

Background: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a heterogeneous connective tissue disease characterized by autoimmunity, vasculopathy and excessive fibrosis. Functional antibodies such as angiotensin II type 1 receptor and endothelin-1 type A receptor have been described in SSc and might be implicated in vasculopathy, in which endothelial cells (EC) are key players. Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) are strong diagnostic and prognosis biomarkers but their pathogenicity in vasculopathy remains unclear.
Objectives: To explore the effect of purified IgG from SSc patients on the proteome of EC and analyse the influence of ANA.
Methods: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) were cultured in presence of purified IgG from: 10 diffuse cutaneous SSc (dcSSc) anti-topoisomerase-I positive patients (dcSSc ATA+), 10 limited cutaneous SSc anticentromere positive patients (lcSSc ACA+), 10 dcSSc anti-RNA polymerase III autoantibodies positive patients (dcSSc RNAP+), 10 healthy controls (HC) and 5 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). After 24h, the proteome was analysed using Liquid Chromatography with tandem Mass Spectrometry. Proteomic data were visualized by principal component analysis (PCA). Differential analysis and enrichment analysis were performed to compare pattern of protein expression between groups
Results: Proteomics identified and quantified 2,141 proteins. PCA showed 3 distinct groups of subjects: a first including mostly dcSSc ATA+, a second including mostly lcSSc ACA+ and third groups more heterogeneous including dcSSc RNAP+ patients, SLE patients and HC ( Figure 1 ). The comparison of HUVEC’s proteome in the presence of purified IgG from dcSSc ATA+ vs HC and lcSSc ACA+ vs HC revealed 614 and 288 differentially expressed proteins respectively. Proteins overexpressed in dSSc ATA+ group were enriched in macromolecule localization and protein binding and overexpressed proteins in lcSSc ACA+ groups were enriched in RNA and mRNA proteins binding. Eleven proteins were commonly overexpressed in dcSSc ATA+ or lcSSc ACA+.
Protein expression profiles in LC-MS/MS analysis.
Principal component analysis (PCA) represented HUVEC protein expression according to the patient ANA status. ATA: purified IgG from diffuse systemic sclerosis anti-topoisomerase-I positive patients; ACA: purified IgG from limited systemic sclerosis anti-centromere positive patients; RNAP: purified IgG from diffuse systemic sclerosis RNA-polymerase III positive patients; SLE: purified IgG from systemic lupus erythematosus patients; HC: purified IgG from healthy controls; HUVEC: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC).
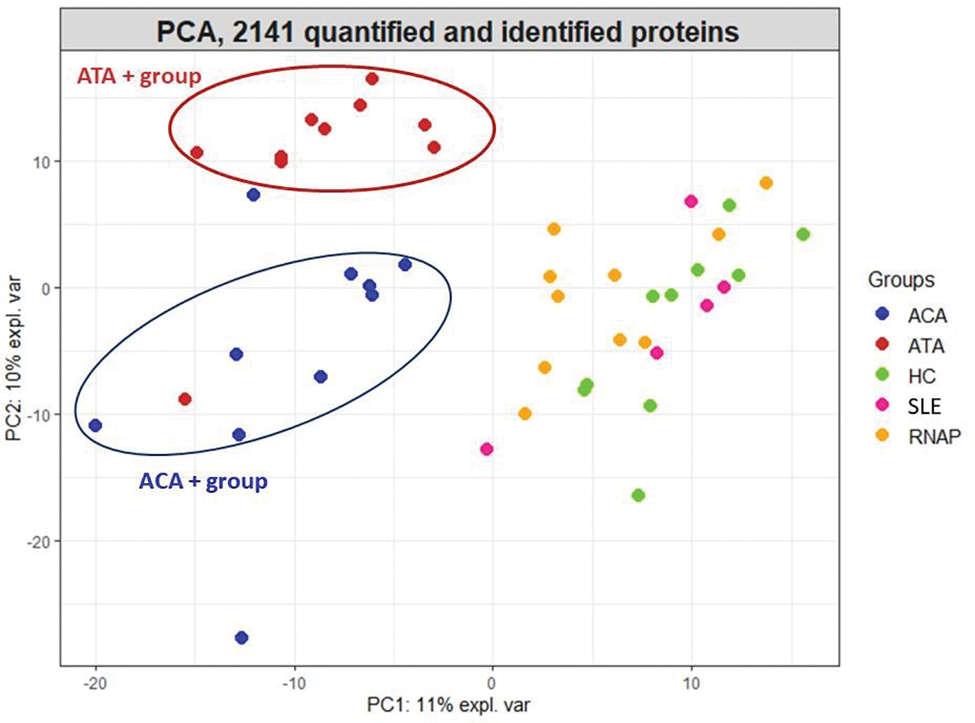
Conclusion: Using a proteomic approach, we identified that IgG from SSc modified EC proteome which appeared explained by ANA status. In particular, IgG from both ATA+ et ACA+ patients induced EC singular and distinct proteomic profiles.
REFERENCES: NIL.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.