

Background: The association between radiomic features derived from sacroiliac joint (SIJ) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and genomic characteristics in axial Spondyloarthritis (axSpA) remains poorly understood. The hypothesis driving this study is that radiomic characteristics of the SIJ-MRI in axSpA might reflect underlying genetic alterations.
Objectives: The primary objective of this study was to explore the correlation between radiomic labels (Radscore) related to axSpA and mRNA expression profiles.
Methods: A retrospective cohort of 1256 patients with low back pain (axSpA=922, non-axSpA=334) was enrolled. Additionally, a prospective cohort of 116 patients (axSpA=60, non-axSpA=56) was included. Radiomics features were derived from SIJ-MRI data of all patients, divided into training (854), testing (370), and internal validation (116 prospective patients) groups and reduced using mRMR and LASSO algorithms. Patients were categorized into Radscore-H(higher than cutoff) and Radscore-L (lower than cutoff) groups based on the cutoff value of radiomics features. Blood sample of these 116 patients were collected and high-throughput sequencing was further performed. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified through comparisons between Radscore-H and Radscore-L, as well as between axSpA and non-axSpA. Overlapping genes were determined and Spearman correlate analysis was performed to explore the correlation between overlapping genes and retained radiomics features.
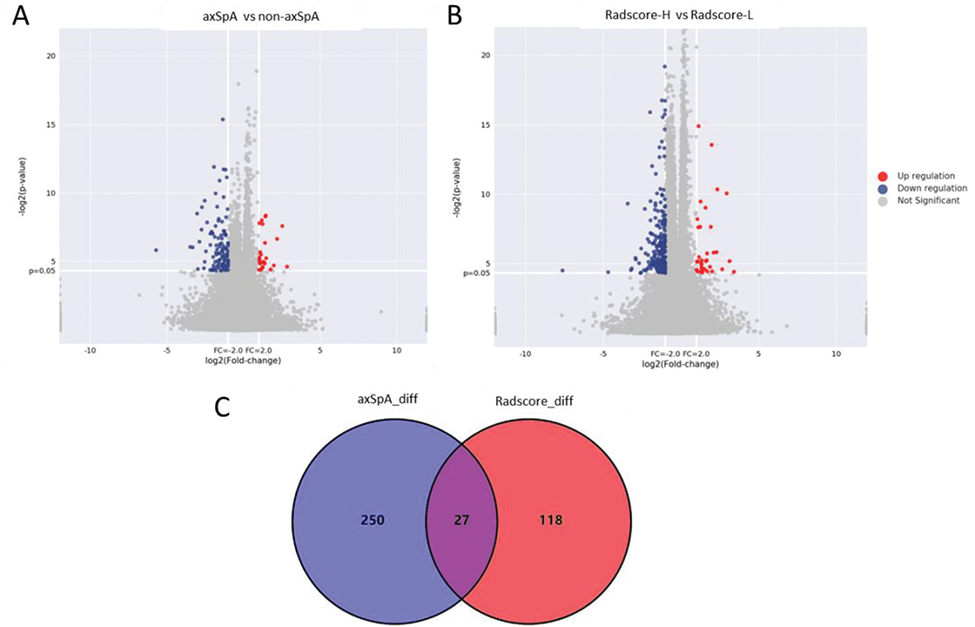
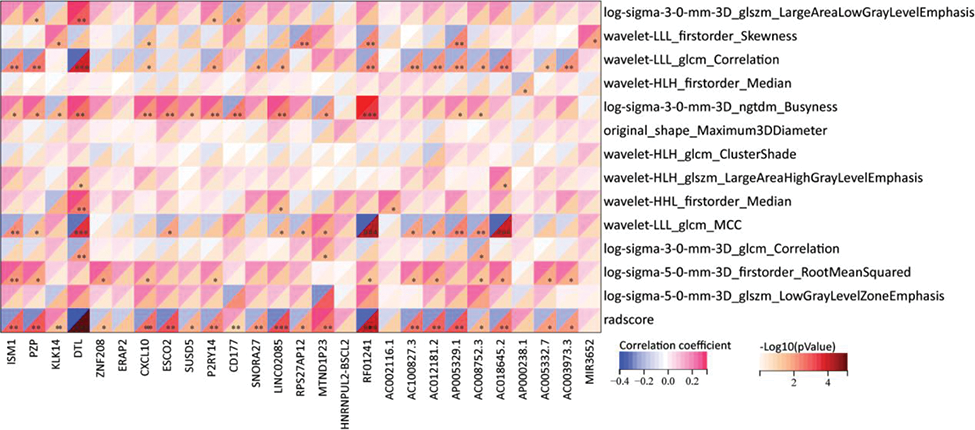
Results: A total of 1037 radiomics features were extracted and reduced to 13 features to construct the Radscore. 227 and 145 DEGs were further identified between axSpA and non-axSpA groups, and between Radscore+ and Radscore- groups, respectively. Among them, 27 overlapping genes were detected. Subsequent correlation analysis determined AC018645.2, AP005329.1, DTL, ESCO2, LINC02085, PZP, with certain genes showed a strong correlation with Radscore and specific radiomic features.
Conclusion: This study suggests that genes such as AC018645. [2], AP005329. [1], DTL, ESCO2, LINC02085, PZP may play a role in the radiographic phenotypes of axial spondyloarthritis. The correlation between these genes and specific radiomic features provides insights into potential genetic mechanisms underlying axSpA radiographic characteristics.
REFERENCES: [1] Chen, M.T., H.A. Lu, S.J. Copley, et al, A Novel Radiogenomics Biomarker for Predicting Treatment Response and Pneumotoxicity From Programmed Cell Death Protein or Ligand-1 Inhibition Immunotherapy in NSCLC[J]. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 2023. 18(6): p. 718-730. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1448-22.2022.
[2] Spielvogel, C.P., S. Stoiber, L. Papp, et al, Radiogenomic markers enable risk stratification and inference of mutational pathway states in head and neck cancer[J]. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, 2023. 50(2): p. 546-558. doi: 10.1007/s00259-022-05973-9.
A comprehensive visualization of gene expression data. (A) Volcano plot in identification DEGs between axSpA and non-axSpA. (B) Volcano plot in identification DEGs between Radscore-H and Radscore-L. (C) Venn plot in identification overlap DEGs of axSpA and non-axSpA, Radscore-H and Radscore-L.
A heatmap showcasing the correlation between included radiomic features and transcriptomics in axial spondyloarthritis.
***: P <0.001; **: P <0.01; *: <0.01≤ P <0.05
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82201997).
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.