

Background: Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) is an autoimmune disease characterised by vascular damage, inflammation, and fibrosis of the skin and organs, with no approved disease modifying treatments. FT011 is a G protein-coupled receptor 68 proton sensing antagonist that has anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory activity. Transcriptomic analysis of kidney tissue from a rat model of chronic kidney disease has shown that FT011 modulates of a broad range of molecular pathways[1], many of which are relevant to the pathogenesis of SSc. Indeed, a Phase 2 trial has shown evidence of clinical benefit of FT011 in diffuse SSc (dcSSc) as assessed by the revised American College of Rheumatology Composite Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis (ACR-CRISS)[2].
Objectives: To determine the treatment effect of FT011 on Revised CRISS-25 and skin transcriptomic profiles in patients with dSSc.
Methods: A phase IIa, randomised, double blind, placebo-controlled study of oral FT011 in patients with dSSc. The study randomised 30 participants (n = 10/group) to placebo, FT011 200 mg or FT011 400 mg QD for 12 weeks (NCT04647890). A post hoc analysis was conducted to evaluate trial results based on revised CRISS-25[3] which incorporates 5 key components: percent predicted forced vital capacity (%pFVC), Modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS), Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI), Patient Global Assessment (PGA), and Clinician Global Assessment (CGA). A clinical improvement based on revised CRISS-25 is defined as a change in at least 2 components from baseline quantitated as:
≥5% increase in %pFVC,
≥25% decrease in mRSS, HAQ-DI, PGA, CGA,
With worsening in no more than one component (by same percent change) and no significant SSc-related event.
Skin biopsies were collected at baseline and week 12 with RNAseq data generated. Pathway enrichment analysis of the top 400 significantly differentially expressed genes (DEGs) from baseline to week 12 was performed. Principal component (PC) analysis of genes from a pre-defined fibrotic signature 1 was used to generate a fibrotic gene signature score for each tissue sample.
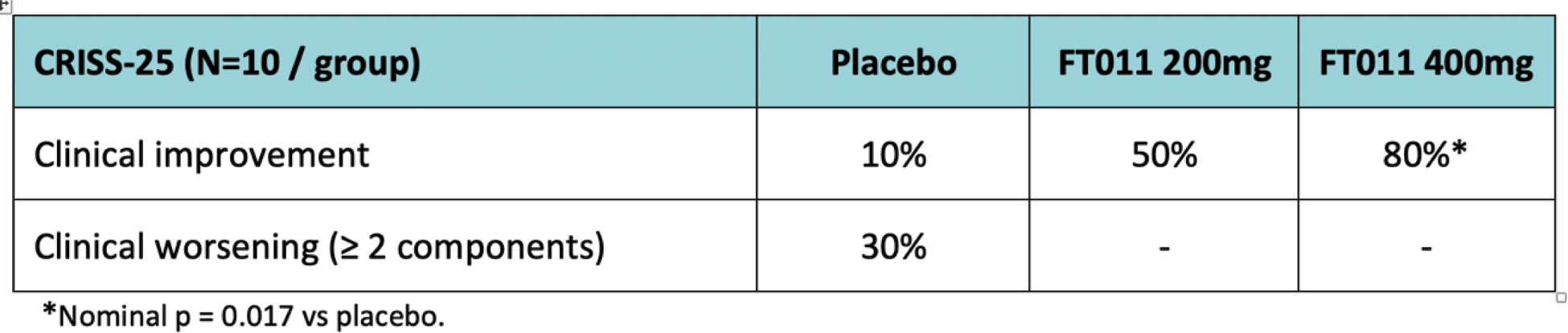
Results: 12-weeks of FT011 treatment led to a significant (nominal p=0.0017) increase in the proportion if patients showed clinical improvement based on the Revised CRISS-25 (Table 1).
Table 1. The proportion of patients (expressed as a percentage) per dose group showing clinical improvement.
Pathway analysis of DEGs from each cohort showed inflammatory pathways were upregulated in the placebo cohort, whereas fibrotic pathways were downregulated after 12 weeks of treatment with FT011 400 mg. Treatment with FT011 400mg led to a decrease in the fibrotic gene signature score, determined by PC analysis, compared to the Placebo cohort (nominal p<0.005), where the score increased from baseline at 12 weeks, signifying the fibrosis and inflammatory signatures worsened in placebo and improved with FT011 treatment based on the gene expression profile in skin (Figure 1).
Change in fibrosis gene signature score from baseline to Week 12 in skin biopsies.
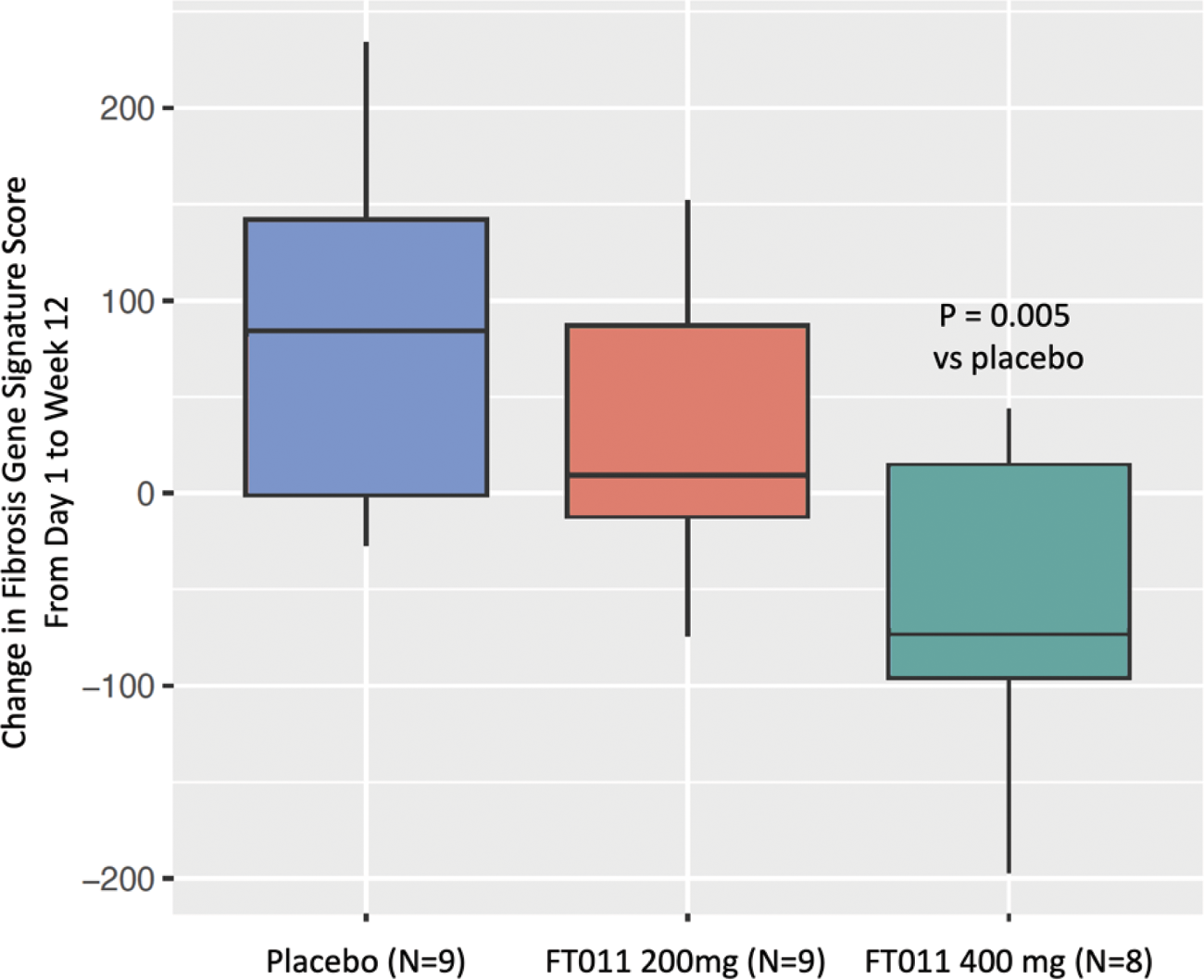
The dose dependent effect, where a greater decrease in the fibrosis gene signature score was observed for the FT011 400 mg group compared to the FT011 200 mg group, is consistent with the clinical efficacy results.
FT011 was safe and well tolerated, with no differences in drug-related treatment-emergent adverse events between groups.
Conclusion: FT011 shows promising efficacy after 12 weeks of treatment using a new composite score, CRISS-25, and this clinical benefit coincides with a downregulation of fibrotic genes and pathways in SSc skin.
REFERENCES: [1] S Eddy, et al., Identification of Non-Invasive Surrogates as Predictors of Response to FT011 in Kidney Disease, ASN Kidney Week 2022, [abstract 3767783].
[2] Denton C et al., FT011 for the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis. Results from a Phase II Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9).
[3] Khanna D, et al., New composite endpoint in early diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis: revisiting the provisional American College of Rheumatology Composite Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80(5):641-650.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: Michelle Papadimitriou Employee of Certa Therapeutics, Lam Tsoi: None declared, Jennifer Fox: None declared, Sean Eddy Receipt of grants from Roche-Genentech, Eli Lilly, Certa Therapeutics, Moderna Tx, Ionis, Astra-Zeneca, Novo Nordisk, Gilead, Janssen, Johann E. Gudjonsson Consultant to AnaptysBio, Almirall, AbbVie, Janssen, BMS, Eli Lilly, Sanofi, Receipt of grants from Eli Lilly, AbbVie, Almirall, Janssen, BMS, Prometheus Biosciences/Merck, Matthias Kretzler Consultant to Janssen, Novo Nordisk, Receipt of grants from Boehringer-Ingelheim, Certa, Travere, Maze therapeutics, Roche, Astra-Zeneca, Novo Nordisk, Moderna, Chinook, RenalytixAI, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Regeneron, Janssen;, Michelle Bradney Employee of Certa Therapeutics, Christopher P Denton Janssen and Boehringer Ingelheim, Consultant to Janssen, GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche, CSL Behring, Corbus, Acceleron, Horizon, Arxx Therapeutics, Lilly, Novartis, Certa, Receipt of grants from GSK, Abbvie, Horizon, Wendy Stevens Speaker to Jannsen, Receipt of grants from Janssen, BI, Darren Kelly Certa Therapeutics Shareholder, Employee of Certa Therapeutics.