

Background: Upadacitinib (UPA), an oral selective JAK inhibitor approved to treat moderately to severely active RA, has been associated with an elevated risk of herpes zoster (HZ). The biological and clinical effect of adjuvant recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) is not well studied in patients with RA receiving UPA. In a substudy of the SELECT-COMPARE trial, most patients with RA receiving UPA 15 mg once daily (QD) and background MTX achieved a satisfactory humoral and cell-mediated immune response to RZV at week (wk) 16 (4 wks postdose 2 of RZV).[1] Long-term data on the immunogenicity of RZV are needed and presented here.
Objectives: To assess the long-term immunogenicity of RZV in patients with RA receiving UPA 15 mg QD with background MTX.
Methods: Patients aged ≥ 50 years with RA from an optional substudy of the ongoing phase 3 SELECT-COMPARE trial (NCT02629159) received 2 RZV doses (at substudy baseline and wk 12). Patients were on stable doses of UPA 15 mg QD and background MTX for ≥ 8 wks before the first dose and ≥ 4 wks after the second dose. Antibody titers were collected at baseline (pre-vaccination), 4 wks postdose 1 (wk 4), 4 wks postdose 2 (wk 16), and 48 wks postdose 2 (wk 60). The primary endpoint was the achievement of humoral response to RZV 4 wks postdose 2, defined as ≥ 4-fold increase in pre-vaccination anti-glycoprotein E (gE) antibody titers (measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay). Secondary endpoints included humoral response to RZV at wks 4 and 60 and geometric mean fold rise (GMFR) from pre-vaccination anti-gE antibody levels at wks 4, 16, and 60. In an exploratory analysis, cell-mediated immunogenicity (CMI) was evaluated at wks 4, 16, and 60 in a subcohort of 40 patients by measuring the frequency of gE-specific CD4+ [2+] T cells expressing ≥ 2 activation markers (IFN-γ, IL-2, TNF-α, CD40 ligand) using intracellular cytokine staining and flow cytometry. CMI response to RZV was defined as a gE-specific CD4+ [2+] T cell frequency increase ≥ 2-fold from baseline. Safety was assessed 30 days post vaccination.
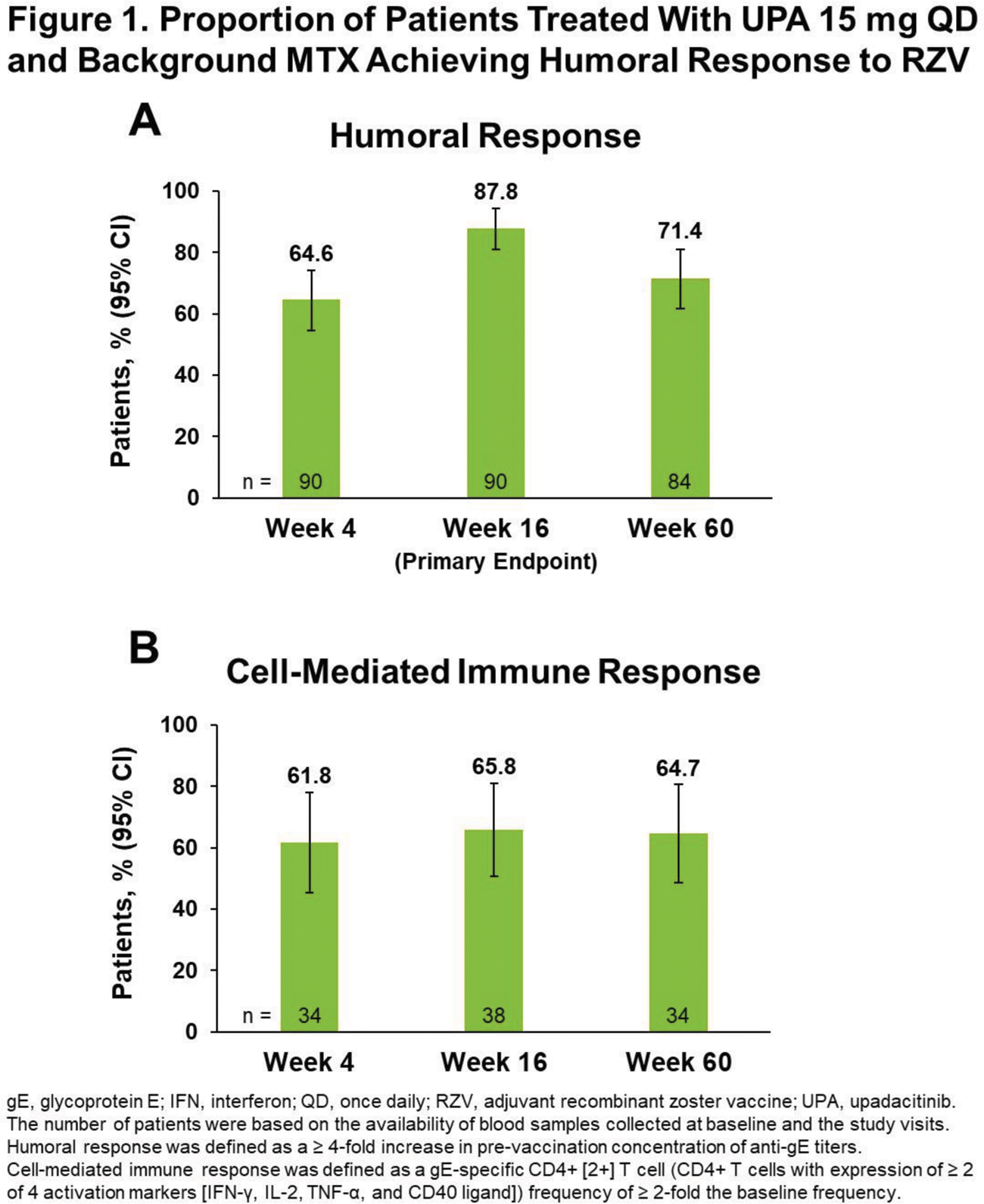
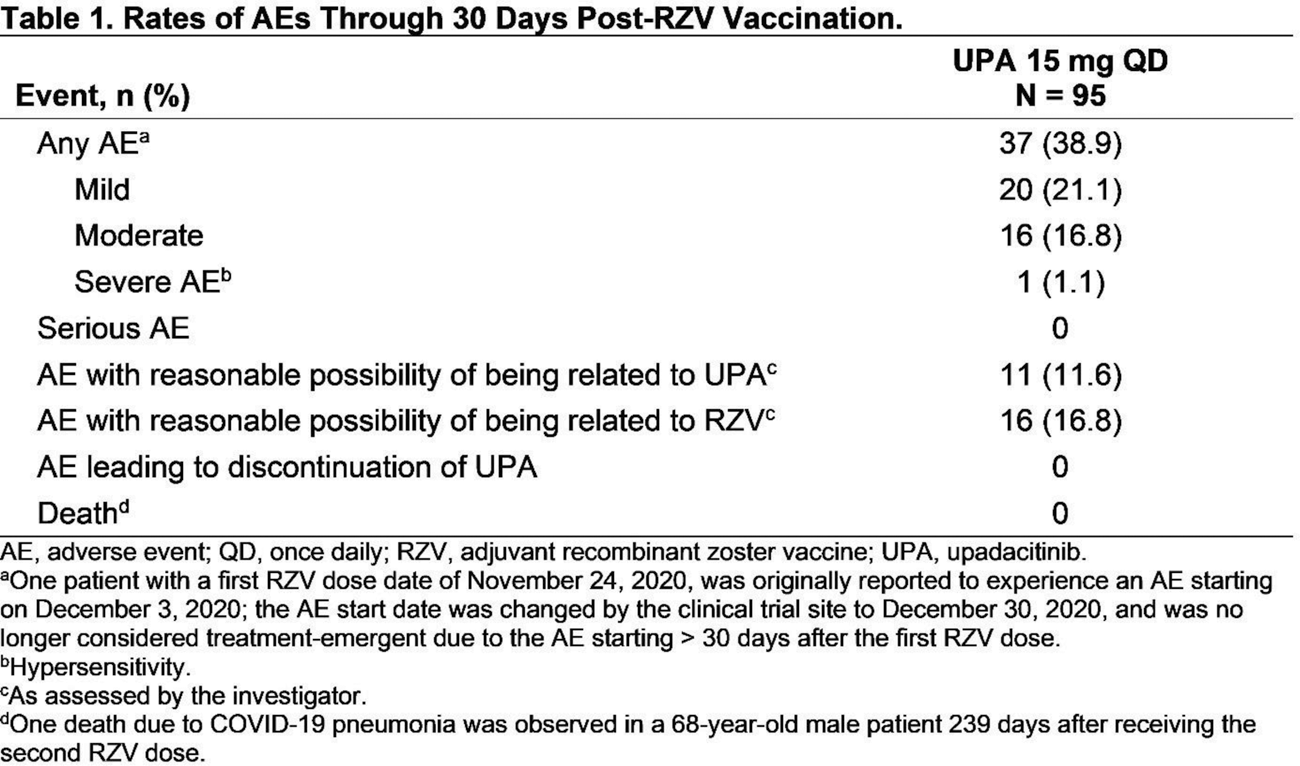
Results: Among 95 patients who received ≥ 1 RZV dose, 93 (97.9%) received both RZV doses, and 86 (90.5%) completed the substudy through wk 60; 5 patients discontinued UPA (adverse event [AE], n = 1; withdrawal by patient, n = 1; lost to follow-up, n = 2; COVID-19, n = 1). Among patients who received both RZV doses, the mean (SD) age was 62.4 (7.5) years at baseline. The median (range) duration of RA was 11.7 (4.9–41.6) years and exposure to UPA was 3.9 (2.9–5.8) years. At substudy baseline, most patients (91/93) were on MTX; half were taking corticosteroids (CS; median [range] dose 5.0 [2.5–10.0] mg/day). Blood samples were available from 90/93 patients at wks 4 and 16 and 84/93 patients at wk 60. Satisfactory humoral responses to RZV occurred in 64.4% (95% CI 54.6, 74.3) of patients at wk 4, 87.8% (81.0, 94.5) at wk 16 (primary endpoint), and 71.4% (61.8, 81.1) at wk 60 ( Figure 1A ). Rates of humoral response at wk 60 were comparable across patients aged 50–64 years (75.0% [95% CI 63.7, 86.3]) and ≥ 65 years (64.3% [46.5, 82.0]) and across those with concomitant CS use (72.7% [59.6, 85.9]) and without concomitant CS use (70.0% [55.8, 84.2]) at baseline. The GMFR from pre-vaccination anti-gE antibody levels was 10.2 (95% CI 7.3, 14.3) at wk 4, 22.6 (15.9, 32.2) at wk 16, and 8.0 (5.9, 10.9) at wk 60. In the CMI subcohort, > 60% of patients achieved cell-mediated immune response to RZV at all timepoints ( Figure 1B ). Within 30 days after either RZV dose, no serious AEs were reported ( Table 1 ). Through wk 60, 1 event of HZ occurred 4 months after the second RZV dose.
Conclusion: Most patients receiving long-term treatment with UPA 15 mg QD and background MTX achieved satisfactory humoral and cell-mediated immune responses to RZV at wks 4, 16, and 60, supporting the immunogenicity of RZV in a patient population with an elevated risk for HZ. RZV was well tolerated with no serious AEs reported within 30 days post-RZV vaccination.
REFERENCES: [1] Winthrop K, et al. Ann Rheum Dis . 2023;82:148.
Acknowledgements: AbbVie funded this study and participated in the study design, research, analysis, data collection, interpretation of data, reviewing, and approval of the abstract. All authors had access to relevant data and participated in the drafting, review, and approval of this abstract. No honoraria or payments were made for authorship. AbbVie and authors thank all the trial investigators and the patients who participated in the study. Medical writing support was provided by Jay Parekh, PharmD, of JB Ashtin, and funded by AbbVie.
Disclosure of Interests: Kevin L. Winthrop KLW has received consulting fees and/or research grants from AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Galapagos, Gilead, Lilly, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB., KLW has received consulting fees and/or research grants from AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Galapagos, Gilead, Lilly, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB., Sara K Penn SKP is a full-time employee of AbbVie, and may hold AbbVie stock or stock options., Justin Klaff JK is a full-time employee of AbbVie, and may hold AbbVie stock or stock options., Yanxi Liu YL is a full-time employee of AbbVie, and may hold AbbVie stock or stock options., Conrado García CG has received medical fees to serve as principal investigator in AbbVie clinical trials., Eduardo Mysler EM has received payment for lectures including service on speakers bureaus from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Gema Biotech, GlaxoSmithKline, Lilly, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, and Sandoz., EM has received honorarium from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Gemmene, GlaxoSmithKline, Lilly, Pfizer, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi and has provided writing assistance, medicines, equipment or administrative support to AbbVie, Pfizer, and Roche., EM has received or has pending grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche., Alvin Wells AW has received honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and Sanofi., Xianwei Bu XB is a full-time employee of AbbVie, and may hold AbbVie stock or stock options., Nasser Khan NK is a full-time employee of AbbVie, and may hold AbbVie stock or stock options., Michael Chen MC is a full-time employee of AbbVie, and may hold AbbVie stock or stock options., Anthony L Cunningham ALC has received honoraria paid to his institution from BioCSL/Sequirus, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Moderna.