

Background: Altered composition of gut microbiota has been demonstrated in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Previously, we found that Prevotella species were enriched in the gut of patients with early RA[1]. In addition, impaired intestinal barrier function was observed in pre-RA patients[2]. However, the precise molecular mechanisms of how gut immune cells altered by Prevotella species contribute to arthritis are largely unknown.
Objectives: This study investigates the impact of Prevotella species, especially P. intestinalis on arthritis development, exploring its influence on immune responses, gut permeability, cytokine profiles, and gene expression in murine models of RA.
Methods: (1) Novel-isolated P. intestinalis or PBS were inoculated into C57BL/6 background mice to perform collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). Our study focused on assessing the incidence of arthritis, composition of gut microbiota by 16S rRNA sequencing, and immune cell populations by Cytek spectral flow cytometry. To further understand the mechanisms, we utilized CD4 knockout (KO) mice for T cell adoptive transfer and IL-23p19 KO mice for CIA. Intraperitoneal injection of recombinant IL-18 (rIL-18) was performed in some CIA experiments. mRNA sequencing was performed on bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) co-cultured with P. intestinalis or other intestinal bacteria such as B. thetaiotaomicron or LPS. These BMDCs were co-cultured with splenic CD4 + T cells and analysed cytokine production and proliferation activity by CFSE labelling. (2) Nineteen patients with RA and 10 healthy controls were enrolled for the ileum biopsy for mRNA sequencing.
Results: (1) P. intestinalis clearly increased the incidence of arthritis by up to 100% across three distinct experiments, contrasting with a 40% incidence rate in control mice (Figure 1A). Single inoculation of P. intestinalis rapidly shifted the gut microbiota (Figure 1B). Notably, P. intestinalis increased Th17 cells in the spleen and Peyer’s patch in the early phase of arthritis. P. intestinalis increased gut permeability before the onset of the disease, indicated by increased FITC-dextran concentration in the serum and reduced mRNA expression of Occludin and Claudin-1 in the ileum. P. intestinalis disrupted the epithelial barrier, leading to a reduction of IL-18 levels in the colon (Figure 1C). rIL-18 treatment decreased the incidence of arthritis, suggesting that IL-18 is an important cytokine to protect epithelial barrier during arthritis. Following barrier disruption, DCs primed by P. intestinalis exhibited increased production of IL-6 in the colon (Figure 1D), contributing to the development of Th17 cell-mediated arthritis. Adoptive transfer of CD4 + T cells from P. intestinalis -treated mice into CD4 KO mice resulted in a higher incidence of arthritis. In addition, IL-23p19 KO mice did not develop the disease in the presence of P. intestinalis , suggesting that IL-17 + CD4 + T cells are the principal effector cells of this model. In vitro analysis, mRNA sequence of BMDCs highlighted that P. intestinalis specifically induced IL-6 and IL-1β independently of LPS stimulation. Moreover, CD4 + T cells co-cultured with P. intestinalis -stimulated DCs exhibited more proliferative capacity and showed increased IL-17A levels in the supernatant, aligning with the data obtained from in vivo analysis. (2) Analysis of mRNA sequence from the ileum of the RA patients revealed significantly lower IL-18 levels compared to healthy controls (Figure 1E). Additionally, a subanalysis revealed that IL-6 levels were increased in new-onset RA patients compared to the controls.
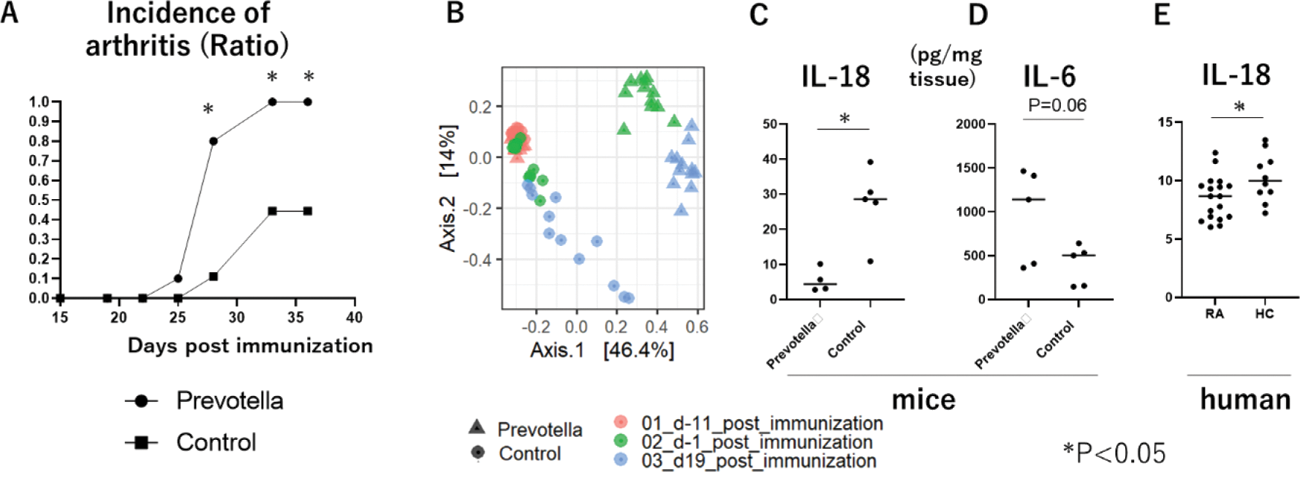
Conclusion: These findings suggest that P. intestinalis triggers excess IL-6-Th17 signaling and deficiency of IL-18 in the intestine, representing novel alterations associated with Prevotella -induced changes observed in murine models of arthritis. Moreover, this imbalance of cytokine expression was also found in human RA.
REFERENCES: [1] Maeda Y,et al. Arthritis Rheumatol.68:2646-2661, 2016.
[2] Tajik N, et al. Nat Commun. 24;11:1995, 2020.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.