

Background: ANCA associated vasculitides (AAV) are heterogeneous group of enigmatic diseases having protracted diagnostic delays and are invariably fatal without therapy. Delayed presentation is usually associated with an increased accrual damage. There is an unmet need to identify reliable markers of disease activity which can predict response to therapy and detect subclinical relapse. Proteomics has great potential to discover a reliable and accurate biomarker by deciphering the molecular basis of AAV.
To study differentially expressed proteins in serum of newly diagnosed treatment naïve AAV patients as compared to their 6 months of post treatment and healthy controls.
To validate the maximal differentially expressed proteins by ELISA.
Methods: 18 treatment naïve patients of AAV fulfilling ACR and CHCC classification criteria and 12 healthy controls (HC) were recruited. Serum samples obtained from patients at their disease onset and 6 months of post treatment and HC were pooled into triplicates and subjected to untargeted label free quantitative proteomics by LC-MS/MS. RAW files generated were analysed with Proteome Discoverer (v2.5) against the UNIPROT Human database using dual SEQUEST and AMANDA search engines. Gene ontology and KEGG pathway analysis to define significantly enriched pathways on the identified differentially expressed proteins(DEP’s) was done, using DAVID database.
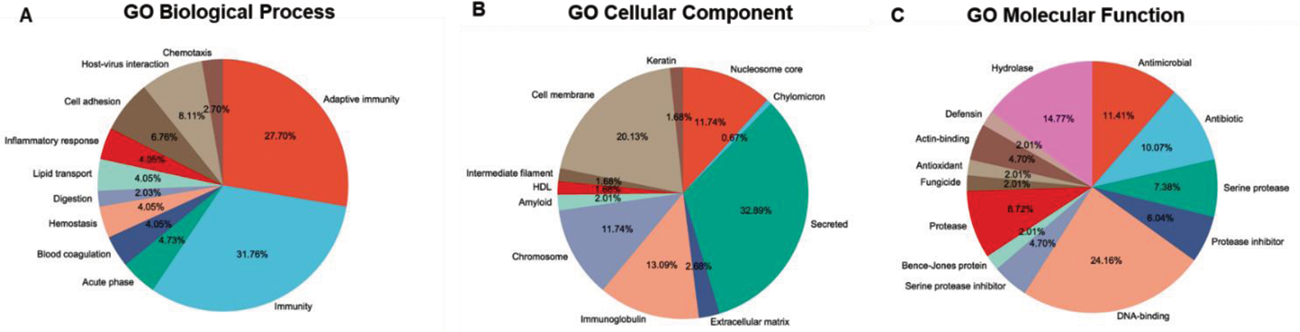
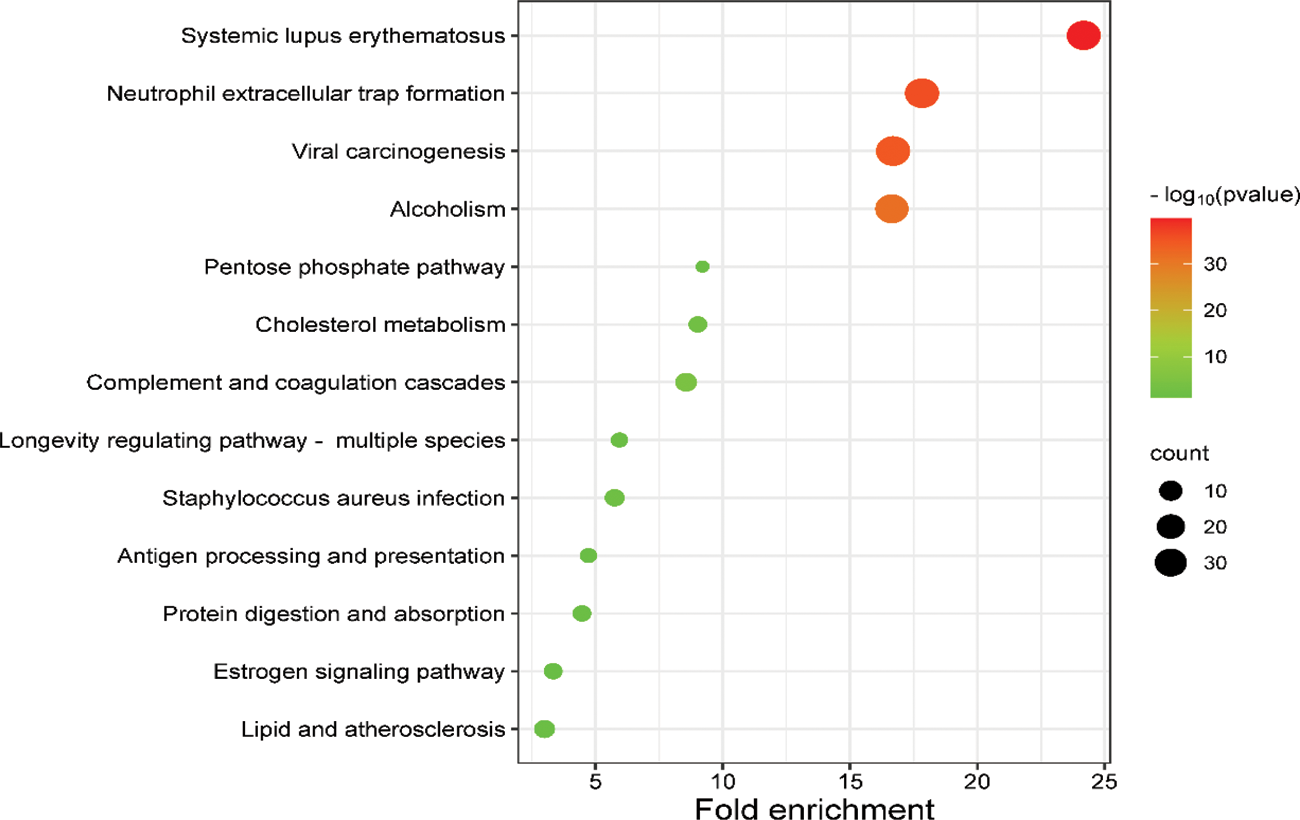
Results: The mean ± SD age of the patients was 45 ± 14.87 years. The mean ± SD BVAS at baseline before starting therapy was 23.50 ± 11.79. After 6 months of therapy, the mean ± SD BVAS was 0.8 ± 1.74. After proteomic profiling, 176 proteins were found to be significantly differentially expressed between active AAV group and post treatment group, out of which 108 proteins were found to be upregulated and 68 proteins were downregulated. 181 proteins were found to be significantly differentially expressed between active AAV group and HC group. Among them 99 proteins were upregulated and 82 proteins were downregulated. On comparing post treatment group and healthy control group, 101 proteins were found to be significantly differentially expressed, with 45 proteins were upregulated and 56 proteins were downregulated. We validated top 2 differentially expressed proteins i.e. Serum Amyloid A (SAA) and CRP were in serum samples of individual patients and HC by ELISA. Levels of SAA and CRP showed similar pattern of expression as observed by LC-MS. On pathways analysis, GO classification analysis showed that differentially expressed proteins were mainly involved in innate and adaptive immunity, cell adhesion, and lipid transport, extracellular matrix modulations and enzymatic processes etc (Figure 1). KEGG pathway analysis showed that differentially expressed proteins are enriched in NET formation, complement and coagulation cascades, and metabolic pathways (Graph 1).
Conclusion: Our results suggests the proteins identified in dyregulated pathways of B cell activation, complement pathways and metabolic pathways can be explored as new targets for future therapeutics. The proteins identified in NET formation and cell adhesion can serve as biomarkers. Moreover, dysregulated metabolic pathway such as AMPK pathway in post treatment group as compared to HC suggests newer strategies to prolong the remission by incorporating metabolism targeting drugs into the maintenance regimens for AAV. However, diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic utility of individual proteins finding warrant validation in future studies.
REFERENCES: [1] Kitching AR, Anders HJ, Basu N, Brouwer E, Gordon J, Jayne DR, et al. ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nat Rev Dis Primer. 2020;6:71.
Functional characterization of DEP‘s in Active AAV group vs post treatment group. DEP‘s were submitted to GO enrichment analysis to obtain generic view of the type of proteins expressed. Groups of GO functional classification with highest number of representative proteins are shown for (A) biological process, (B) cellular component, (C) molecular function.
KEGG pathway of active AAV vs post treatment AAV/HC. Bubble chart shows enrichment of DEP‘s in signalling pathways.
Acknowledgements: To my fellow DM residents and all faculty members of our IM2 unit.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.