

Background: Patients with inflammatory myopathies (IM), especially dermatomyositis, are at increased risk of cancer. In addition, cancer is associated with approximately 5% of systemic vasculitides, including IgA vasculitis. In adults with IgAV, malignancy represents one of the possible triggers of vasculitis.
Objectives: We aimed to investigate differences in cancer type/location and their temporal occurrence in well-defined and prospectively followed groups of IM and IgAV patients.
Methods: Adults diagnosed with MI or IgAV between January 2010 and November 2022 and followed up in our outpatient clinic were included. Episodes of cancer that developed in the 3 years before or after the diagnosis of IM or IgAV were recorded. Episodes of non-melanoma skin cancer were excluded from the analysis. Cancer episodes were divided into 3 groups: 1) cancer diagnosed in the 3 years before the diagnosis of IM or IgAV; 2) cancer diagnosed at the same time as IM or IgAV; 3) cancer diagnosed in the 3 years of follow-up.
Results: In a cohort of 158 IM patients (110 (69.6%) women; median age at IM diagnosis 63.6 (52.6-72.2) years), we found 28 different cancers in 27 patients (17.1%; 12 (55.6%) women; median age at IM diagnosis 64.8 (60.0-71.9) years).
In the group of 305 patients with IgAV (124 (40.7%) women; median (IQR) age at IgAV diagnosis 63.5 (45.6-75.8) years), we recorded 24 different cancers in 22 patients (7.2%; 5 (22.7%) women; median (IQR) age at diagnosis of IgAV 73.7 (64.9-79.2) years).
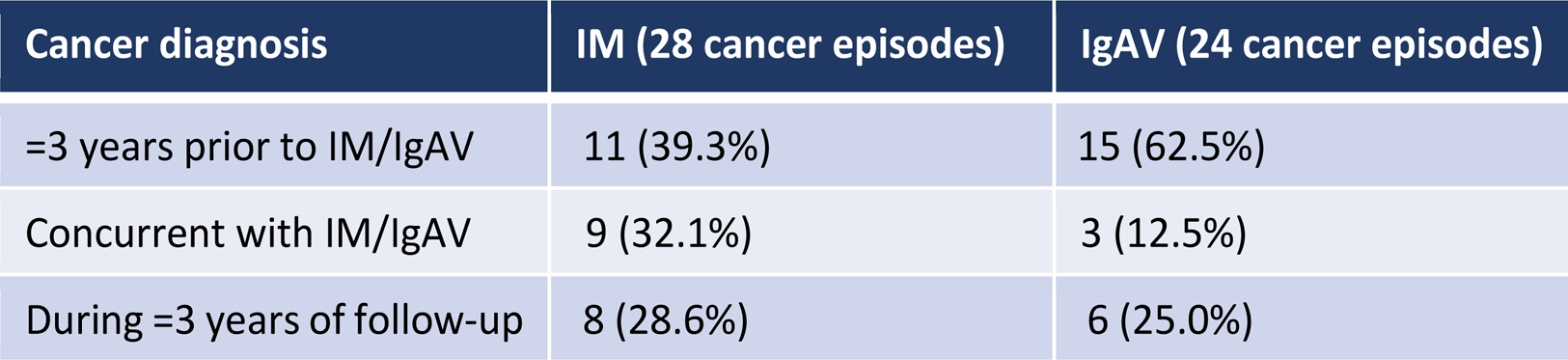
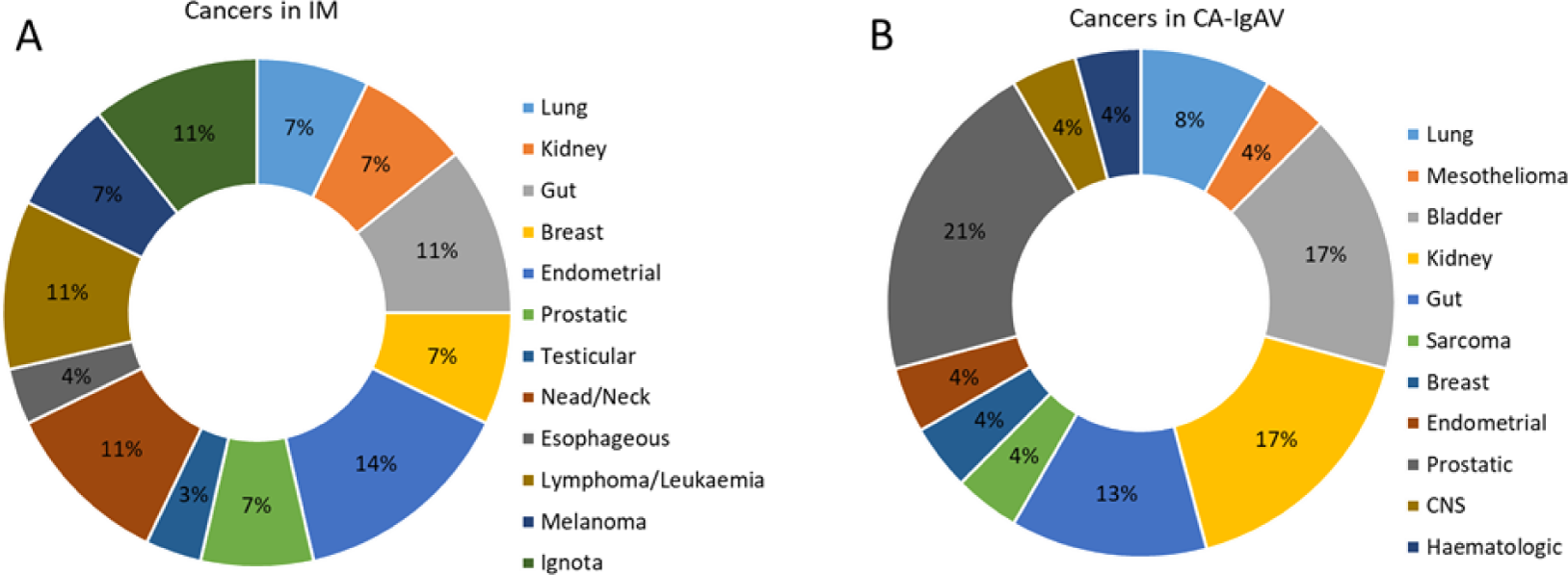
The temporal relationship between cancer diagnosis and IM or IgAV is presented in Table 1. Figure 1 shows the site of cancer diagnosed in patients with IM or IgAV. In contrast to IgAV, where prostatic, kidney and bladder cancers together accounted for 55% of all cancers, these cancers accounted for only 14% of IM cancers. IM patients had a more aggressive cancer course, resulting in 11 out of 27 deaths during follow-up (40.7%), while 4 out of 22 IgAV patients (18.2%) died of cancer progression during follow-up.
Table 1. Temporal association between cancer diagnosis and diagnosis of IM or IgAV
Location of cancers in IM (A) or IgAV (B)
Conclusion: While most IgAV patients were diagnosed with cancer in the three years before the diagnosis of vasculitis, the timing of cancer onset was more uniform in IM patients. The two groups compared also differed in terms of the location of the cancer and its aggressiveness/prognosis.
REFERENCES: NIL.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.