

Background: Epigenetic processes promote development of pathogenic cell types in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), but precise molecular mechanisms behind these effects remain largely unexplored. Survivin has recently been identified as important regulator of histone deposition on chromatin preventing accumulation of the repressive H3K27me3 mark (1,2).
Objectives: In this study, we investigate if survivin affects acetylation of histone H3K27 in CD4+ T cells, and how this is associated with effect of immunosuppressive RA treatment.
Methods: Chromatin of CD4+ cells (n=12) treated with or without the survivin-inhibitor YM155 was immunoprecipitated with antibodies to histone H3K27ac and sequenced (ChIP-seq, Illumina). Peaks with change >30% in deposition of H3K27ac upon YM155-treatment were annotated to the genomic regulatory elements (RE) via GeneHancer database, which also gave information of genes connected to these RE. Transcriptomics of CD4+ cells isolated from RA patients treated with MTX (n=18), TNFi (n=10), JAKi (n=24) and having no DMARDs (n=7), by RNA sequencing, deposited GSE201669. The genes differentially expressed (DEG, nominal p<0.05) upon JAKi-treatment compared to other treatments were identified by DESeq2 (R-studio, Bioconductor). External transcriptome datasets of CD4+ cells isolated from patients before and after treatment with MTX (n = 28, GSE176440), abatacept (n = 14, GSE121827), and tocilizumab (n = 12, GSE113156). Treatment affected DEG were identified by DESeq2 (R-studio, Bioconductor). The enrichment analysis of DEG for biological processes within Gene ontology library were analyzed through String database. Over-representation analysis was done at
Results: Inhibiting survivin with YM155 in CD4+ cells induced a significant (>30%) change in 17% (1967 of 11529 peaks) of H3K27ac-peaks. These survivin-sensitive H3K27ac peaks were located within 339 cis-RE, connected to 1022 protein-coding genes expressed in CD4+ cells. Biological pathway analysis revealed that the top biological processes enriched among the these 1022 genes were mRNA metabolic process (GO:0016071 FDR = 0.0043), Cellular response to DNA damage stimulus (GO:0006974 FDR = 0.0029), DNA metabolic process (GO:0006259 FDR 0.033), RNA processing (GO:0006396 FDR 0.00058), RNA metabolic process (GO:0016070 FDR = 2.70e-05), and Cellular response to stress (GO:0033554 FDR = 0.00099). Together, these processes has a significant overlap and comprised 28% (286 of 1022) of the genes connected to the changed H3K27ac- genes.
Immunosuppressive treatment had a significant imprint on H3K27ac connected genes, which were found over-represented among the DEG after treatment with MTX (p = 6e-49, OR = 1.77), abatacept (p = 1.6e-25, OR = 2.31), tocilizumab (p = 1.9e-7, OR = 1.51) and JAKi (p = 0, OR = 3.52) (all by Enrichr: Epigenomics roadmap). Furthermore, we found that JAKi and Mtx affected the same processes of transcription, RNA processing and translation; TGFb and SMAD signaling; NOTCH signaling; and DNA damage response as controlled by the genes connected to changed H3K27ac (JAKi p = 0.010 OR = ∞, Mtx p = 0.0001 OR = 3.2).
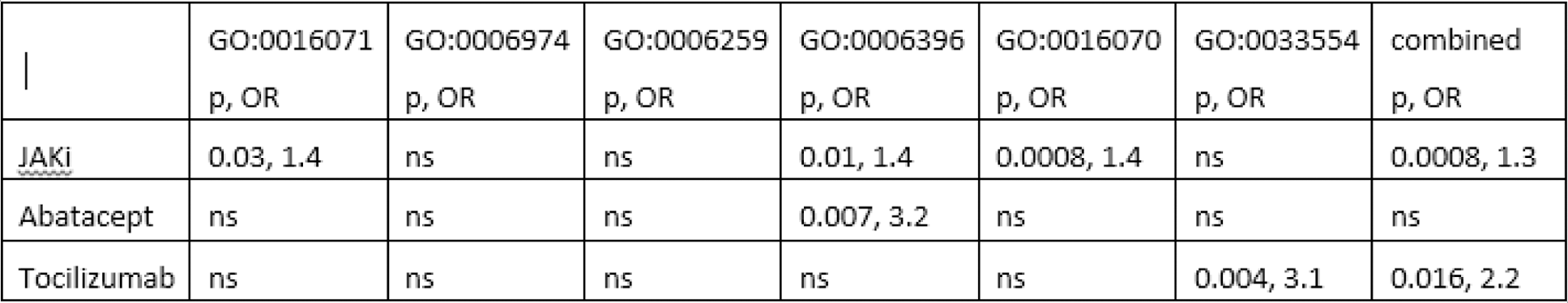
In the top enriched GO:BP of the genes connected to changed H3K27ac, the DEG of the treatments were enriched to different extent (Table 1). In total, JAKi affected 219, abatacept 17, tocilizubam 17 and MTX 48 of the genes within the top GO:BP.
Conclusion: Immunosuppressive treatment affects genes under the epigenetic control in transcription, RNA processing and DNA damage response exerted through the survivin-sensitive H3K27ac deposition. Molecular signature of CD4+T cells reflecting activation of these processes could assist individual treatment choice in RA patients.
Table 1.
REFERENCES: [1] Jensen, M.. et al. (2023) Survivin prevents the polycomb repressor complex 2 from methylating histone 3 lysine 27. iScience , 26 , 106976.
[2] Erlandsson, M.C.. et al. (2022) Survivin promotes a glycolytic switch in CD4(+) T cells by suppressing the transcription of PFKFB3 in rheumatoid arthritis. iScience , 25 , 105526.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.