

Background: Biologic drugs (bDMARDs) have dramatically changed the disease course in juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA). However, scarce evidence about their long-term efficacy and safety is available.
Objectives: The aim of this study is to illustrate the long-term efficacy and safety of etanercept (ETN) and adalimumab (ADA) as first-line therapy in a monocentric cohort of JIA patients.
Methods: Clinical data of patients with long-term AIG treated with ETN or ADA were retrospectively collected. The retention rate of the two bDMARDs was estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method.
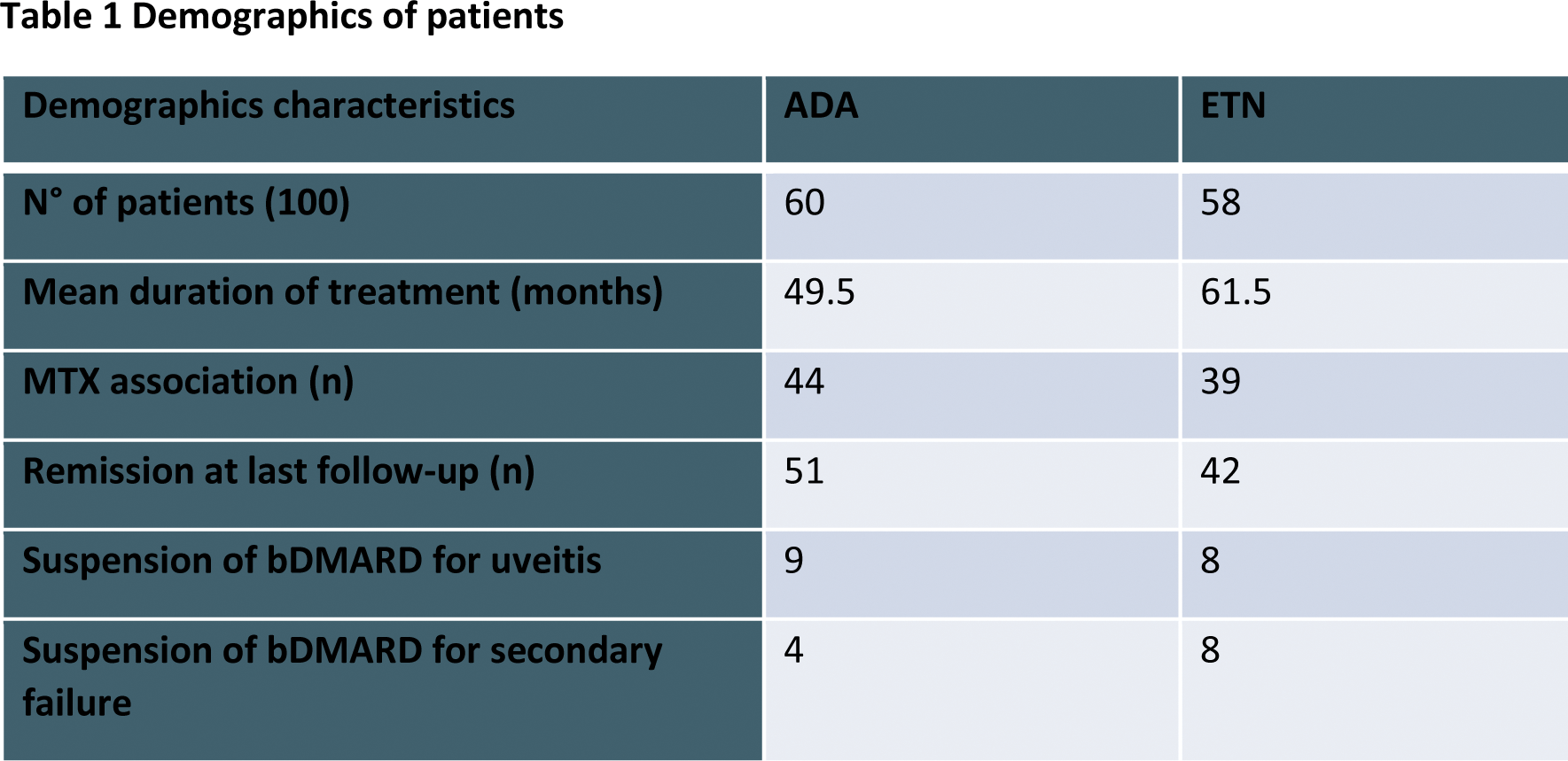
Results: Of the 118 patients included (72% female), 58 were treated with ETN and 60 with ADA. The most common diagnosis was oligoarticular JIA (55%), followed by polyarticular JIA (30%). The median age at disease onset was 3 years (1-7), with a median follow-up of 14 years. The median time to referral was 2 months (1-5 months). The median duration of treatment was 61.5 months for ETN and 49.5 months for ADA.
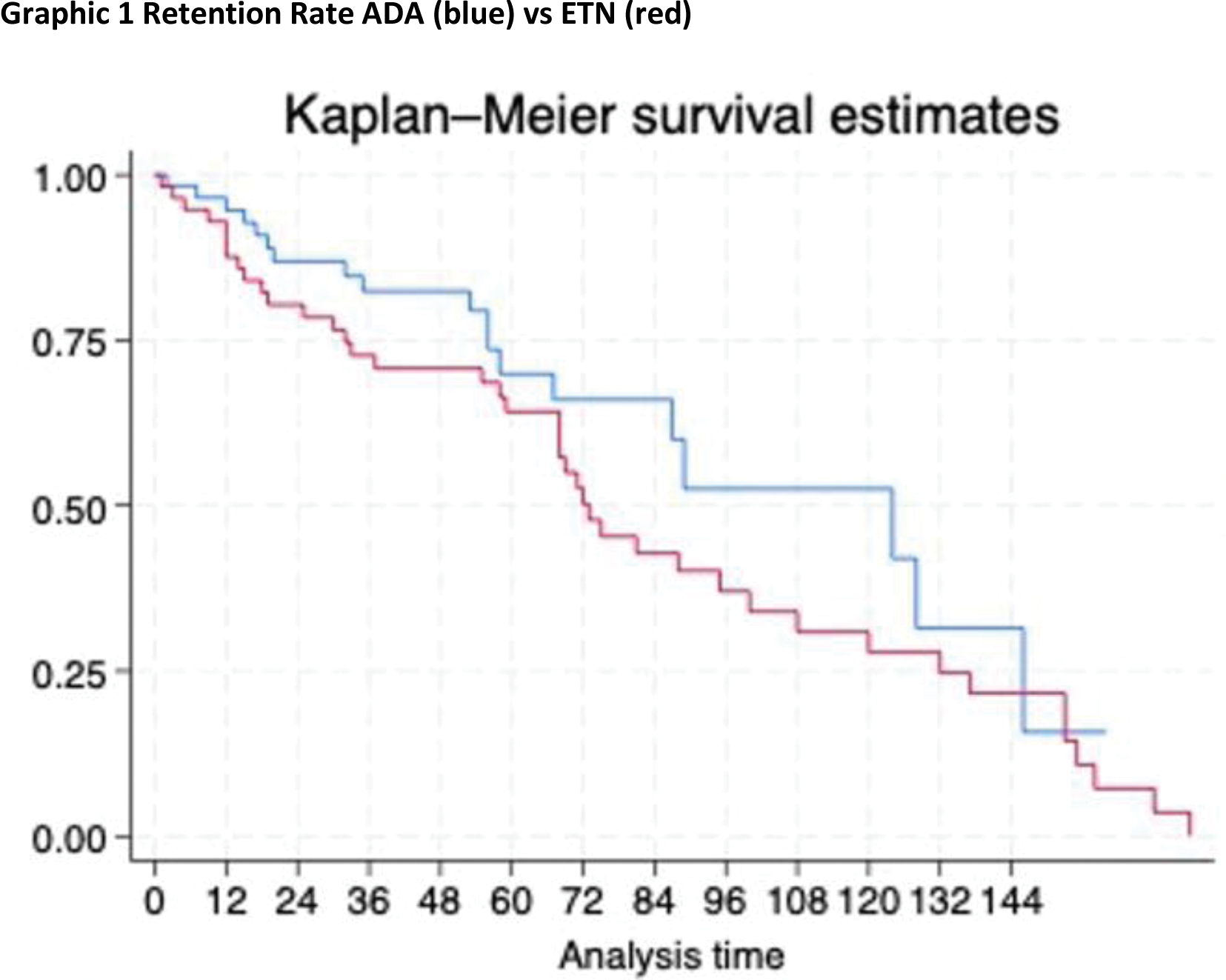
At 1 year of treatment, the retention rate was 85% in patients treated with ADA and 91% in case of ETN therapy, at 2 years it was 70% in ADA and 73% in ETN, at 5 years it was 31% in ADA and 50% in ETN.
In 62 cases (52%), bDMARD treatment was discontinued due to: sustained remission (17%; 4 in ADA group and 7 in ETN group), secondary non-response (19%; 4 in ADA and 8 in ETN), active uveitis (27%; 9 in ADA group and 8 in ETN group), while 19% of patients discontinued first-line bDMARD due to occurrence of adverse events (3 in ADA group and 9 in ETN), such as gastro-intestinal side effects (n=1 ADA, n=2 ETN) and development of anxious-depressive symptoms (n=2 ADA, n=1 ETN). Recurrent infectious events (n 3), occurrence of allergic reactions (n 2) and elevation of liver function tests (n 1) appeared more frequently in the ETN population.
At the last follow-up, 44% of patients in ADA and 39% of patients in ETN were on methotrexate or leflunomide in combination with bDMARD. 85.9% of patients had achieved sustained clinical remission.
Conclusion: Long-term treatment with ETN and ADA has been shown to be effective and safe for patients with JIA, as evidenced by the high retention rate recorded in our cohort. Most patients maintain current therapy for years to preserve remission status.
REFERENCES: NIL.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.