

Background: Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) is frequently associated with refractory chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP), despite current treatments. Dupilumab demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of severe and uncontrolled CRSwNP.
Objectives: We aimed to assess safety and efficacy of dupilumab in refractory CRSwNP in EGPA and analyze changes in nasal smears and tissue infiltrates.
Methods: Consecutive EGPA patients suffering from refractory CRSwNP were enrolled prospectively between December 2021 and October 2023. Demographic, clinical, biological data and nasal cytology were collected at each evaluation.
Assessment included patient-reported outcomes such as Asthma Control Test (ACT), Nasal Congestion Score (NCS), Sino-Nasal Outcome Test (SNOT-22), Visual Analogue Scales (VAS)), as well as objective measures including Peak Nasal Inspiratory Flow (PNIF), Nasal Polyp Score (NPS) and Sniffin’ Sticks Identification Test (SSIT).
Complete response was defined by Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (BVAS)=0 and prednisone dose ≤4 mg/day, and partial response by BVAS=0 and prednisone dose >4 mg/day.
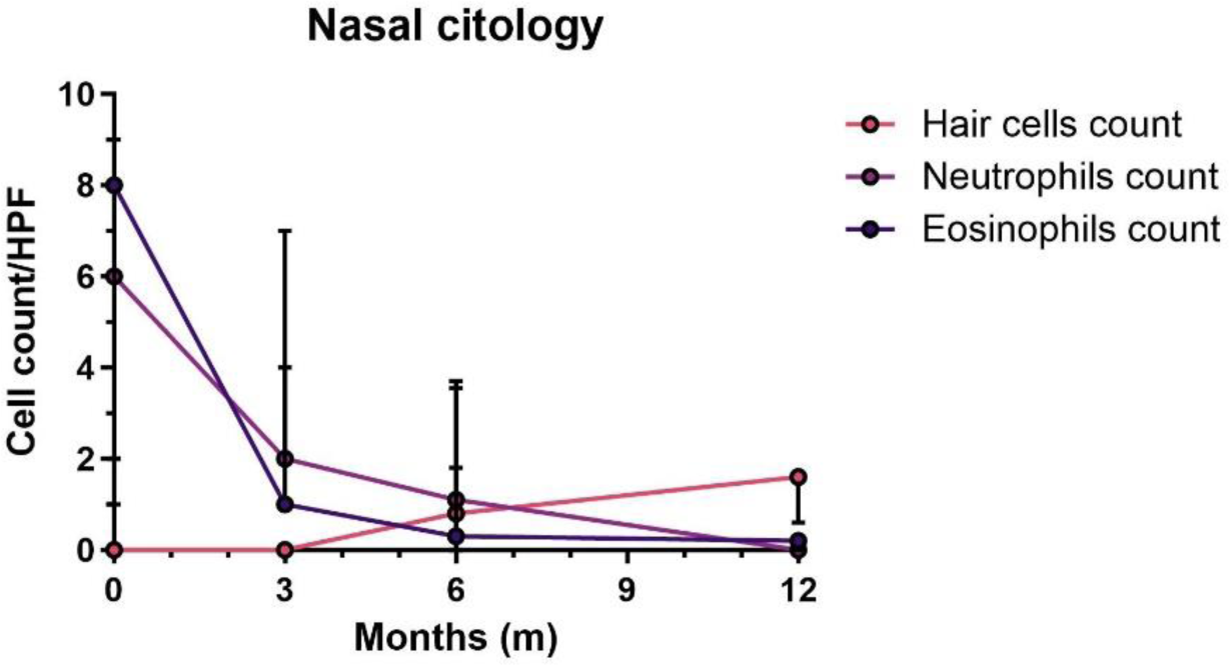
Results: The study included 9 EGPA patients (age at diagnosis 51 [46-59] years, male 66.6%), with BVAS at diagnosis of 16 [11.5-19.5]. Median eosinophils at diagnosis were 4810/mmc [2100-9180], reduced to 330/mmc [175-640] at dupilumab initiation. Dupilumab was mainly used as third-line therapy, after a median disease duration of 66 [65-128] months. Two (22.2%) patients were previously treated with anti-IL5/IL-5R therapy. Median duration of treatment with dupilumab was 8 [3.5-6] months.
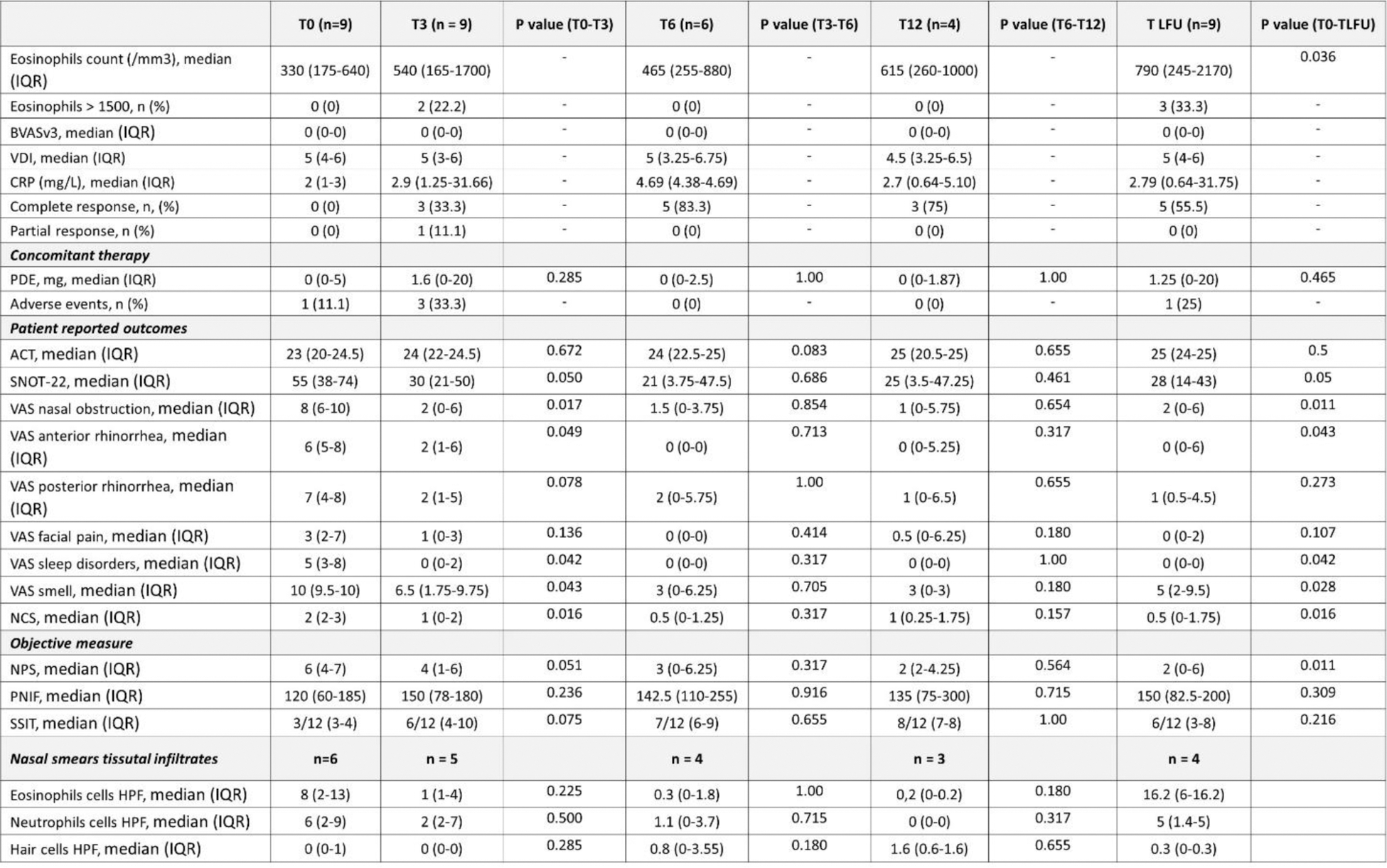
A total of 26 nasal cytology tests were performed (min 2 – max 4 for each patient). At baseline, 66.7% patients showed a nasal cytology with eosinophilic patterns, 16.7% a neutrophilic pattern and 16.7% a mixed (eosinophils-neutrophils) pattern. The median eosinophils count was 8 (2-13) cells per field at the start of dupilumab, reduced to 0.2 (0-0.2) at 12 months, whereas median neutrophils count was (2-9) cells per field at the start of dupilumab, reduced to 0 (0-0) at 12 months.
No differences were observed in median eosinophils count, prednisone dose and VDI during follow-up.
Significant improvement was observed in VAS-nasal obstruction (p=0.011), VAS-smell (p=0.028), VAS anterior rhinorrhea (p=0.043), VAS sleep disorders (p=0.042), NCS (p=0.016), SNOT-22 (p=0.05) and NPS (p=0.011).
At last follow-up complete response was achieved by 6 (66.6%) patients. Adverse events were reported in 4 (44.4%) patients. Hypereosinophilia occured in 2 (22.2%) patients within the first 3 months, leading to dupilumab discontinuation.
Conclusion: Dupilumab showed improvement in patient reported outcomes and objective measures when used in refractory CRSwNP in EGPA. Treatment was associated with a good safety profile.
REFERENCES: NIL.
Table 1.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.