

Background: Inflammatory pathologies are at the center of various medical specialties and benefit from treatments known as conventional, as well as an entire array of biological treatments. It is the 3rd group of diseases in France after cancer and cardiovascular diseases. Their incidence is estimated at 5 million people, with more women being affected. The therapeutic arsenal is very broad, ranging from conventional synthetic treatments to biologics. These latter ones have often been the subject of studies yielding heterogeneous results regarding their infectious and mortality risks.
Objectives: The main objective of this study is the analysis of mortality and its causes in intensive care/reanimation units among patients with chronic inflammatory diseases treated with conventional or biopharmaceutical therapy on a national scale, using the French PMSI database, encompassing all hospital stays on a national scale.
Methods: This is a retrospective, descriptive study with inclusion criteria requiring hospitalization or a declaration of a long-term condition with a diagnostic code for the inflammatory disease of interest between 2012 and 2020. Patients must have had at least one dispensing of conventional or biologic treatment after the initial diagnosis of the inflammatory disease, with a first stay in an intensive care or reanimation unit occurring after the index date between 2015 and February 29, 2020. Exclusion criteria for patients included age younger than 17 years and the first dispensing of treatment before the date of the initial diagnosis of the inflammatory disease. All comparisons between conventional treatment and biologic therapies were performed using the Chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, or Student’s t-test.
Results: In total, 13,816 patients were included. The patients had a mean age of 63 at inclusion, with 7,307 patients being male (52.9%, p <0.01%). Within 90 days after the first admission to the intensive care/reanimation service, 11.6% of the patients died, including 9.4% within 30 days and 7.3% during hospitalization. When comparing patients treated with conventional treatment and biologic therapy prior to their entry into intensive care, more patients died in the conventional treatment group (82.2% of deaths in the conventional treatment group and 17.4% of deaths in the biologic therapy group, p <0.01%). More deaths were observed due to cardiovascular (27%), infectious (15%), gastroenterological (12%), and oncological (12%) conditions, regardless of treatment, as well as in the conventional treatment group. However, there were as many deaths from oncological causes (19%) as from cardiovascular causes (19%) in the biologic therapy group. Hypertension (66.8%) and renal insufficiency (50.4%) were the most frequently associated comorbidities with mortality.
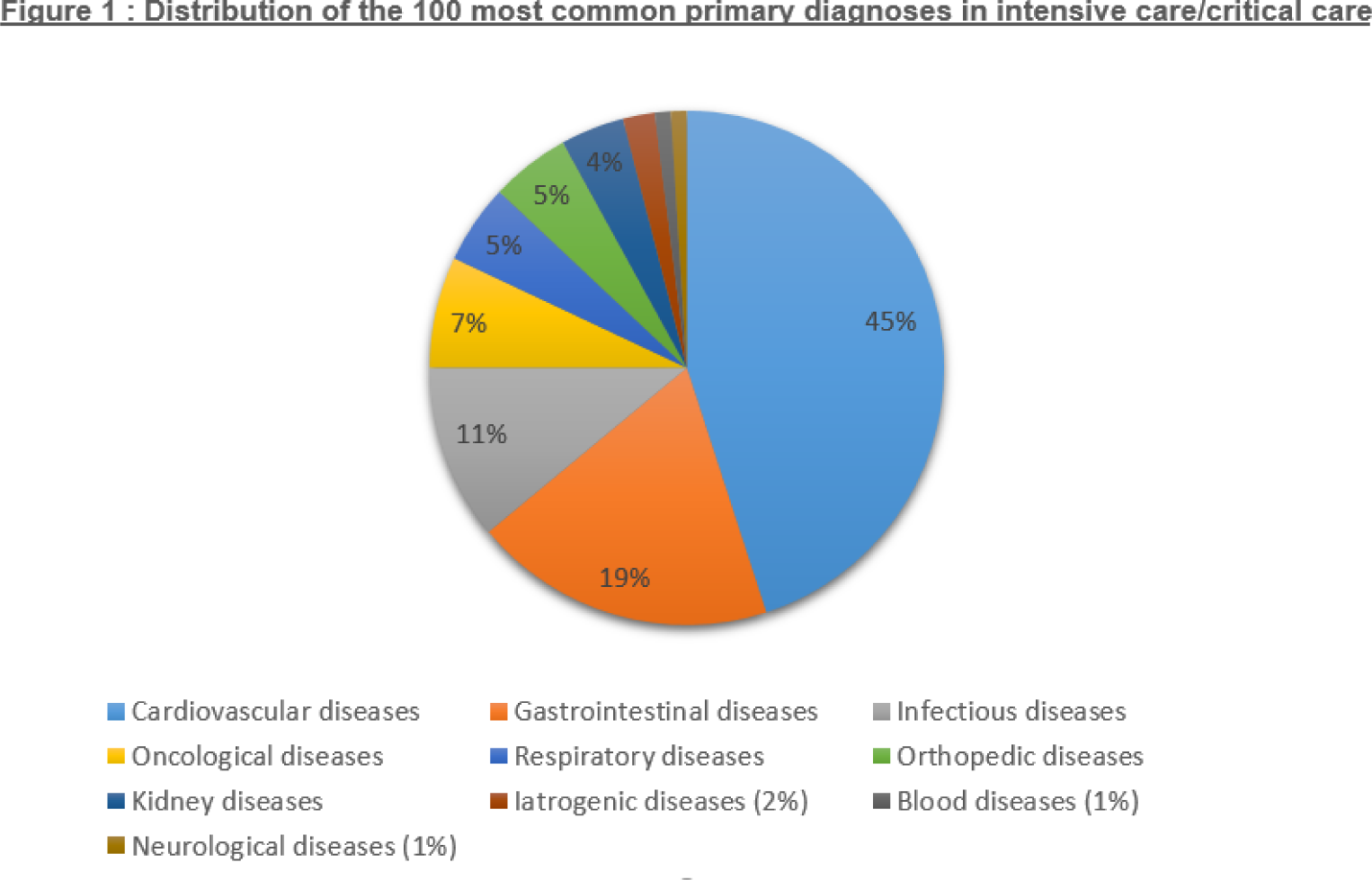
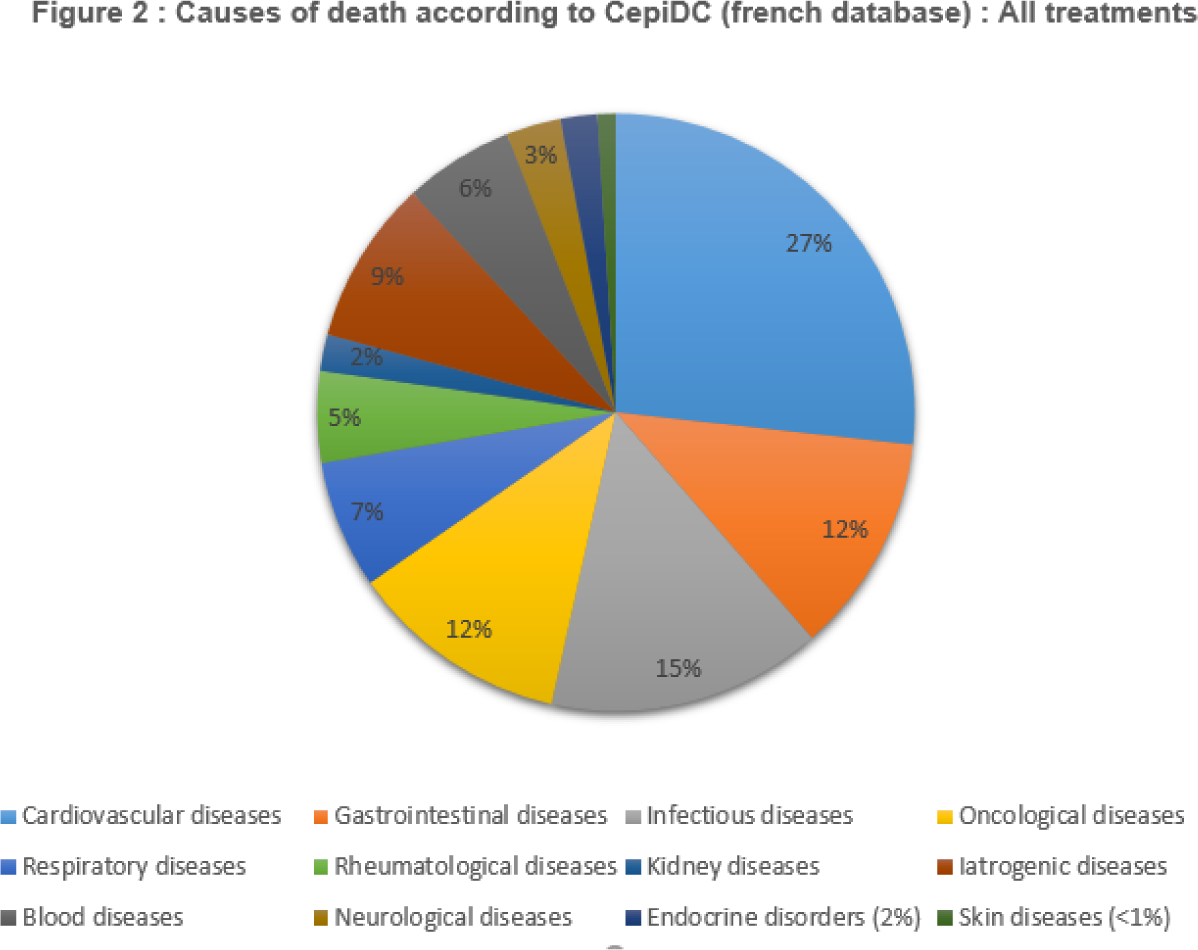
Conclusion: Mortality in intensive care/reanimation during the initial stay of patients afflicted by inflammatory pathologies is of greater concern for those treated with conventional treatments. Causes of death, much like the reasons for hospitalization, tend to be cardiovascular and requieres more prevention and care management.
REFERENCES: [1] Singh JA, Wells GA, Christensen R, Tanjong Ghogomu E, Maxwell LJ, MacDonald JK, et al. Adverse effects of biologics: a network meta-analysis and Cochrane overview. Cochrane Musculoskeletal Group, éditeur. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016(4).
Acknowledgements: The authors wish to thank the department of medical information, the department of clinical pharmacology and the intensive care unit of the CHU Amiens Picardie for their help in this work.
Disclosure of Interests: Yannis Hamidou: None declared, Vincent Goeb Received consultancies from Lilly, Novartis, Abbvie and Medac, Jean Marc Sobhy Danial Received consultancies from Novartis.