

Background: Osteoarthritis (OA) has long been thought to be only of local mechanical origin. However, it has been shown recently that there is a phenotype of OA with inflammatory properties.
Objectives: We hypothesize that circulating neutrophils are involved in disease pathogenesis suggesting a systemic involvement in this “local” disease.
Methods: We investigated the cytosolic proteome of blood neutrophils from four OA patients with an inflammatory knee osteoarthritis and compared it to the cytosolic proteome of blood neutrophils from three healthy controls (HC). Functional analysis was generated through the use of the software Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA). We further investigated in vitro the physiological apoptosis of isolated circulating neutrophils from ten other OA patients compared to neutrophils from HC of similar age, used Western blot analysis to confirm the results of specific proteins of the proteome analysis and measured the glycogen content in neutrophil cytosol.
Results: Based on the differentially regulated proteins, IPA predicts a downregulation of the glycogen degradation pathway as the most important difference between blood neutrophils from OA patients and those from HC, suggesting a disturbance in glycogen storage or use in OA neutrophils. Further, IPA predicts an inhibition of cell death of immune cells and an activation of senescence of cells. One of the differentially regulated proteins involved in survival is PCNA, which is found to be increased in circulating neutrophils from OA patients. When measuring the glycogen content in blood neutrophils from OA patients compared with that from HC, we found no difference in glycogen content. However, we found a significant difference in the content of glycogen between neutrophils at a basal state and apoptotic neutrophils in both groups, suggesting that neutrophils use glycogen during their apoptosis. There was no correlation between the basal glycogen concentration of the cells and the percentage of apoptosis in neutrophils from both HC and OA, suggesting that the initial glycogen concentration has not a direct impact on the process of apoptosis of neutrophils. Annexin-V labeling showed a significantly delayed physiologic apoptosis in neutrophils from OA patients compared to HC. Further, the increase in PCNA found in the proteome of neutrophils from OA patients was confirmed in our validation cohort by an increased measurement by Western blot analysis.
Conclusion: Our findings uncover for the first time a dysregulation in circulating neutrophils in OA that could have an impact on the disease pathogenesis and demonstrate a systemic involvement in OA. We provide evidence that cytosolic proteins of circulating neutrophils of OA patients are disturbed in terms of glycogen metabolism and apoptosis, which might result in a higher survival rate. Molecular mechanisms underlying these disturbances remain to be elucidated.
REFERENCES: [1] Chaney, S., et al., The Involvement of Neutrophils in the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Biomedicines, 2022. 10(7).
[2] Sadiku, P., et al., Neutrophils fuel effective immune responses through gluconeogenesis and glycogenesis. Cell Metab, 2021. 33(5): p. 1062-1064.
[3] Ohayon, D., et al., Cytosolic PCNA interacts with p47phox and controls NADPH oxidase NOX2 activation in neutrophils. J Exp Med, 2019. 216(11): p. 2669-2687.
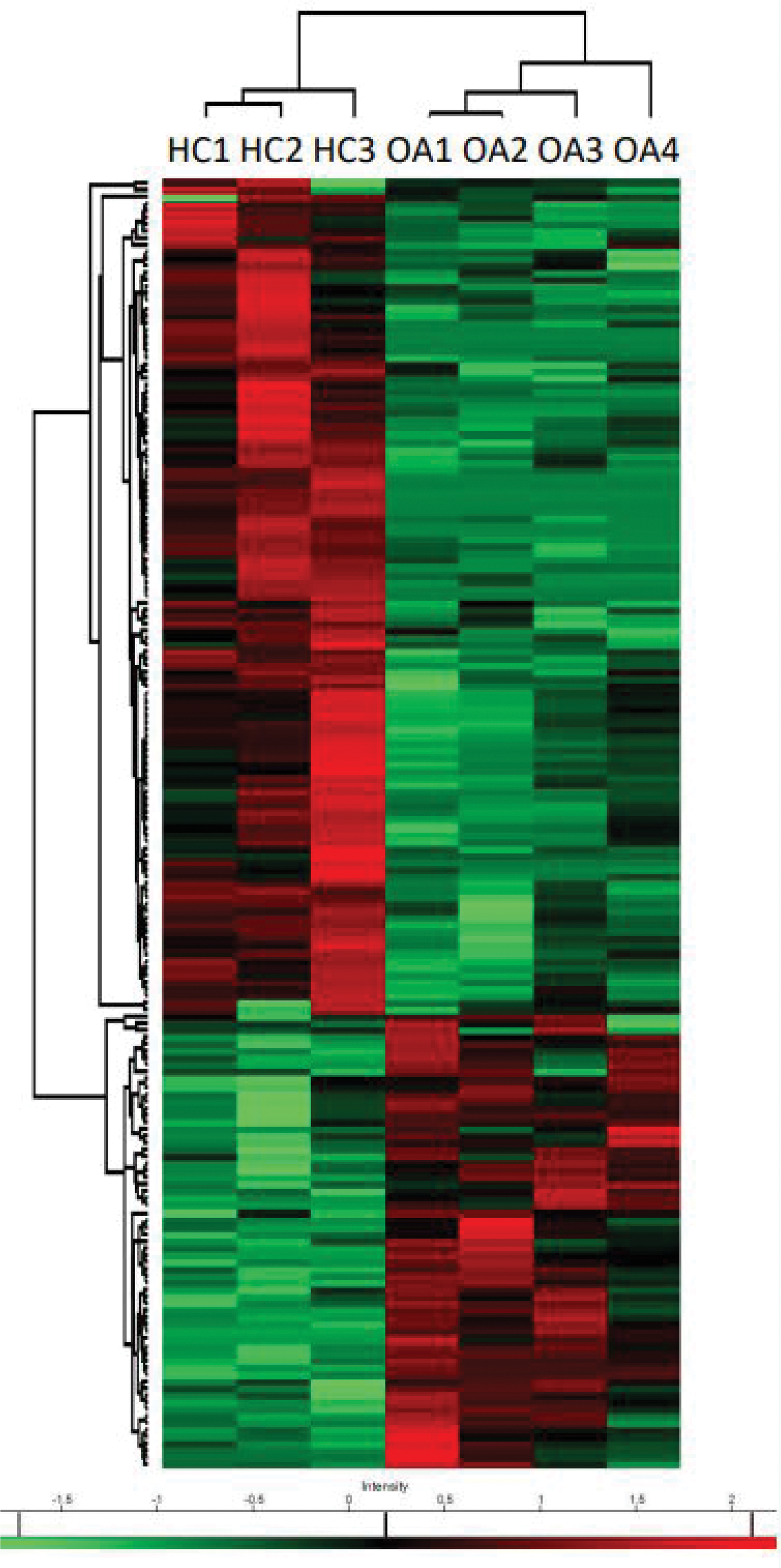
Heat map of differentially expressed proteins between neutrophil cytosol from blood of healthy control (HC) and osteoarthritis patients (OA). The proteins (rows) and samples (columns) are hierarchically clustered using Pearson correlation and average linkage on z -score quantification intensities. Each number indicates one patient. Color depicts the z -score changes in protein intensities respective to baseline expression levels, red: overexpression and green: underexpression.
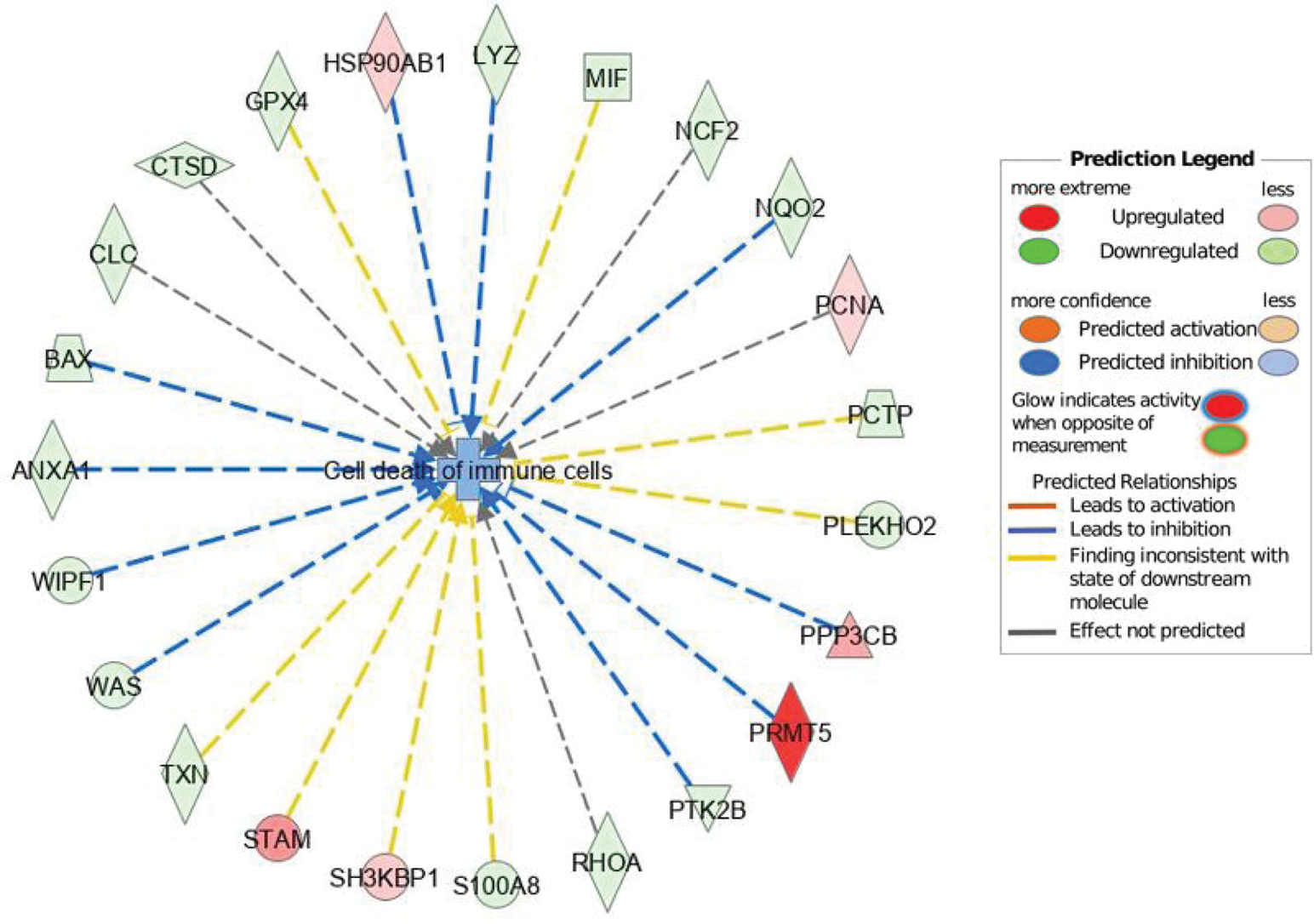
Specific network of cell death pathway shows differentially expressed proteins in the cytosol of blood neutrophils from OA patients and HC. Red and green indicate increased or decreased measurement of proteins in neutrophils from OA patients compared to HC. Blue indicates predicted inhibition as shown in the colored legend.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: Jennifer Amsler: None declared, Morgane Le Gall One hour seminar for CHUGAI-Roche 22/03/2018, Camille Daste: None declared, François Rannou Eli Lilly, Fidia, Ipsen, Thuasne, Véronique Witko-Sarsat: None declared.