

Background: Primary Sjogren’s syndrome is one of the systemic autoimmune diseases. In recent years, studies have suggested that CD8 + T cells also play an important role in the pathogenesis of pSS, but the specific molecular mechanism by which CD8 + T cells cause exocrine gland damage is still unclear[1]. Therefore, in-depth study of the molecular regulatory mechanism of CD8 + T will help us clarify the specific role of CD8 + T cell subsets in the pathogenesis of pSS and find potential new targets for the treatment of pSS.
Objectives: The aim of this study is to: 1) detect the frequency of CD8 + T cells in peripheral blood, and screen and validate CD8 + T cell genes through transcriptome sequencing analysis; 2) Exploring the mechanism of CD8 + T cell cytotoxicity and mitochondrial dynamics disorders.
Methods: We obtained 11 human SG biopsy samples from pSS patients and 5 SG samples from non-SS control individuals who had sicca symptom but not meeting any of the classification criteria of pSS.The peripheral blood samples from 5 patients with pSS and 3 healthy controls were also collected and digested into single-cell suspensions, and subjected to scRNA-seq.Phenotypical analysis of CD8 + T cell in PBMCs from 37 pSS patients and 40 healthy donors (HD) was performed by flow cytometry.Isolating CD8 + T cells from PBMCs and observing their morphology under transmission electron microscopy.Transcriptional analysis of sorted CD8 + T cell from 6 pSS patients and 5 HD was performed by RNA-seq. Differential gene expression was validated using RT-PCR and WB. Additionally, primary CD8 + T cells cultured in vitro were used to detect their functional effects under activation or inhibition of TLR2.Simultaneously detect the morphology and function of mitochondria in primary CD8+T cells after cultivation.
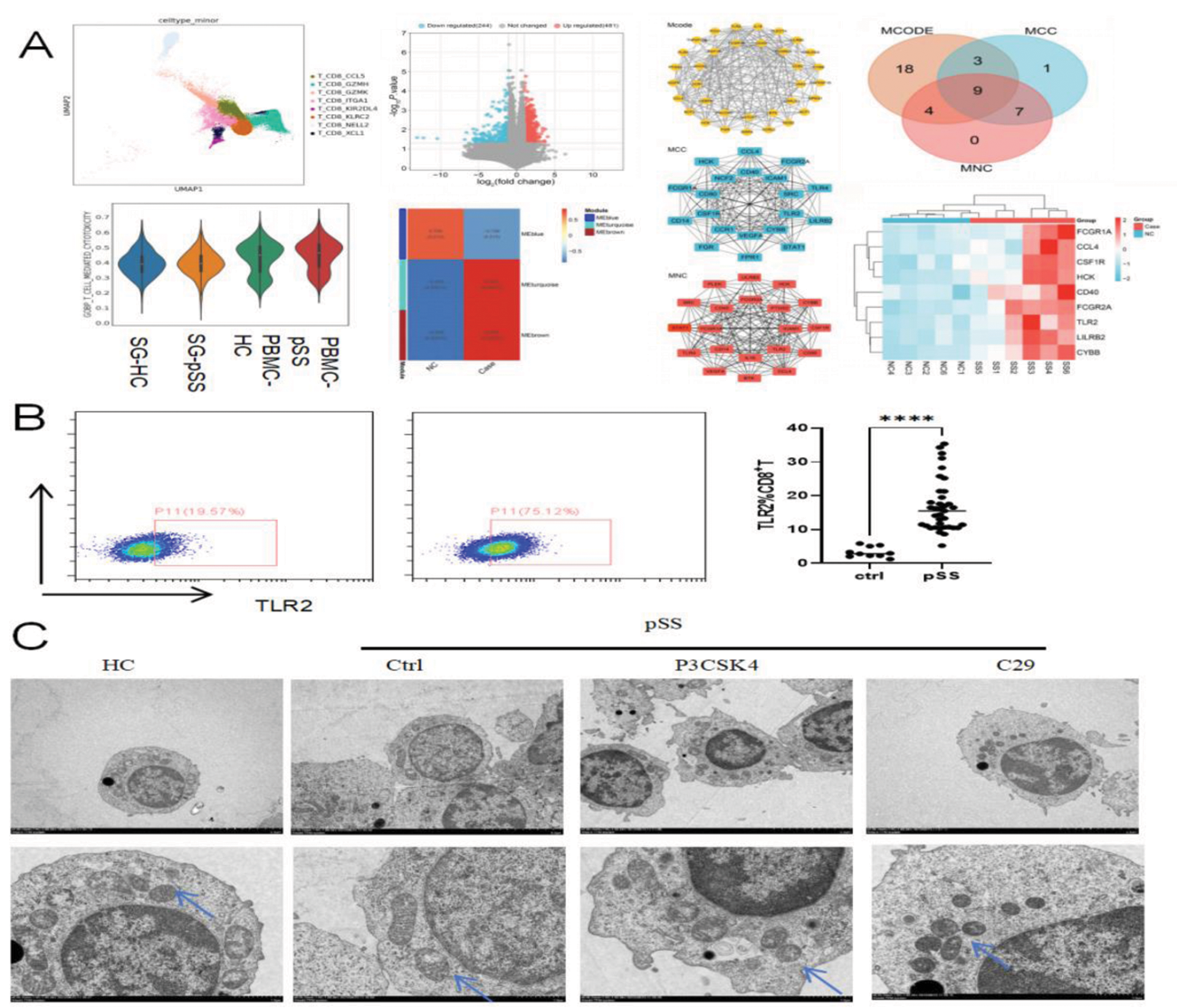
Results: Here, We obtained a total of 79,596 immune cell transcriptomes by the integration of PBMCs and SG scRNA-seq data. Among these, cytotoxic CD8 + T cells significantly expand in peripheral blood of pSS. And we observed an increase in the proportion of CD8 + T cells in the blood of pSS patients, exhibiting cytotoxic effects (p<0.01) and enhanced inflammatory response(p<0.05). Besides the organelle damage was also observed in CD8 + T cells of pSS patients by TEM. The transcriptome sequencing results identified 9 key genes through the bioinformatics algorithm, among which TLR2 was found to have the most significant expression difference (p<0.001) by RT-PCR. During in vitro culture of CD8 + T cells, activation of TLR2 expression significantly promoted the cytotoxicity and inflammatory response of CD8 + T cells (p<0.05). Specially mitochondria observed with partial or complete loss of cristae and increase significantly in autophagosomes was observed under transmission electron microscopy (p<0.01).The seahorse experiment confirmed that TLR2 affects both basal and maximal oxidative mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in CD8 + T cell. JC-1 results showed impaired mitochondrial membrane potential, and WB detected a significant increase in the expression of mitochondrial autophagy proteins PINK1 and Parkin.These findings suggest that mitophagy in CD8 + T cells is associated with their cytotoxic effects.
Conclusion: In summary, our research results demonstrate the TLR2 promotes cytotoxicity and inflammatory response of CD8 + T cells by activating mitophagy, which further leads to the pathogenic role of CD8 + T cells in pSS.Our research provides new potential therapeutic targets for pSS.
REFERENCES: [1] Gao CY, Yao Y, Li L, et al. Tissue-Resident Memory CD8 + T Cells Acting as Mediators of Salivary Gland Damage in a Murine Model of Sjögren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(1):121-132.
TLR2 promotes cytotoxicity and inflammatory response of CD8 + T cells by activating mitophagy in primary Sjogren’s syndrome.(A)scRNA-seq and RNA-Seq results of peripheral blood CD8 + T cells; (B)Flow cytometry verification of differential expression of TLR2 in peripheral blood CD8 + T cells; (C)Observation of the effects of TLR2 inhibitors and ligands on the mitochondrial structure of CD8 + T cells under transmission electron microscopy.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.