

Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory rheumatic condition that often requires targeted therapies like rituximab. Understanding baseline predictors of response is crucial for optimizing treatment outcomes. This retrospective study aims to investigate various patient characteristics, baseline patient-reported outcomes, laboratory levels, and immunological markers as potential predictors of rituximab response in RA.
Objectives: The primary objective is to identify baseline factors associated with rituximab response in RA patients in a real-life setting.
Methods: A monocentric retrospective study between 2008 and 2023 was conducted. RA patients receiving rituximab were included. Patients below age 18 were excluded. Patient characteristics, disease-related variables, baseline patient-reported outcomes, and laboratory parameters were collected. The study employed statistical tests, including chi-square tests and t-tests, to compare variables between patients with and without a response to rituximab.
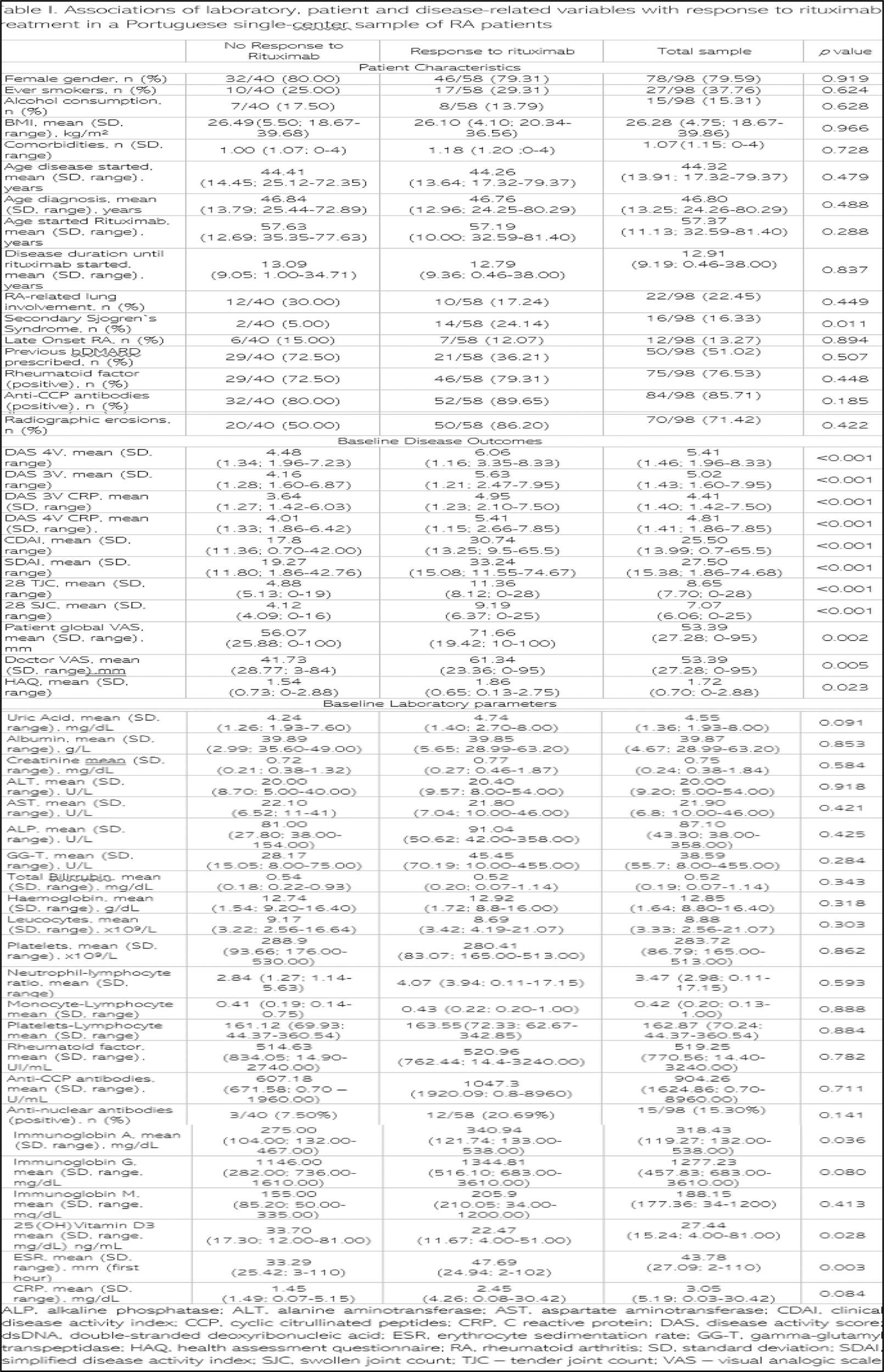
Results: Out of 745 RA patients, 98 met the study inclusion criteria. Among the notable findings (see Table 1), we observed a significantly higher response rate to rituximab in RA patients with secondary Sjogren`s syndrome (p=0.011). Baseline patient-reported outcomes (HAQ and PG-VAS), DG-VAS, disease activity scores (DAS, CDAI, SDAI), 28 TJC and 28 SJC were significantly higher in the responder group (p<0.001). Baseline serum levels of immunoglobulin A (p=0.036) and 25(OH)vitamin D3 (p=0.028), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (p=0.003) also displayed significant associations with rituximab response. Moreover, baseline serum levels of immunoglobulin G and CRP were numerically higher in the rituximab responder group (p=0.080 and p=0.084, respectively).
Conclusion: This retrospective study provides valuable insights into baseline predictors of rituximab response in RA. Secondary Sjogren`s syndrome, higher baseline disease activity, and specific laboratory parameters such as serum immunoglobulin A and ESR emerge as potential indicators of a favorable response to rituximab treatment. These findings contribute to the ongoing efforts to personalize RA treatment strategies and enhance therapeutic effectiveness with rituximab. Further prospective studies are warranted to validate and expand upon these observations, fostering more precise and individualized management approaches in RA patients undergoing rituximab therapy.
REFERENCES: [1] Rituximab and tocilizumab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Nicolás González-Vacarezza1, Alicia Alemán 1, Graciela González 1, Ana Pérez 1. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2014 Jul;30(3):282-8. DOI: 10.1017/S0266462314000221. Epub 2014 Jul 28.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.