

Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) pathogenesis involves a range of immune cells, for instance T-cells, neutrophils and macrophages. They produce proinflammatory factors, such as proteolytic enzymes, which interact with tissues and tissue components such as collagens, leading to a release of unique tissue and cellular metabolites. Some of these reflect immune cell activity when measured in blood. From previous studies, we know that T-cell activity may be quantified by measuring C4G, a metabolite of Granzyme B (a cytotoxic granule enzyme) mediated degradation of type IV collagen 1 . Macrophage activity may be quantified by measuring a fragment of citrullinated and MMP-degraded vimentin, VICM 2 . Neutrophil activity may be quantified by measuring CPa9-HNE, a specific fragment generated by human neutrophil elastase degradation of calprotectin 3 . Quantifying the unique metabolites reflecting the immune cell activity may provide a deeper understanding of the tissues affected by RA, and be more relevant to disease activity and progression than simply quantifying the immune cell number or cytokines 4 .
Objectives: To investigate the association between the unique immune cell activity metabolites (UCAMs) VICM, C4G and CPa9-HNE, and clinical outcomes in RA before and after intervention with an anti-IL6R treatment.
Methods: This is an explorative post-hoc analysis of left-over samples from the AMBITION trial (NCT00109408). The three UCAMs biomarkers were measured pre- and post-treatment in serum samples (8 weeks) in 169 RA patients treated with either tocilizumab (TCZ, 8 mg/kg), placebo or methotrexate (MTX) monotherapy (7.5-20 mg/kg). Biomarker levels were correlated to clinical outcomes by Spearman’s correlation. Comparison between treatment and response groups were done by ANCOVA, adjusted for age, sex, BMI, and disease duration.
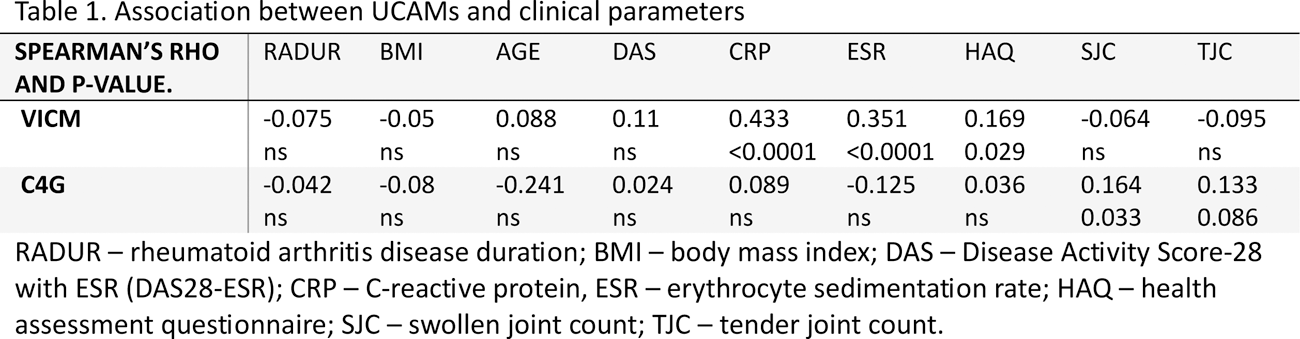
Results: Patients had a median (IQR) age of 50 (42-59) and were primarily female (79%) and white (88%). Median disease duration and DAS28-ESR were 3.1 (0.6-10) years and 6.9 (6.2-7.4), respectively. Interestingly, baseline median level of CPa9-HNE was 30 (10-52), but 108 samples were not quantifiable. In comparison, the reported CPa9-HNE median level in serum of active Crohn’s disease patients were 275 (195-414 ) 3 . Furthermore, VICM was significantly correlated with CRP, ESR and HAQ (Table 1), while C4G was correlated to SJC. Additionally, patients treated with TCZ had significantly decreased levels of VICM and C4G compared to the placebo group (Figure 1).
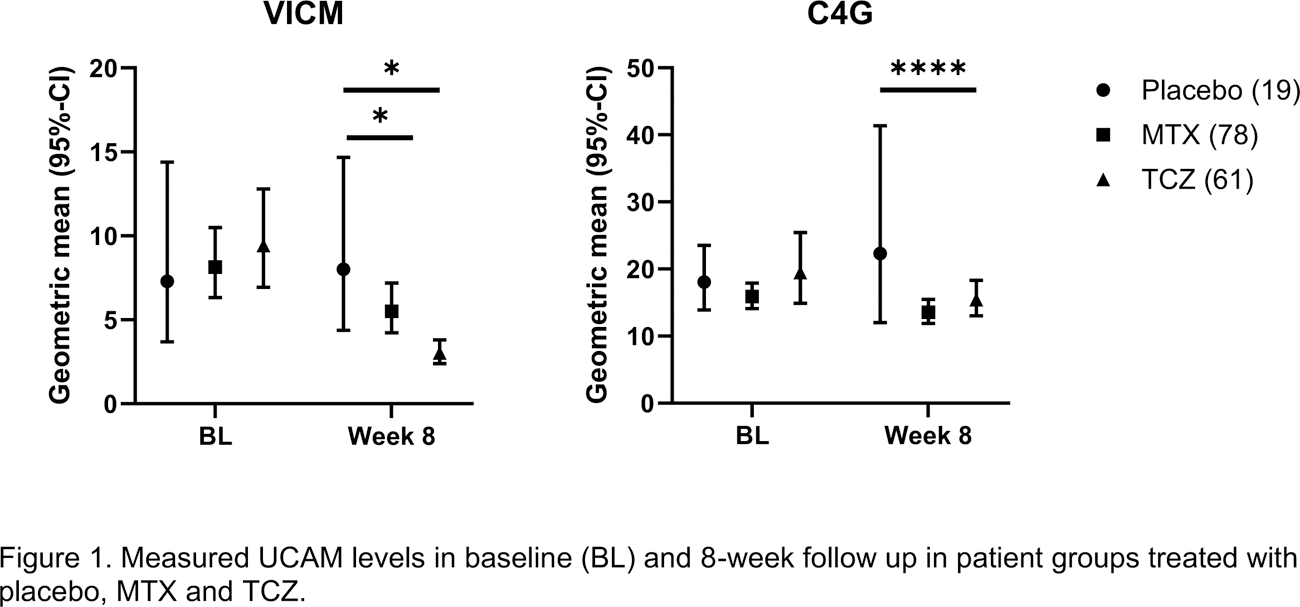
Conclusion: The proven efficacious treatment anti-IL-6R demonstrated a clear effect on T-cell and macrophage derived UCAMs. VICM (macrophage activity) and C4G (T-cell activity) were both quantifiable and associated with different clinical measures and were modulated by tocilizumab – an anti-IL6R treatment. The calprotectin marker CPa9-HNE was unquantifiable in a significant number of patients, indicating that neutrophil activity is low in RA. C4G is a novel blood marker measuring granzyme B action on type IV collagen and, therefore, a reflection of deep tissue remodeling induced directly by T-cells.
REFERENCES: [1] Jensen, C. et al. Granzyme B Degraded Type IV Collagen Products in Serum Identify Melanoma Patients Responding to Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Cancers (Basel) 12, 1–15 (2020).
[2] Mortensen JH et al. The VICM biomarker is released from activated macrophages and inhibited by anti-GM-CSFRα-mAb treatment in rheumatoid arthritis patients - PubMed. Clin Exp Rheumatol 73–80
[3] Mortensen, J. H. et al. A Specific Calprotectin Neo-epitope [CPa9-HNE] in Serum from Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients Is Associated with Neutrophil Activity and Endoscopic Severity. J Crohns Colitis 16, 1447–1460 (2022).
[4] Drobinski, P. J., Bay-Jensen, A. C., Karsdal, M. A., Sardar, S. & Siebuhr, A. S. Connective tissue remodelling is differently modulated by tocilizumab versus methotrexate monotherapy in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: the AMBITION study. Arthritis Res Ther 23, (2021).
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.