

Background: In the changing healthcare landscape, digital resources are essential for patient education and self-management. However, their effectiveness depends on patients’ electronic health literacy (eHL), a multifaceted skill set enabling individuals to seek, understand, and utilize health information from electronic sources. Despite its growing importance, there is a lack of comprehensive data regarding eHL levels among Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Disease (RMD) patients.
Objectives: to assess eHL in patients with RMDs and explore potential differences by patient factors.
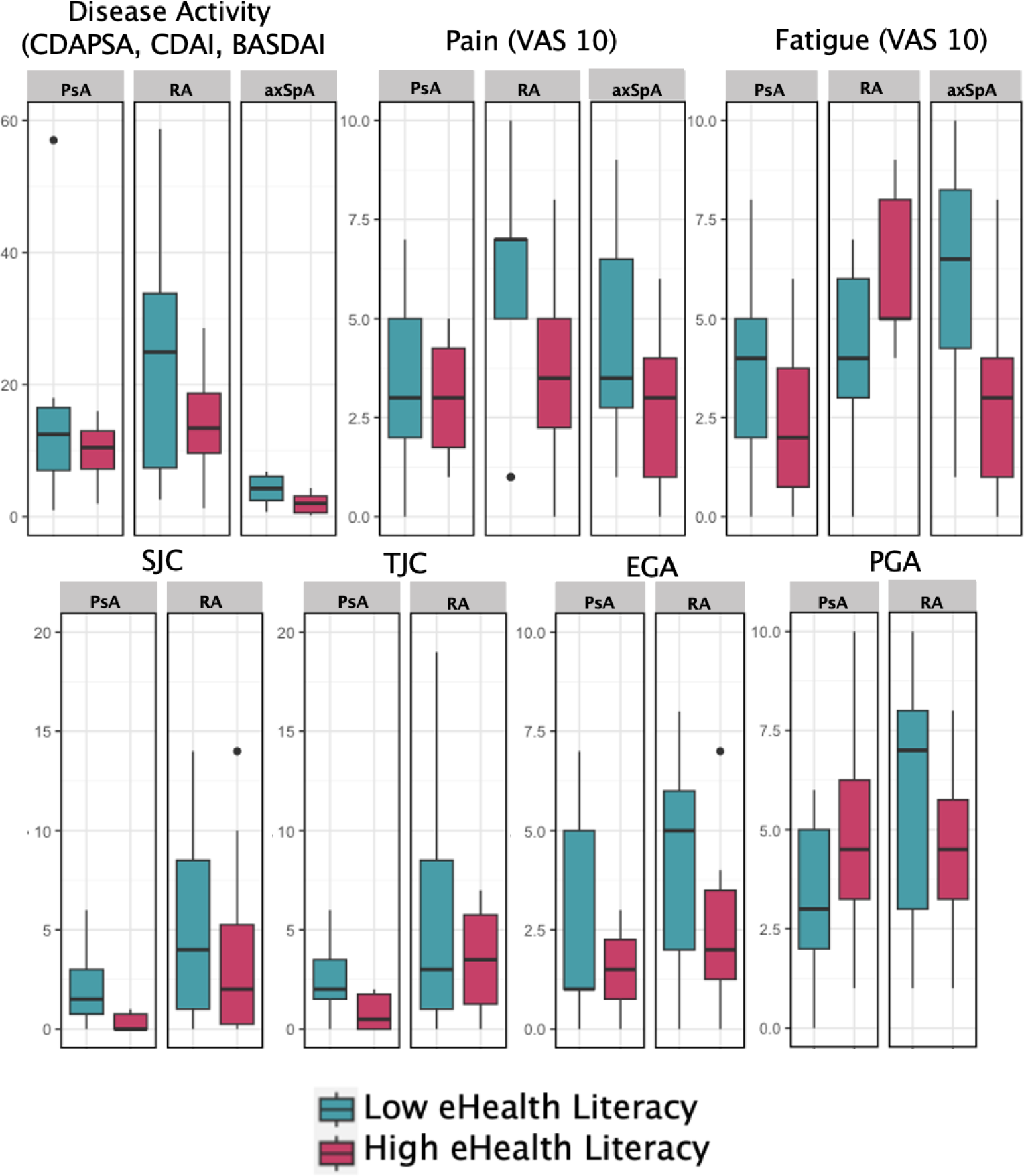
Methods: All adult RMD patients (≥18yrs) visiting the outpatient rheumatology department of the Medical University of Vienna from June 2023 onwards were asked to complete the German revised electronic health literacy scale (Gr-eHeals), a validated 8-item questionnaire evaluating eHL via a total score from 1 (least) – 5 (best). Sex, age and diagnosis were collected. In patients with inflammatory arthritis (Rheumatoid Arthritis [RA], Psoriatic Arthritis [PsA] and Axial Spondyloarthritis [AxSpA]), data were additionally linked to existing patient registries to explore the association of eHL and disease activity. Patients were stratified into quartiles of eHL and differences in measures of disease activity (CDAI, cDAPSA, BASDAI, Pain (VAS/10), Fatigue (VAS/10), Evaluator Global Assessment [EGA], Patient Global Assessment [PGA], Swollen Joint Count [SJC] and Tender Joint Count [TJC] were compared between patients scoring in the lowest 25% and highest 25% of Gr-eHeals (low eHL ≤ 25%, high eHL ≥ 25%).
Results: Out of 445 returned Gr-eHeals questionnaires, 384 (mean age: 52.3±16.2, 71.6% female, Gr-eHeals mean: 3.6±1.2) complete questionnaires with RMD diagnosis comprising of RA n=96, PsA & axSpA n=79, Myositis & Vasculitis n=35, Connective Tissue Diseases n=90, and others n=84, were included. Decreasing Gr-eHeals scores were observed with increasing age, while no differences across sex or disease entities were found. A trend of lower disease activity was found in high compared to low eHL as assessed by CDAI and BASDAI in patients with RA and AxSpA respectively. Furthermore, numerical differences in physician derived measures of disease activity like SJC, TJC and EGA, with mostly higher scores in the low eHL group as well as in patient-derived outcomes (pain, fatigue) could be depicted. These findings were not congruent in all entities of inflammatory arthritis (Figure 1).
Conclusion: This one of the largest studies providing an overview of eHL in people with RMDs. As expected, this competency is less pronounced in older patients independent of RMD. Patients with high eHL seem to show lower disease activity for RA and axSpA, which still warrants deeper characterisation to better understand the importance and influencing factors in the arena of managing RMDs.
REFERENCES: NIL.
eHealth literacy and measures of disease activity
Acknowledgements: We are grateful to colleagues form out outpatient clinic in assisting in facilitation of the study.
Disclosure of Interests: Nasim Nakhost Lotfi: None declared, Helga Lechner-Radner AbbVie, Lilly, Pfizer, UCB, Janssen, Paul Studenic AstraZeneca, AbbVie.