

Background: Accelerated atherosclerosis and associated cardiovascular morbidity have been extensively studied in patients with rheumatic diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and Sjogren’s syndrome. However, the risk of subclinical atherosclerosis and lipid profiles in patients with Wegener’s Granulomatosis (WG) have not been elucidated well.
Objectives: To perform a systematic review and meta-analysis to examine whether WG is associated with an increased carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT; a surrogate marker for atherosclerosis) when compared with healthy control subjects. We further aimed to compare the lipid profiles among the WG patients and the healthy controls.
Methods: Studies evaluating the lipid profiles and the relationship between WG and CIMT were systematically searched in the PubMed, Google Scholar and EMBASE databases from inception to January 2024. The overall mean differences (MD) and 95% confidence interval (CI) of CIMT and lipid profiles between WG patients and control groups were calculated by fixed-effects or random-effect model analysis using Revman 5.1 software. The between-study heterogeneity of effect size was quantified using the Q statistic and I 2 .
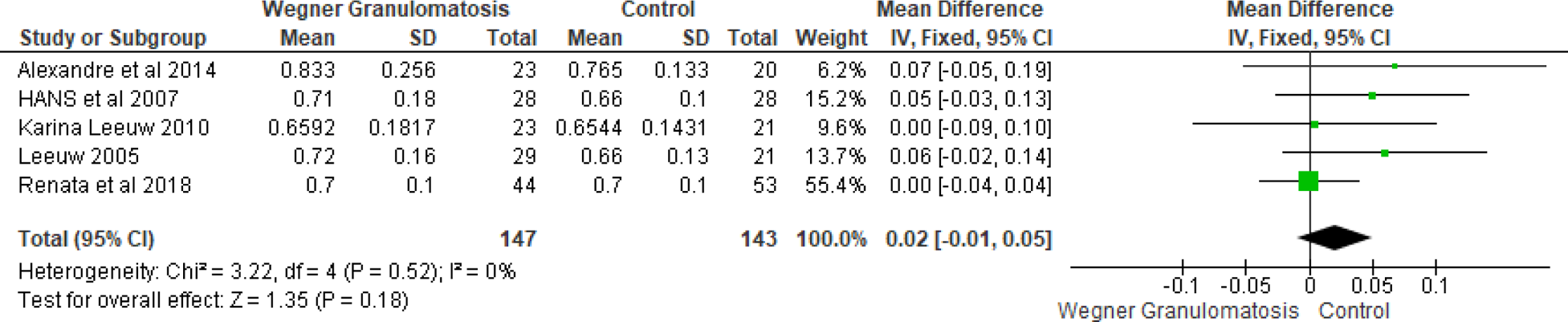
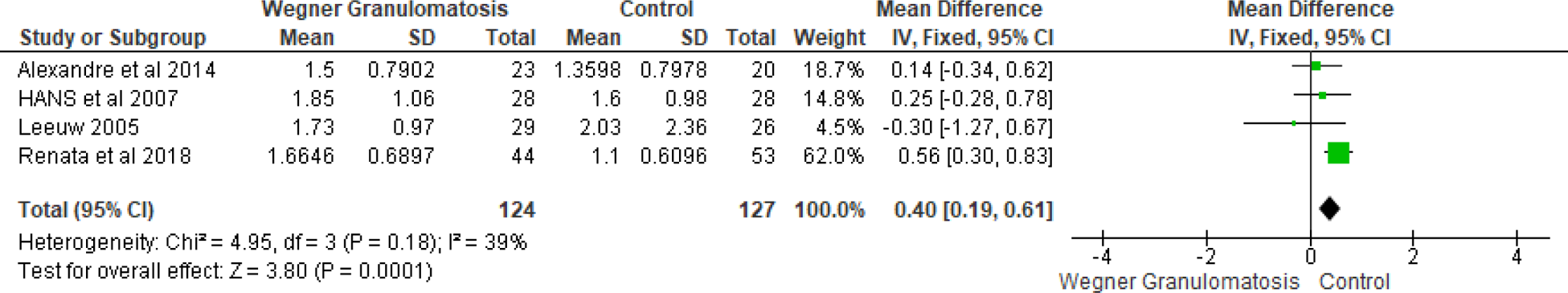
Results: A total of 242 patients from five studies were reviewed in this analysis. There was no significant difference in CIMT between WG and control groups. [MD=0.02, CI= -0.01-0.05, I 2 =0%, P value =0.18] (Figure 1) Similarly, there was no significant differences in total cholesterol [MD=0.04, CI= -0.18-0.26, I 2 =0%, P value =0.74], low density lipoprotein [MD=-0.07, CI= -0.42-0.28, I 2 =64%, P value =0.71] and high-density lipoprotein [MD=-0.07, CI= -0.16-0.03, I 2 =0%, P value =0.15] between WG and control groups. However, triglyceride level was significantly higher in WG patients as compared to healthy controls. [MD=0.40, CI= 0.19-0.61, I 2 =39%, P value =0.0001] (Figure 2).
Conclusion: This study suggests that WG is not associated with subclinical atherosclerosis and deranged lipid profile. Further studies need to be conducted to prove the correlation of subclinical atherosclerosis in WG patients. REFERENCES: NIL.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.