

Background: Artificial intelligence (AI)-driven chatbots like ChatGPT are gaining recognition for their healthcare applications, yet the efficacy of ChatGPT4 in specialized medical consultations remains underexplored, particularly in rheumatology.
Objectives: This study compares the proficiency of ChatGPT4’ responses with practicing rheumatologists to inquiries from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, 95 frequently asked questions (FAQs) were curated from the Kidney Online platform (
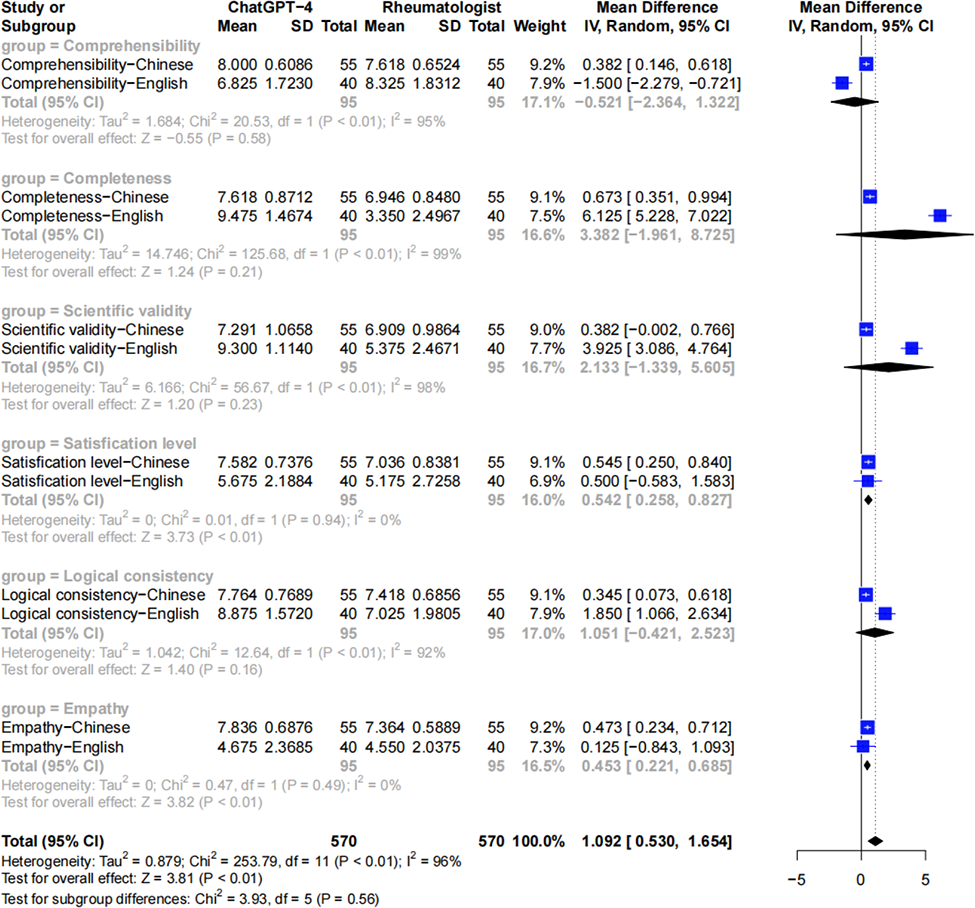
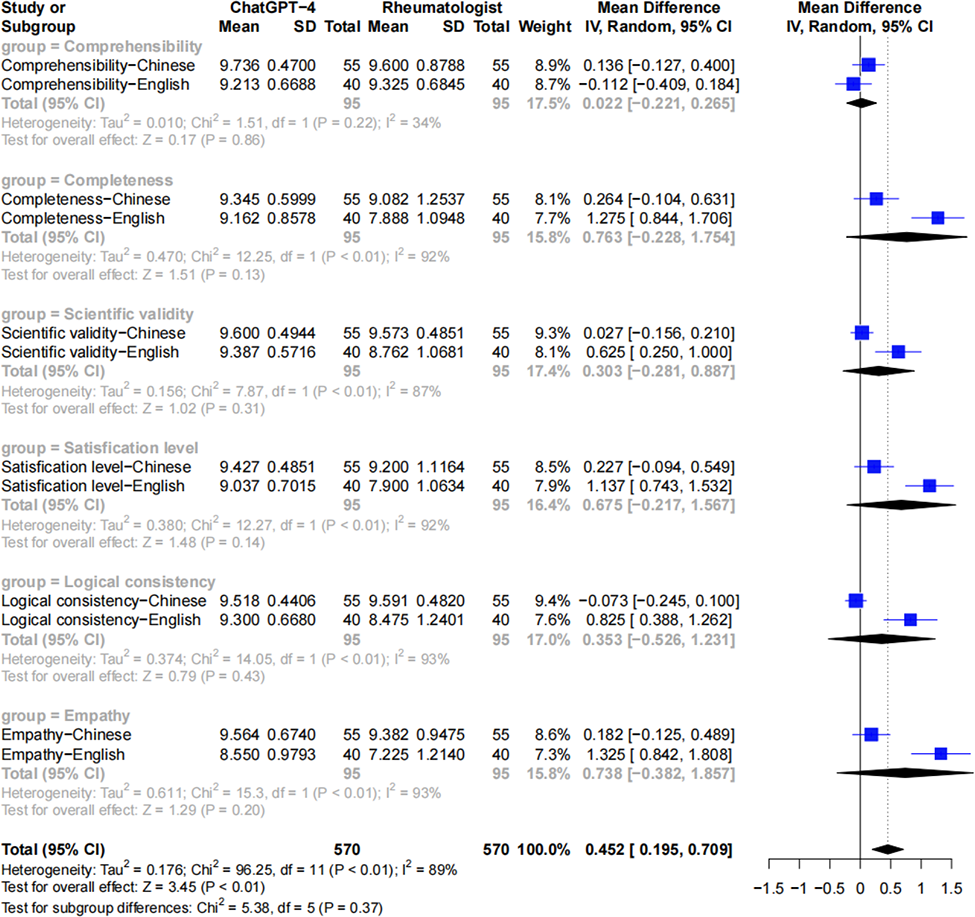
Results: Rheumatologists’ scoring revealed that ChatGPT4-generated responses outperformed those from rheumatologists in satisfaction level and empathy, with mean differences of 0.542 (95% CI, 0.258 to 0.827; P< 0.01) and 0.453 (95% CI, 0.221 to 0.685; P <0.01), respectively (Figure 1). No significant differences were observed in scientific validity, logical consistency, comprehensibility or completeness (Figure 1). From the SLE patients’ perspective, ChatGPT4-generated responses were comparable with the rheumatologist-provided answers in all 6 domains (Figure 2).
Conclusion: ChatGPT4 demonstrated comparable, possibly better in certain domains, to address the FAQs from patients with SLE, when compared with the answers provided by specialists. This study showed the potential of applying ChatGPT4 to improve the consultation in rheumatology.
Rheumatologists’ evaluation revealed that ChatGPT4-generated responses notably outperformed those from rheumatologists in terms of satisfaction level and empathy.
Patients’ evaluation revealed that ChatGPT4-generated responses mirrored rheumatologists-provided answers in terms of scientific validity, logical consistency, comprehensibility, completeness, satisfaction level and empathy.
REFERENCES: NIL.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.