

Background: Spatial heterogeneity in the presence and molecular composition of disease lesions is a hallmark of interstitial lung disease (ILD), including systemic sclerosis (SSc)-ILD. High-dimensional image analysis, i.e. radiomics of standard-of-care high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scans offers quantitative insight into organ-scale pathophysiology, creating digital fingerprints of disease.
Objectives: In this study, we aimed to integrate spatially-resolved CT-extracted radiomic profiles with matched histopathological and molecular data to decipher the cellular programs underlying the spatial heterogeneity in SSc-ILD, and to assess how these cellular programs are reflected in radiomic phenotypes.
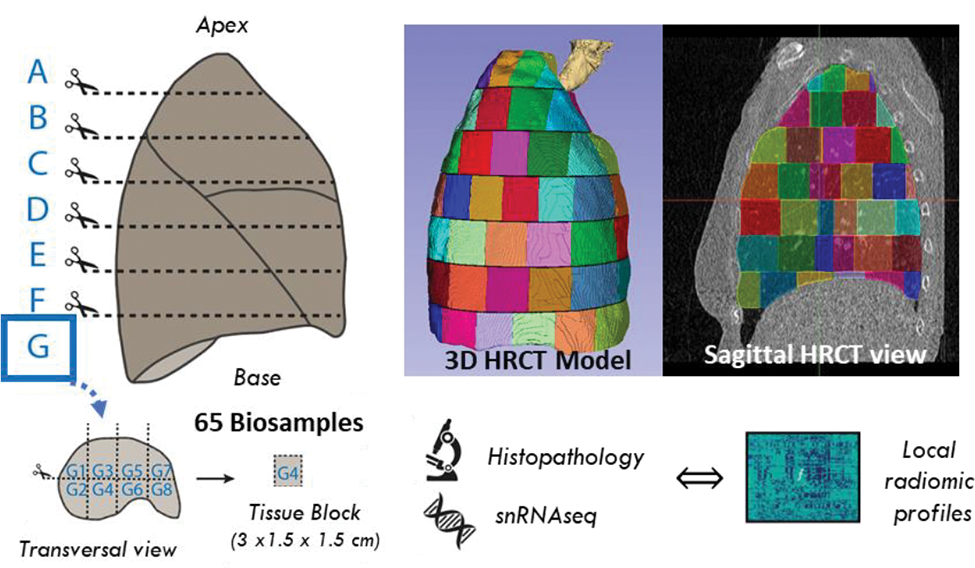
Methods: The whole right lung of a 75-year-old female SSc-ILD patient with shortness of breath, dry cough, compromised lung function and fibrotic lesions on CT was systematically dissected into 65 well-defined samples within 5 hours post-mortem (Figure 1).
The same sampling scheme was applied to segment the clinical pre-operative HRCT scan and 1’386 radiomic features were extracted for every 3D sample volume using the open-source software Z-rad. Spatial association of regional radiomics profiles was performed with CT-colocalized histopathology, including fibrosis extent, evaluated using Ashcroft scoring and morphological patterns, and molecular data from single-nuclei RNA-sequencing (snRNAseq). Single-cell data were analysed using “scanpy” following current single-cell best practices. Differential cellular abundance testing, pathway activation and cell-cell communication were inferred using “Milo”, “GSEApy” and “CellChat”, respectively.
Results: Within the lung, radiomic profiles significantly differed with spatial location, revealing a typical apical to basal gradient characteristic for the spatial heterogeneity in SSc-ILD as evidenced by principal component analysis and unsupervised clustering. To assess whether those differences in radiomic profiles would also translate to the molecular level, including changes in cellular composition, we performed snRNAseq of 14 distal lung regions, representatively sampled from the lung’s apex to base. We profiled more than 124,000 cells and identified more than 50 different cell types and states. We observed striking location-specific alterations in cellular composition, gene expression profiles and cellular crosstalk/cell-cell communication networks, particularly in the alveolar niche. Spatial location-resolved relative cell frequency analysis revealed significant changes in cell type composition consistent with the corresponding radiomic and histopathological phenotype. For instance, we found higher frequencies of immune cell types, such as T and dendritic cells in highly inflammatory regions and myofibroblasts in fibrotic regions. Integration of radiomics and transcriptomics data revealed spatial radiomic modules with distinct cellular profiles, including an apical-predominant T cell exhaustion and a basal-predominant macrophage-driven fibrogenic program.
Conclusion: Our unique approach for in-depth tissue phenotyping provides novel pathophysiological insights into the spatial heterogeneity of SSc-ILD. Furthermore, our study underscores the potential of radiomics as virtual organ-scale biopsies, offering a comprehensive understanding of disease patterns at both macroscopic and molecular levels.
REFERENCES: NIL.
Systematic dissection of the whole right lung of a SSc-ILD patient into 65 well-defined samples for histopathological and single nuclei transcriptomic profiling. The same sampling strategy for segmentation was applied to the clinical HRCT scan. This enables the spatial association of the local radiomics profiles and CT-colocalized histopathological and molecular data.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: Janine Gote-Schniering: None declared, Michael Ammeter: None declared, Yuexin Chen: None declared, Michaela Mueller: None declared, Shuhong Zhou: None declared, Laurens De Sadeleer: None declared, Matthias Brunner: None declared, Oliver Distler Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Medscape, 4P-Pharma, Abbvie, Acceleron, Alcimed, Altavant Siences, Amgen, AnaMar, Arxx, AstraZeneca, Baecon, Blade, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Corbus, CSL Behring, Galapagos, Glenmark, Horizon, Inventiva, Kymera, Lupin, Miltenyi Biotec, Mitsubishi Tanabe, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Prometheus, Redxpharna, Roivant, Sanofi and Topadur, Kymera, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Hubert S. Gabrys: None declared, Stephanie Tanadini-Lang: None declared, Malte D. Luecken: None declared, Stijn Verleden: None declared, Britta Maurer Boehringer-Ingelheim, GSK, Novartis, Otsuka, MSD, Novartis, Boehringer Ingelheim, Jannsen-Cilag, GSK, Novartis, Herbert Schiller: None declared.