

Background: In our previous Sjögren’s Disease (SjD) Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) in European populations, significant single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) peaks were identified between PRDM1 and ATG5 [1]. ATG5 is an autophagy-related protein that plays a crucial role in neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation, degranulation, and limiting autoantigens in blood. Dysregulated autophagy has been implicated in SjD and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) pathology and poor disease outcomes [2, 3]. The transcriptional repressor PRDM1 plays a role in regulating lymphocyte differentiation [4].
Objectives: Identify and functionally evaluate SjD and SLE risk variants in the PRDM1-ATG5 risk locus.
Methods: By conducting a meta-analysis of SjD and SLE GWAS datasets, we defined a credible SNP set in the PRDM1-ATG5 locus. A GWAS involving 15,691 SjD and SLE cases and 52,521 population controls of European ancestry was performed, and SNP-trait associations were tested using logistic regression models in PLINK. Bioinformatic analyses (RegulomeDB, HaploReg v4.2, promoter capture Hi-C, eQTLs, etc.) further prioritized SNPs. A CRISPR inhibition (CRISPRi) assay was used to assess the effects of these SNPs on ATG5 expression. Luciferase assays in A235 salivary gland epithelial cell line, PLB985 malignant myelomonoblasts, and GM12878 EBV-transformed B cells tested the activation and/or repressive activity of candidate SNPs.
Results: Our investigation revealed several candidate functional SNPs within the PRDM1-ATG5 region. Among them, rs533733 (p=1.15E-18), rs34582442 (p=2.79E-08), rs34599047 (p=2.82E-08), rs77846660 (p=8.39E-04), and rs56886418 (p=4.23E-03) emerged as noteworthy, suggesting their involvement in the regulatory landscape of this locus. Expanding our focus, the inclusion of rs1152966 (p=3.39E-15), rs11152964 (p=7.18E-11), rs573775 (p=6.13E-06), and rs12175062 (p=2.67E-03) in the analysis revealed a broader understanding of eQTLs and chromatin accessibility and modification patterns associated with these SNPs. The extensive influence of these SNPs was observed across various cell types, including minor salivary glands and blood cells, emphasizing their relevance in the pathogenesis of SjD and SLE. Functional assays further elucidated the allele-specific effects of selected SNPs. Notably, rs56885418 and rs3804333 demonstrated a significant decrease in enhancer activity, while rs533733 and rs62422881 exhibited an increase in enhancer activity, particularly in the A253 cell line. These findings underscore the dynamic regulatory impact of these SNPs on gene expression, providing valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms at play in the PRDM1-ATG5 locus.
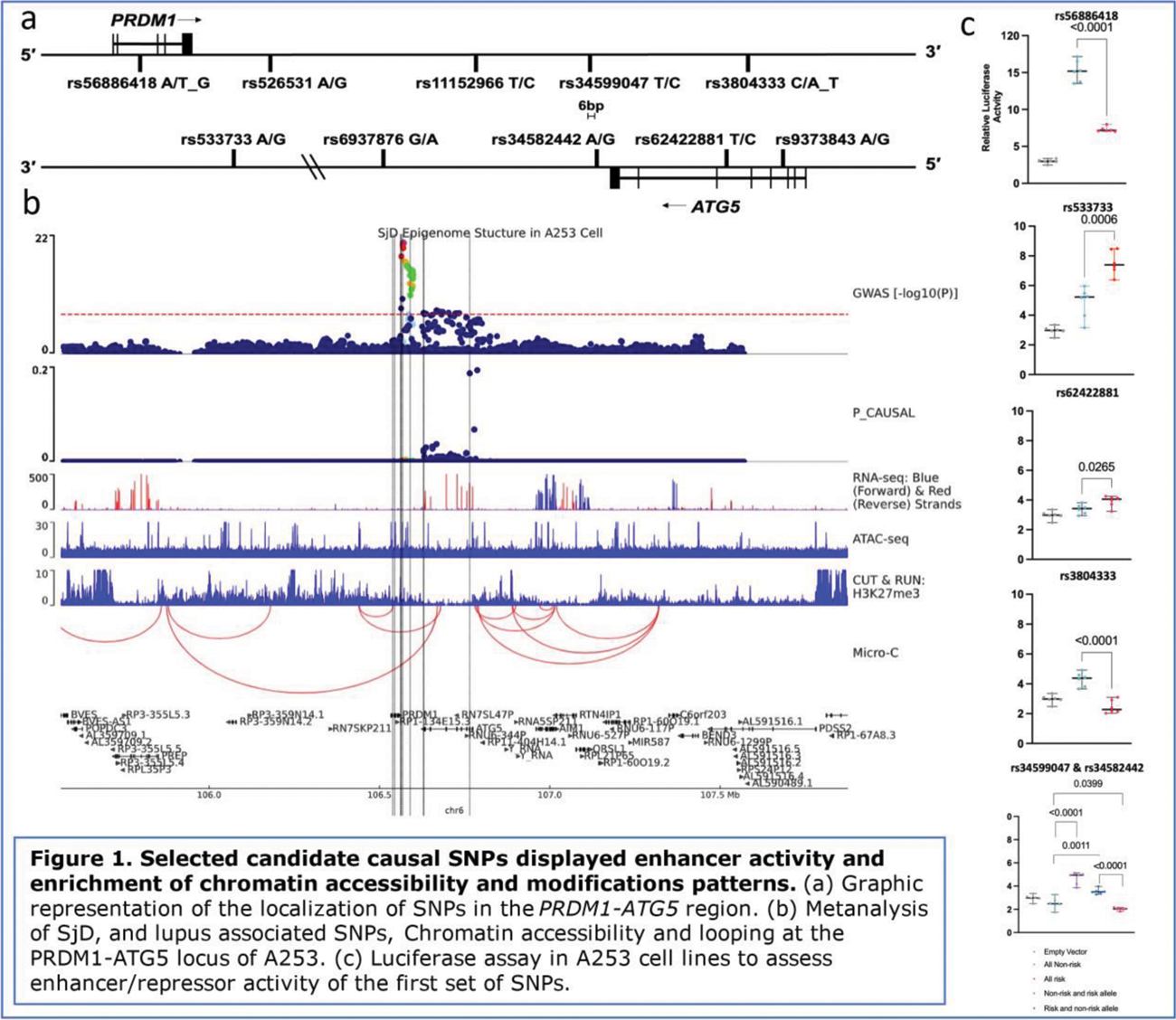
Conclusion: Functional characterization of SNPs in the PRDM1-ATG5 locus provides new insights into the regulatory mechanisms governing gene expression in SjD and SLE. Ongoing studies will focus on in vitro validation of predicted functional SNPs in A235 and GM12878 cells.
REFERENCES: [1] Khatri B, et al. Nat Commun. 2022 Jul;13(1):4287.
[2] Byun YS, et al. Sci Rep. 2017 Dec;7(1):17280.
[3] Wible DJ, et al. Cell Discov. 2019; 5:42.
[4] Kallies A, Nutt SL. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007 Apr;19(2):156-62.
Acknowledgements: National Institutes of Health (NIH): R01AR071410, R01AR073855, R01AR065953, P50AR060804, U01DE028891; National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2021R1A6A1A03038899); Sjögren’s Foundation; Presbyterian Health Foundation; Jerome L. Greene Foundation.
Disclosure of Interests: Marcin Radziszewski: None declared, Mandi M Wiley: None declared, Bhuwan Khatri: None declared, Astrid Rasmussen: None declared, Kandice L Tessneer: None declared, Kwangwoo Kim: None declared, Edward M. Vital: None declared, Nick Dand: None declared, Chen Gong: None declared, David Morris: None declared, Phil Tombleson: None declared, Elena Pontarini: None declared, Michele Bombardieri: None declared, Maureen Rischmueller: None declared, Marie Wahren-Herlenius: None declared, Marika Kvarnström: None declared, Torsten Witte: None declared, Hendrika Bootsma: None declared, Gwenny M. Verstappen: None declared, Frans G.M. Kroese: None declared, Arjan Vissink: None declared, Sarah Pringle: None declared, Athanasios Tzioufas: None declared, Clio Mavragani: None declared, Alan Baer Received consulting fees from Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS) and iCell Gene Therapeutics., Marta Alarcon-Riquelme: None declared, Javier Martin: None declared, Xavier Mariette: None declared, Gaetane Nocturne: None declared, Jacques-Olivier Pers: None declared, Jacques-Eric Gottenberg: None declared, Wan-Fai Ng I have consulted for Novartis, BMS, Janssen, Sanofi, Abbvie, IQVIA, Argenx, Resolve Therapeutics., Caroline Shiboski: None declared, Kimberly E Taylor: None declared, Lindsey Criswell: None declared, Blake M Warner: None declared, A Darise Farris Grant/research support from Johnson and Johnson Innovative Medicine (formerly Janssen; ended 12/31/2023)., Patrick M Gaffney: None declared, Judith A. James: None declared, R Hal Scofield Received consulting fees from Johnson and Johnson Innovative Medicine (formerly Janssen) and Merk Pharmaceuticals., Joel M Guthridge: None declared, Daniel J Wallace: None declared, Swamy Venuturupali: None declared, Michael T Brennan: None declared, Juliana Imgenberg-Kreuz: None declared, Lars Ronnblom: None declared, Eva Baecklund: None declared, Maija-leena Eloranta: None declared, Lara A Aqrawi: None declared, Øyvind Palm: None declared, Johan G Brun: None declared, Daniel Hammenfors: None declared, Malin V Jonsson: None declared, Silke Appel: None declared, Sara Magnusson Bucher: None declared, Helena Forsblad-d’Elia: None declared, Thomas Mandl Employee of UCB., Per Eriksson: None declared, Sang-Cheol Bae: None declared, Timothy J Vyse: None declared, Betty Tsao: None declared, Gunnel Nordmark: None declared, Christopher J Lessard Grant/research support from Johnson and Johnson Innovative Medicine (formerly Janssen; ended 12/31/2023).