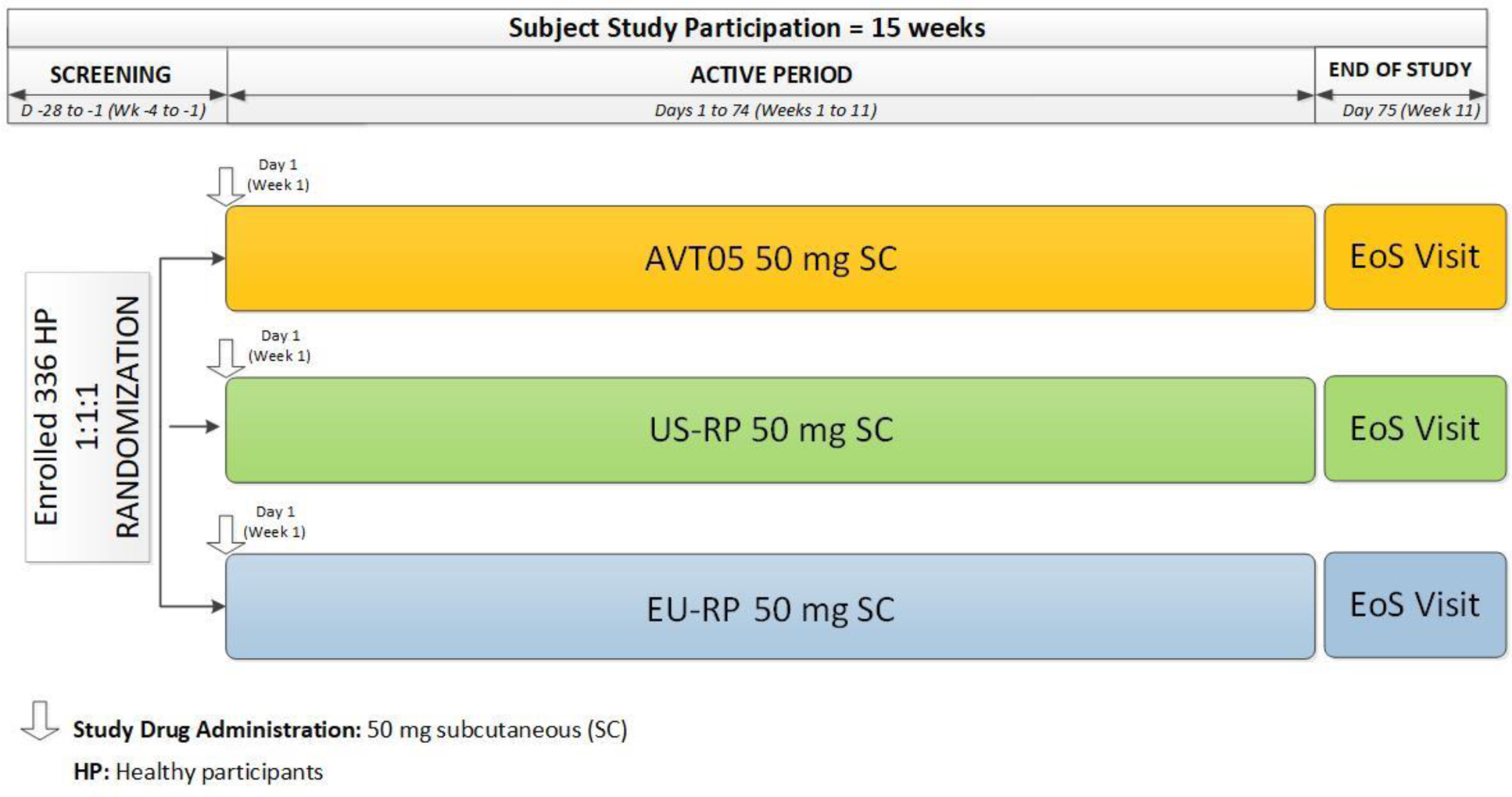
Methods: 336 healthy male and female participants aged 18 to 55 years were randomized in a 1:1:1 ratio to AVT05, US-RP or EU-RP ( Figure 1 ). Participants received a single 50 mg/0.5 mL subcutaneous injection on Day 1 and were followed until Day 75. The primary PK endpoints were maximum serum concentration (C max ) and area under the serum concentration-time curve from time zero to infinity (AUC 0-inf ). PK similarity is demonstrated if the 90% confidence intervals (CIs) for the geometric mean ratio (GMR) for both AUC 0-inf and C max contained entirely within the prespecified margins of 80.00% and 125.00% for all six pairwise treatment comparisons ( Figure 1 ). Secondary endpoints were additional PK parameters (AUC 0-t , T max , K el , t 1/2 , Vz/F, and CL/F), safety, tolerability and immunogenicity.
Results: Demographic and baseline characteristics were balanced between the treatment groups. The 90% CI for GMR of both primary PK parameters (AUC 0-inf and C max ) for all three pairwise comparisons was within the prespecified margins of 80.00% and 125.00% ( Figure 2 ). The secondary PK parameters were also comparable among the treatment arms. The mean serum golimumab concentrations through Day 75 post-dose were similar between treatment arms.
Overall, 66.1% of participants experienced at least one treatment-emergent adverse event (TEAE) during the study period. The frequency of TEAEs was comparable among the treatment arms. Majority of the TEAEs were mild to moderate in severity. There were 2 serious TEAEs reported (1(0.9%) each in AVT05 and EU-RP arms), neither of which were considered treatment-related. Local administration site reactions were mild in severity and observed in 6.1%, 10.8% and 5.5% of participants in the AVT05, EU-RP and US-RP arms, respectively. Overall, 87 (75.7%), 92 (82.9%) and 89 (80.9%) participants in the AVT05, EU-RP and US-RP arms, respectively, were anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) positive, among those 66 (57.4%), 68 (61.3%) and 61 (55.5%) participants, respectively, were neutralizing antibodies (NAbs) positive at least once during the study. The primary PK parameters (AUC 0-inf and C max ) were slightly lower in ADA positive participants compared to ADA negative ones.
Conclusion: Following a single dose administration, the study supported a demonstration of pharmacokinetic similarity between AVT05 and EU-and US-RP in healthy participants. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity profiles were comparable between the treatment arms.
REFERENCES: NIL.
Study Schematic for AVT05-GL-P01
PK Similarity Assessment of Serum Golimumab Pharmacokinetic Parameters by Treatment (Pharmacokinetic Population)
AUC 0-inf : Area under the concentration-curve from time zero extrapolated to infinite time. CI: confidence interval. C max : Maximum serum concentration. EU-RP: EU reference product. h: hour. LS: Least-Squares. mL: millilitre. ng: nanogram. US-RP: US reference product, PK: pharmacokinetic.
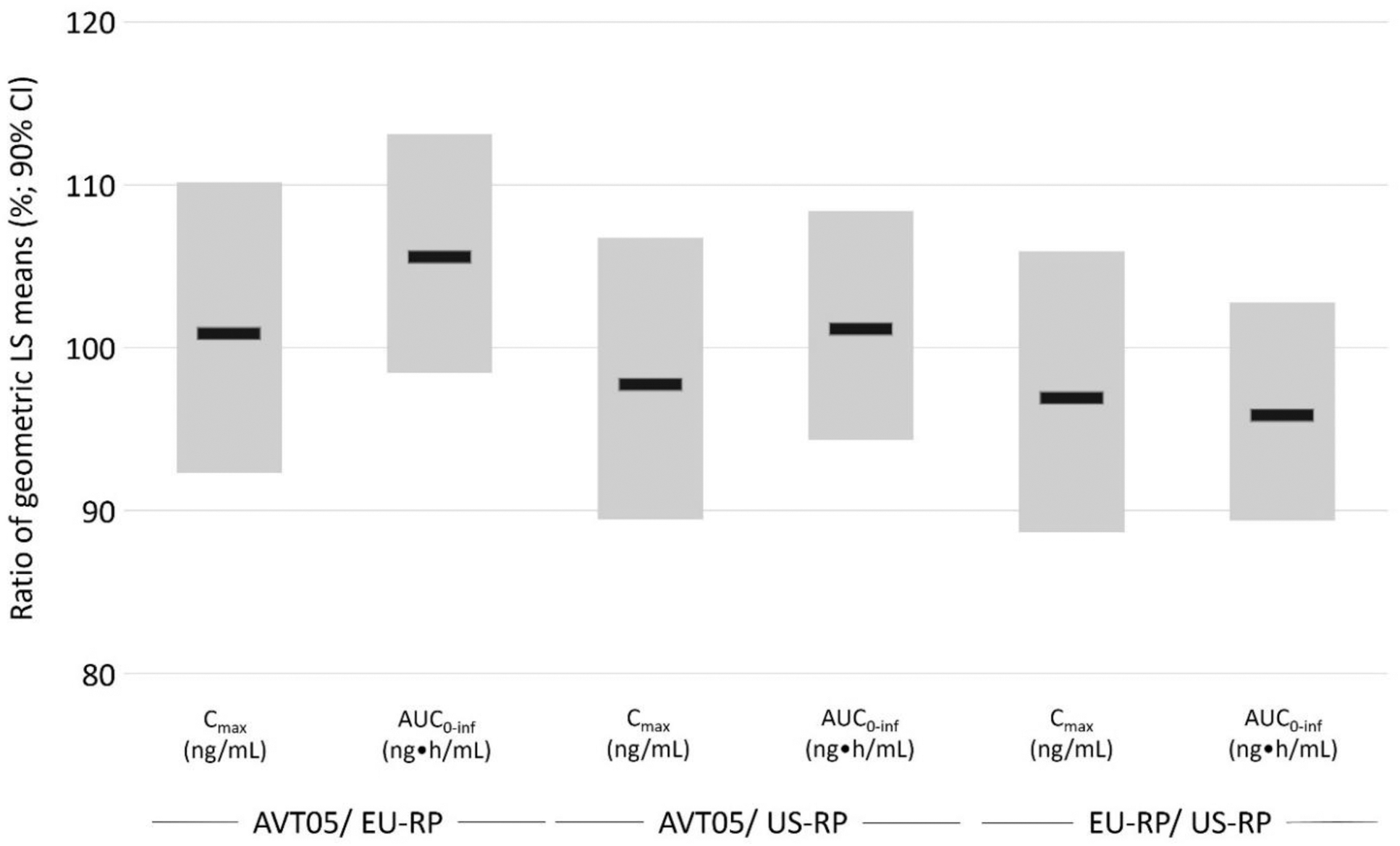
The statistical model is an analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) on the logarithmic scale (i.e. using natural log transformed values of C max , and AUC 0-inf ) and includes fixed effects for treatment, gender as factor, and body weight at baseline as the continuous covariate. 90% confidence interval for ratio of LS mean is constructed from the one-sided lower 5% CL and one-sided upper 5% CL. PK similarity is determined if, for each pairwise comparison, the 90% confidence intervals for the ratios of geometric LS means are entirely contained with the equivalence margin 80.00% to 125.00%.
Acknowledgements: The authors thank the study participants and all the investigators who contributed. The authors additionally thank Shital Desai and Lorna Rettig of Alvotech for medical writing assistance.
Disclosure of Interests: Christopher Wynne New Zealand Clinical Research, Ulrike Lorch Ulrike Lorch is employee of Richmond Pharmacology Ltd. that received payment for carrying out the study., Edrich Krantz Edrich Krantz is employee of Farmovs Integrated research solutions, Bloemfontein, South Africa that received payment for carrying out the study., Rohit Katial Rohit Katial is employee of, and hold shares in, New Zealand Clinical Research, Auckland, New Zealand that received payment for carrying out the study., Thomas Ashdown Thomas Ashdown are employees of Richmond Pharmacology Ltd. that received payment for carrying out the study., Fausto Berti Fausto Berti is employees at Alvotech.