

Background: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a complex and chronic autoimmune connective tissue disease, characterized by vasculopathy, abnormal and excessive deposition of extra cellular matrix in the skin and internal organs and presence of autoantibodies.Patients with SSc have increased susceptibility to infections, primarily stemming from the disease itself and its associated complications.
Objectives: This study aims to look for the spectrum of infections and the factors predisposing to infection in patients with systemic sclerosis.
Methods: In this retrospective study, demographic, clinical features, details of infections, immunosuppressive therapy, and outcomes of patients with SSc attending clinics at department of Clinical Immunology and Rheumatology, Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India from 1990-2022 were captured. Multivariable-adjusted logistic regression was applied to identify independent predictors of infection.
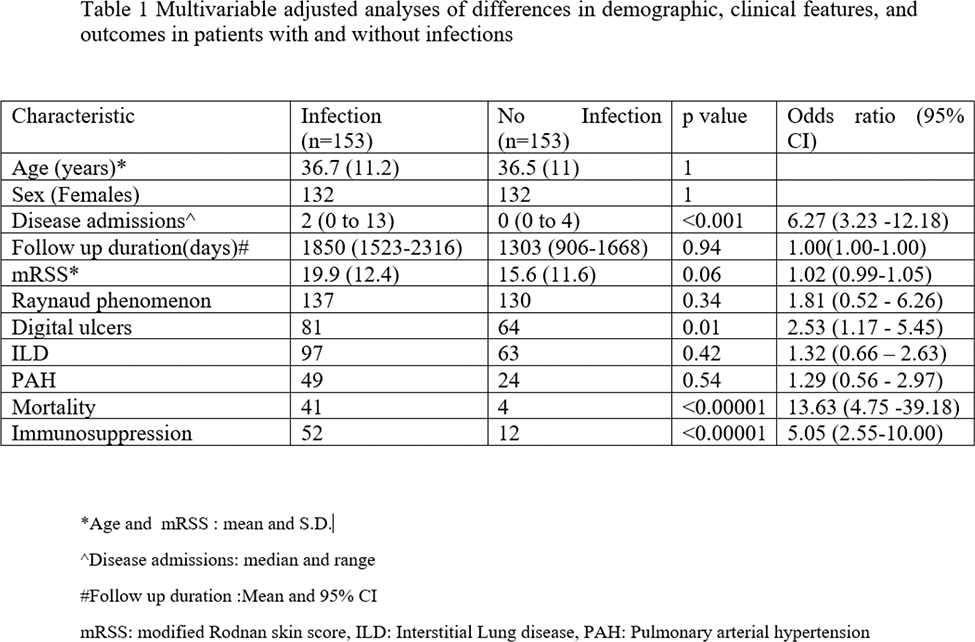
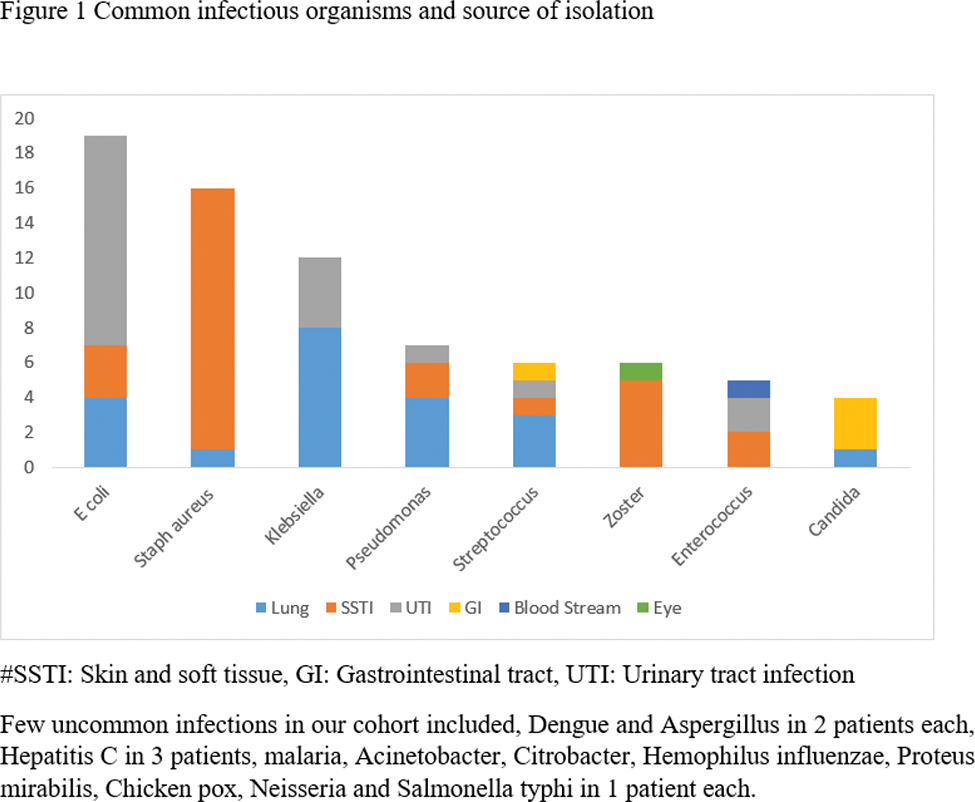
Results: Data of 880 patients, mean age 35.5±12 years, and female: male ratio 7.7:1, were analyzed. One hundred and fifty-three patients had at least 1 infection with a total of 233 infectious episodes. Infections were most common in lung followed by skin and soft tissue. Tuberculosis was diagnosed in 45 patients (29.4%). Klebsiella was the commonest non-tubercular organism in lung and Escherichia coli in urinary tract infections. In comparison to matched control group, patients with infection had a greater number of admissions due to active disease, odds ratio (OR) 6.27 (3.23-12.18, p<0.001), were receiving immunosuppressive medication OR, 5.05 (2.55-10.00, p<0.0001)), and had more digital ulcers OR, 2.53 (1.17-5.45, p<0.01). Patient who had infection had more likelihood for death OR, 13.63 (4.75 -39.18, P<0.0001).
Conclusion: Tuberculosis remains the commonest disease and lung remains the major site of infection in patients with SSc. Number of hospital admissions, digital ulcers and immunosuppressive therapy are predictors of serious infection in patients with SSc. Infections are a major cause of mortality in SSc.
REFERENCES: [1] Barahona-Correa JE, De la Hoz A, López MJ, Garzón J, Allanore Y, Quintana-López G. Infections and systemic sclerosis: an emerging challenge. Rev Colomb Reumatol Engl Ed. 2020 Apr 1;27:62–84.
[2] Rongioletti F, Ferreli C, Atzori L, Bottoni U, Soda G. Scleroderma with an update about clinico-pathological correlation. G Ital Dermatol E Venereol Organo Uff Soc Ital Dermatol E Sifilogr. 2018 Apr;153(2):208–15.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.