

Background: Recent studies in metabolomics and lipidomics have increasingly focused on rheumatoid arthritis (RA), revealing significant insights[1, 2]. Notably, Ceramide has been identified at higher concentrations in the peripheral blood and tissue samples of RA patients compared to healthy controls and other disease groups[3]. Ceramide level is closely associated with markers of inflammation and bone destruction[4, 5]. However, the impact of inhibiting Ceramide metabolism on RA remains unclear.
Objectives: This study aims to assess the effects of the Ceramide synthesis inhibitor myriocin on fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in RA patients. We also aim to examine the inflammatory markers and abnormal proliferation of FLS. Furthermore, we validate our findings using a mouse model of inflammatory arthritis.
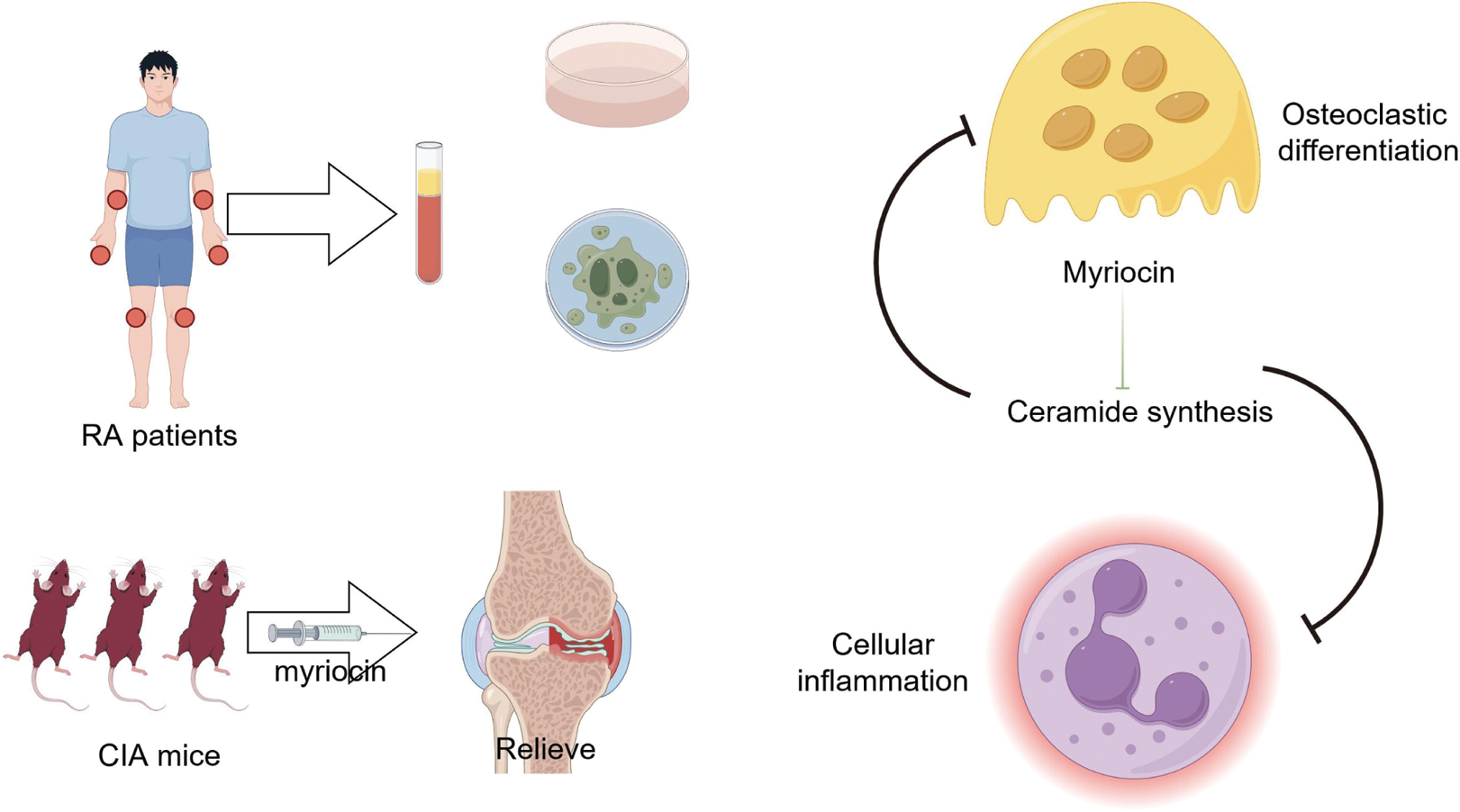
Methods: FLS and PBMCs from active RA patients were cultured with 5 μM myriocin or a vehicle control for 24 hours. The chemokines and cytokines released into culture supernatants were quantified by ELISA, and the invasive properties of FLS were assessed via migration assays. Additionally, we used type II collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in SD mice, injecting myriocin at various stages to monitor inflammation and bone metabolism markers. We also extracted primary macrophages from healthy SD mice, inducing osteoclasts (OC) with M-CSF and RANKL, and intervened with different concentrations of myriocin. Results were analyzed through TRAP staining. Furthermore, we induced an inflammatory macrophage model using LPS and applied the same interventions, analyzing outcomes through ELISA.
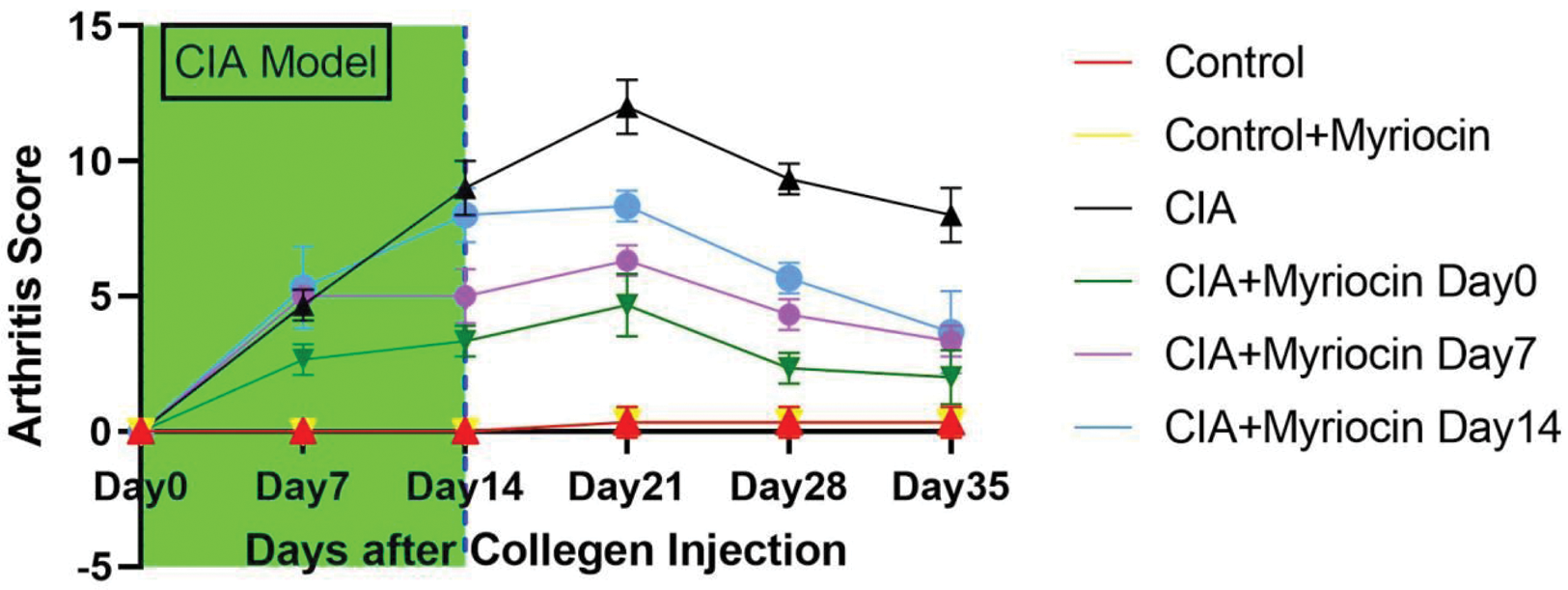
Results: Twenty RA patients were recruited for the study. Myriocin significantly reduced the expression of chemokines in RA patient PBMCs and effectively inhibited the migration and proliferation of FLS. In the CIA mouse model, mice injected with myriocin showed a faster reduction in inflammation and quicker alleviation of joint symptoms compared to saline-injected mice. However, myriocin did not significantly affect bone metabolism markers. During osteoclast induction, high doses of myriocin were required to inhibit the differentiation process. In the inflammatory macrophage experiments, myriocin effectively inhibited inflammation at various concentrations, with the effect positively correlating with the dose.
Conclusion: The Ceramide metabolism inhibitor myriocin effectively alleviates RA inflammation and improves peripheral immune status. However, its role in regulating the bone destruction process in RA requires further investigation. This study contributes to understanding the therapeutic potential of targeting ceramide metabolism in RA and highlights the need for more comprehensive research on its effects on bone health.
REFERENCES: [1] Ke JT, Zhang H, Bu YH, Gan PR, Chen FY, Dong XT, et al. Metabonomic analysis of abnormal sphingolipid metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts in hypoxia microenvironment and intervention of geniposide. FRONT PHARMACOL. 2022 2022/1/20;13:969408.
[2] Luan H, Chen S, Zhao L, Liu S, Luan T. Precise Lipidomics Decipher Circulating Ceramide and Sphingomyelin Cycle Associated with the Progression of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J PROTEOME RES. 2023 2023/12/1;22(12):3893-900.
[3] Meshcheryakova A, Mechtcheriakova D, Pietschmann P. Sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling in bone remodeling: multifaceted roles and therapeutic potential. EXPERT OPIN THER TAR. 2017 2017/7/1;21(7):725-37.
[4] Alexandropoulou I, Grammatikopoulou MG, Gkouskou KK, Pritsa AA, Vassilakou T, Rigopoulou E, et al. Ceramides in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases: Existing Evidence and Therapeutic Considerations for Diet as an Anticeramide Treatment. NUTRIENTS. 2023 2023/1/2;15(1).
[5] Yang Z, Liang Q, Liang H, Chen W, Li C, Xiao Y, et al. Single-cell RNA transcriptomic and plasma Lipidomic reveal the potential mechanisms of a Methotrexate-based therapy against Rheumatoid Arthritis. PHYTOMEDICINE. 2023 2023/7/1;115:154816.
Schematic of the whole study
Myriocin reduces arthritis score in CIA model
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.