

Background: Fibroblast activation protein α (FAPα) is a cell surface serine protease expressed by activated fibroblasts, and it was found that FAP-deficiency mice have less cartilage degradation, inflammation, and bone erosion. Moreover, the fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients have higher expression of FAPα in synovium tissue.
Objectives: We evaluated the ability of the 68 Ga-labelled FAPI as a diagnostic method for RA diagnosis. We also investigated that 177 Lu-labelled FAPI could lead to amelioration of RA by depletion of FAP + FLS and subsequent inhibition of lymphocyte function.
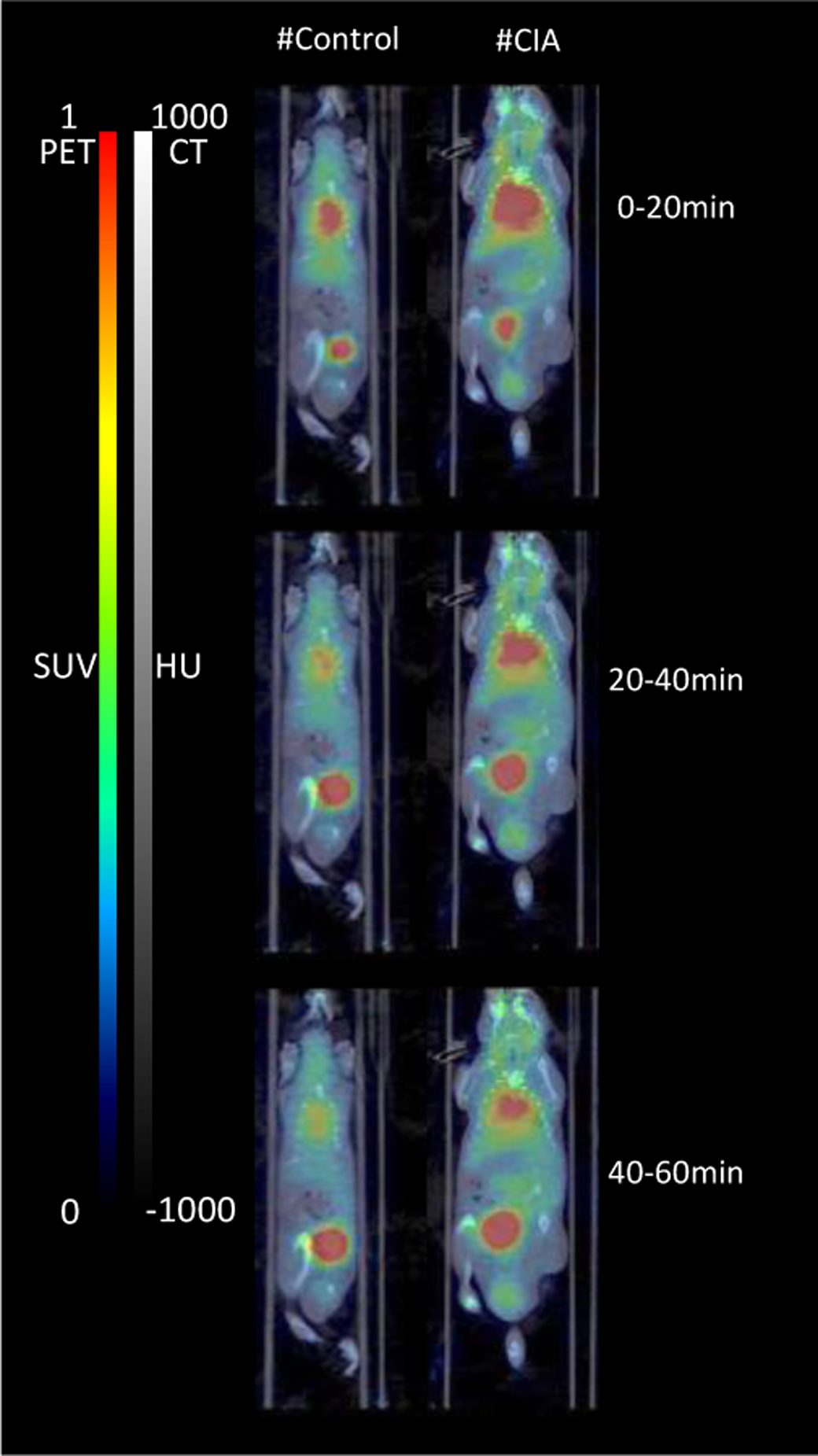
Methods: The collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) DBA1/J mice were used as the inflammatory arthritis model. The images from 68 Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT examinations of CIA mice were analyzed, and the tracer uptakes would be quantified by the standardized uptake value (SUV) and compared with the disease score and incidence rate. Then 177 Lu-labeled FAPI-04 was used to target FAPα-expressed cells in CIA mice as radiation therapy.
Results: The paws in CIA mice with higher SUV since 1 week after booster immunization had a higher incidence rate of arthritis. The SUV also correlated with arthritis scores because the expression of FAPα increased in CIA mice. Moreover, the 177 Lu-labeled FAPI-04 treated group has a lower arthritis score compared with untreated CIA mice.
Conclusion: We provide the basic features of FAPα- expressed FLSs in RA pathophysiology and advances in targeted therapies. We present that Ga 68 -FAPI-04 can be a useful tracer for predicting arthritis, and targeting to FAPα- expressed FLSs may be a potential way for arthritis treatment.
Biodistribution and accumulation of 68Ga-FAPI-04 in collagen-induced arthritis mice
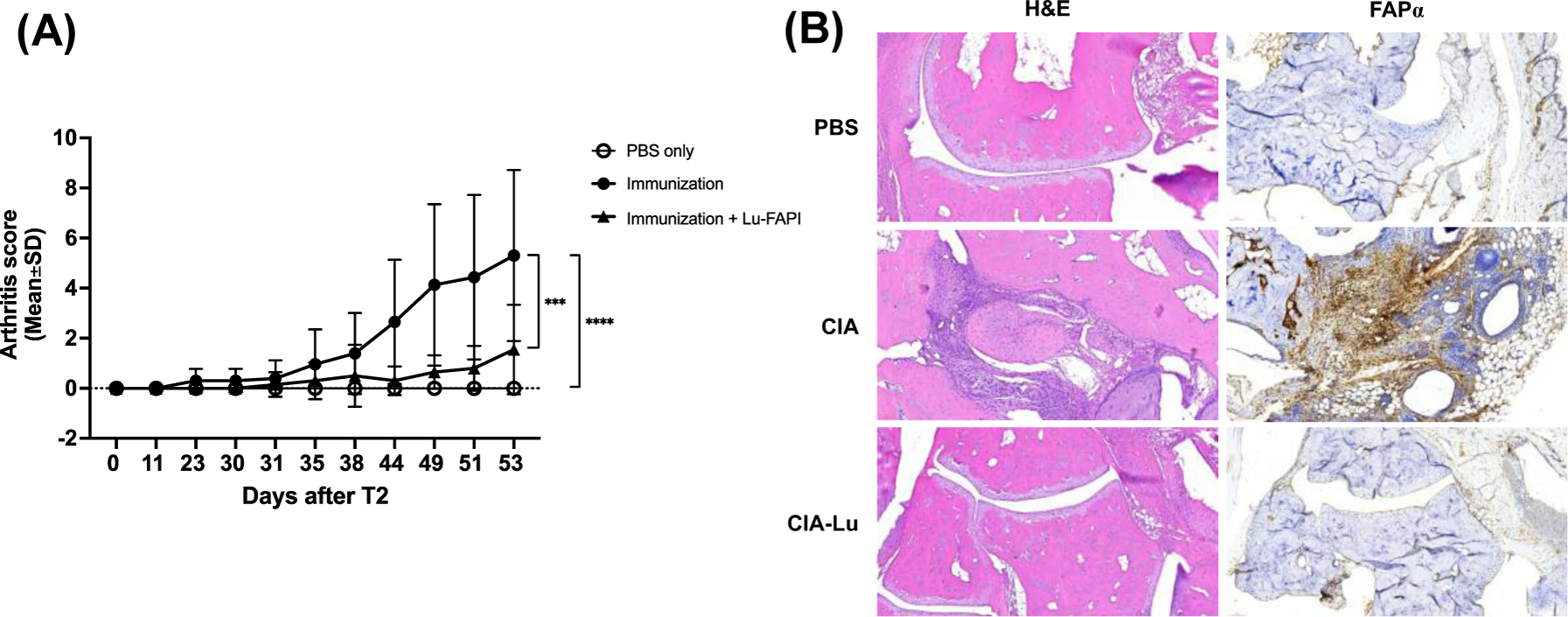
The assessment of the effect of 177Lu-labelled FAPI on arthritis severity The mice were immunized by type II bovine collagen, and injected 177Ga-FAPI-04 via IV injection at 31after T2. (A) The arthritis scores were recorded and presented as graph. (B) The mouse paw tissues were fixed, decalcified and embedded in paraffin for each section. The sections were stained with H&E and IHC staining. (*, p-value< 0.05 by one-way ANOVA)
REFERENCES: NIL.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by grants from the Keelung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan, R.O.C. (CMRPG2K0172 and CMRPG2K0173) and NSTC-Granted Research Projects (NSTC 112-2314-B-182 -015 -MY3).
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.