

Background: One of the main characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is angiogenesis, which is linked to both the disease’s activity and duration. Two key proteins, vimentin and αvβ3 integrin, are critically involved in angiogenesis in RA. As a result, both may be used as diagnostic candidates for early detection and precise RA treatment. Positron emission tomography (PET) scans using radiotracers for αvβ3 and vimentin may provide non-invasive monitoring of angiogenesis which is currently being investigated in a rat model of arthritis.
Objectives: To investigate the potential of integrin and vimentin as targets for molecular imaging of angiogenesis in RA in a preclinical Antigen-Induced Arthritis (AIA) rat model of arthritis.
Methods: AIA rats’ knee tissues were examined using immunohistochemical (IHC) staining to determine the expression of vimentin and integrin αvβ3. For both targets we have PET tracers available. In the AIA model, following systemic immunization by injecting a mixture of methylated bovine serum albumin (mBSA) in complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA) and a customized Bordetella pertussis (CBP) antigen, arthritis is induced in one knee with the contralateral knee serving as control [1]. QuPath software was used to analyze stained sections from AIA and their contralateral control knees, and healthy rat knees (mean ± SEM). In addition to IHC, we investigated the inhibitory effects of microdose Fluciclatide, a small synthetic cyclic peptide that has a high affinity for integrins αvβ3/5. This was performed in a 3D spheroid angiogenesis model [2]. Statistical analysis involved one-way ANOVA for all experiments (n=3-6).
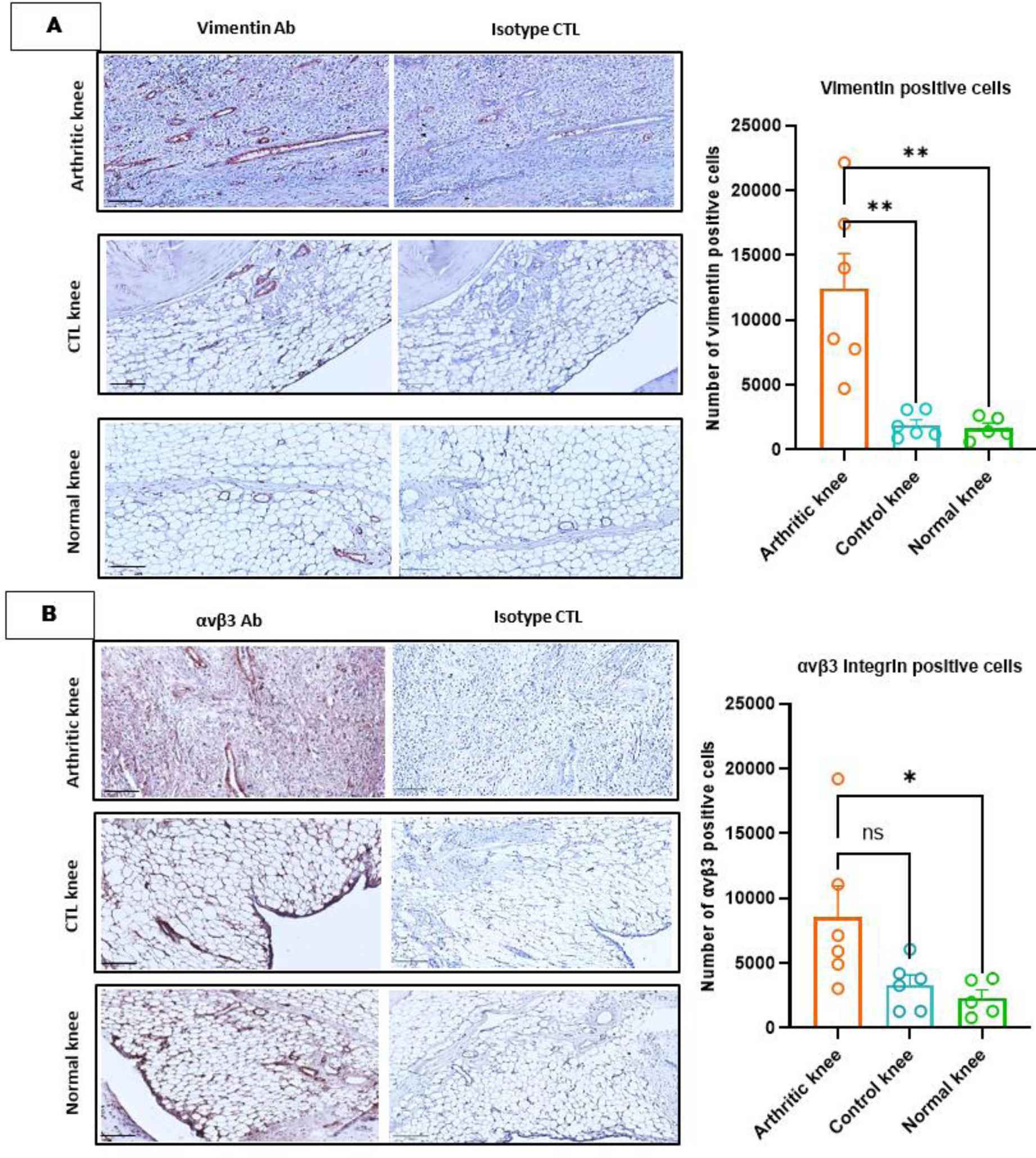
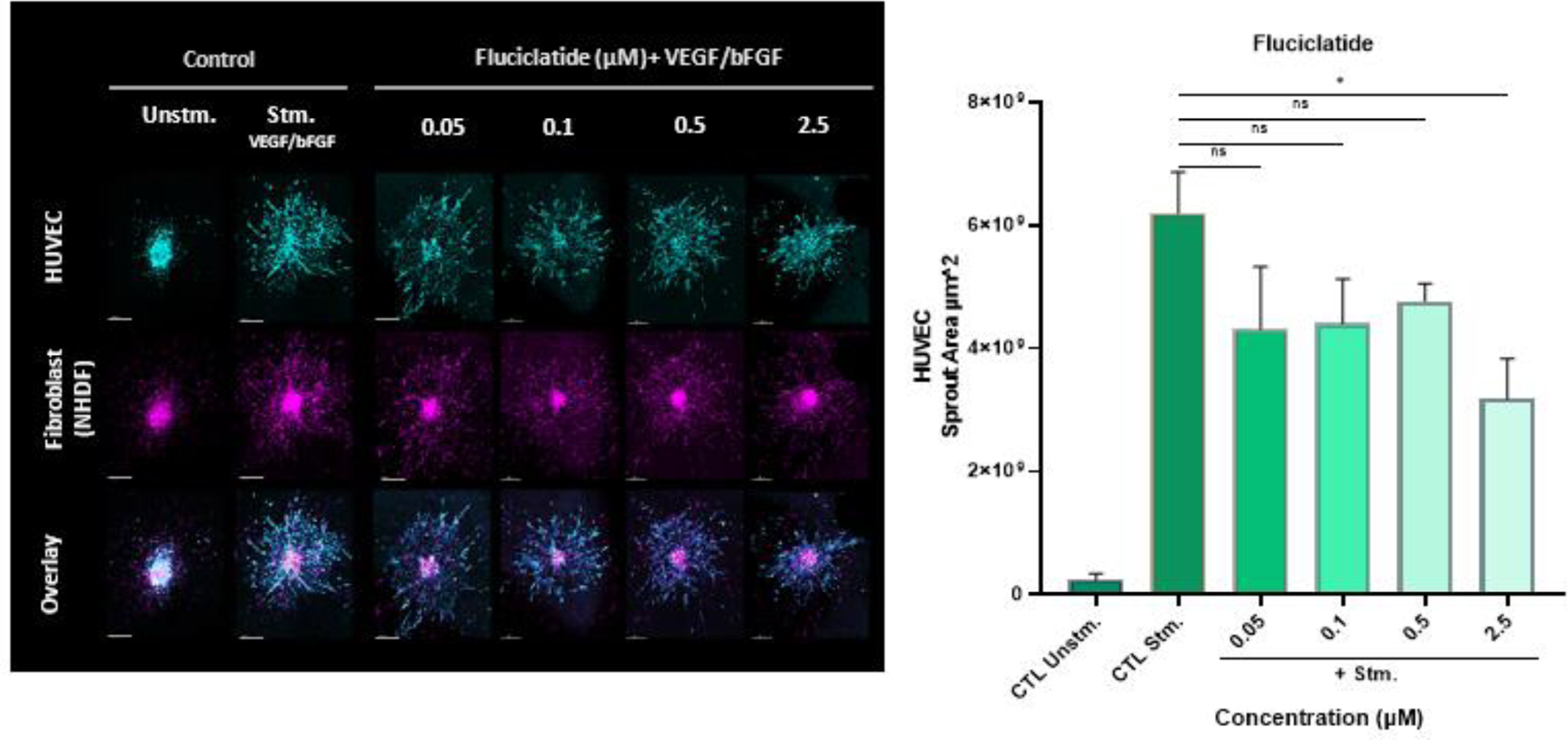
Results: In arthritic knee tissues, vimentin expression was markedly and significantly increased in arthritic compared to both control and normal knees (6.5 and 7.5 fold respectively, p≤ 0.001) (Figure 1A). Additionally, αvβ3 expression was elevated in arthritic knees compared to normal rat knees (3.7-fold, p<0.05), and contralateral knees (2.6-fold), however this difference did not achieve statistical significance (Figure 1B). With demonstrated efficacy in cancer imaging research, [ 18 F]-Fluciclatide has potential in RA imaging as well. The 3D spheroid angiogenesis model demonstrated that Fluciclatide at microdoses ≤ 0.5 μM does not exhibit inhibitory biologic effects, making it a viable agent for in vivo imaging (Figure 2).
Conclusion: The current study shows that the AIA model is suitable to study novel PET tracers targeting both vimentin and integrin αvβ3 for angiogenesis imaging in arthritis. Moreover, markedly increased vimentin and integrin αvβ3 expression in arthritic knees underscores aberrant angiogenesis that provide valuable insights into arthritis pathology. Ongoing PET imaging with [ 18 F]-Fluciclatide for αvβ3 [3] and 89 Zr-anti-vimentin nanobodies [4] holds promise for precise visualization and assessment of angiogenesis in RA.
REFERENCES: [1] Chandrupatla DM, et al. Biomed Res Int . 2015;2015:509295.
[2] Maracle, C.X., et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017;56(2):294-302.
[3] Battle, M.R., et al. J Nucl Med . 2011;52(3):424-430.
[4] van Beijnum, J.R., et al. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):2842.
IHC staining of vimentin (A) and integrin αvβ3 (B) in AIA and healthy rats knee tissues. The scale bars represent 200 μm for the reference images and 100 μm for the magnified images. Quantitative analysis of stained sections from AIA knees, their respective control knees, as well as healthy rat knees was conducted using QuPath software by training object classifier for recognizing positive cells. The data is presented as mean ± SEM for AIA rats (n=6) and normal rats (n=5). (**p≤ 0.001, *p< 0.05, ns:not significant)
Representative confocal pictures (10X) of the 3D spheroid-based model of angiogenesis composed of endothelial cells (EC) (cyan) and normal human dermal fibroblasts (NHDF) (magenta) and impact of microdosing of Fluciclatide on sprouting. Cell tracker dyes was used to monitor cells. Significant induction of sprouting was observed following stimulation with the growth factors VEGF/bFGF. Data represents Mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. All the scale bars are 200 μm. (* p<0.05, ns: not significant)
REFERENCES: NIL.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.