

Background: Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is associated with substantial disability and impaired quality of life. Treatment aims at decreasing pain and improving function combining non-pharmacological (education, exercise, and weight reduction) and pharmacological modalities (topical, oral NSAIDs, and intraarticular corticosteroids). A challenge is to reduce the consumption of oral NSAIDs due to their side effects. Oral enzyme combination (OEC) therapy with bromelain, trypsin, and flavonoid rutin has proven to be efficacious in several painful musculoskeletal disorders and OA, but its mechanism of action is not fully known.
Objectives: We assessed whether OEC could modulate pathways involved in the reduction of inflammation, and consequently improve clinical symptoms, in people with knee OA.
Methods: This was a randomized, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled, 8-week crossover, multicenter, exploratory study (NCT05038410) involving patients (age ≥ 40 years, BMI ≤35 kg/m 2 ) with symptomatic knee OA (radiological Kellgren & Lawrence grade II-III, pain at rest or walking ≥40 on a 1-100 Visual Analogue Scale [VAS]). Key exclusion criteria were previous use of corticosteroids, food supplements, or symptomatic slow-acting drugs within the previous 3 months. OEC (and matching PBO) was administrated as 2 x 3 tablets/day. The pre-defined exploratory endpoints were the changes over time of markers of 1) systemic inflammation, including pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, and growth factors (e.g., IL-10), 2) the innate immune response, including the anti-protease and acute-phase-protein α-2-macroglobulin (A2M), and 3) cartilage remodeling in serum and urine (e.g., serum Coll2-1NO2 and urinary CTX-II). Secondary endpoints included the patient-reported (VAS 0-100) Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS) (global as well as subdomain scores). General safety parameters as well as specific hemorheological safety parameters were also assessed. Data were analyzed for the modified intention to treat (mITT) population using a generalized linear mixed model analysis after 8 weeks of treatments based on the changes from baseline (BL) of each period before and after cross-over and effect estimates were given as ratios of geometric means and their 95% confidence interval.
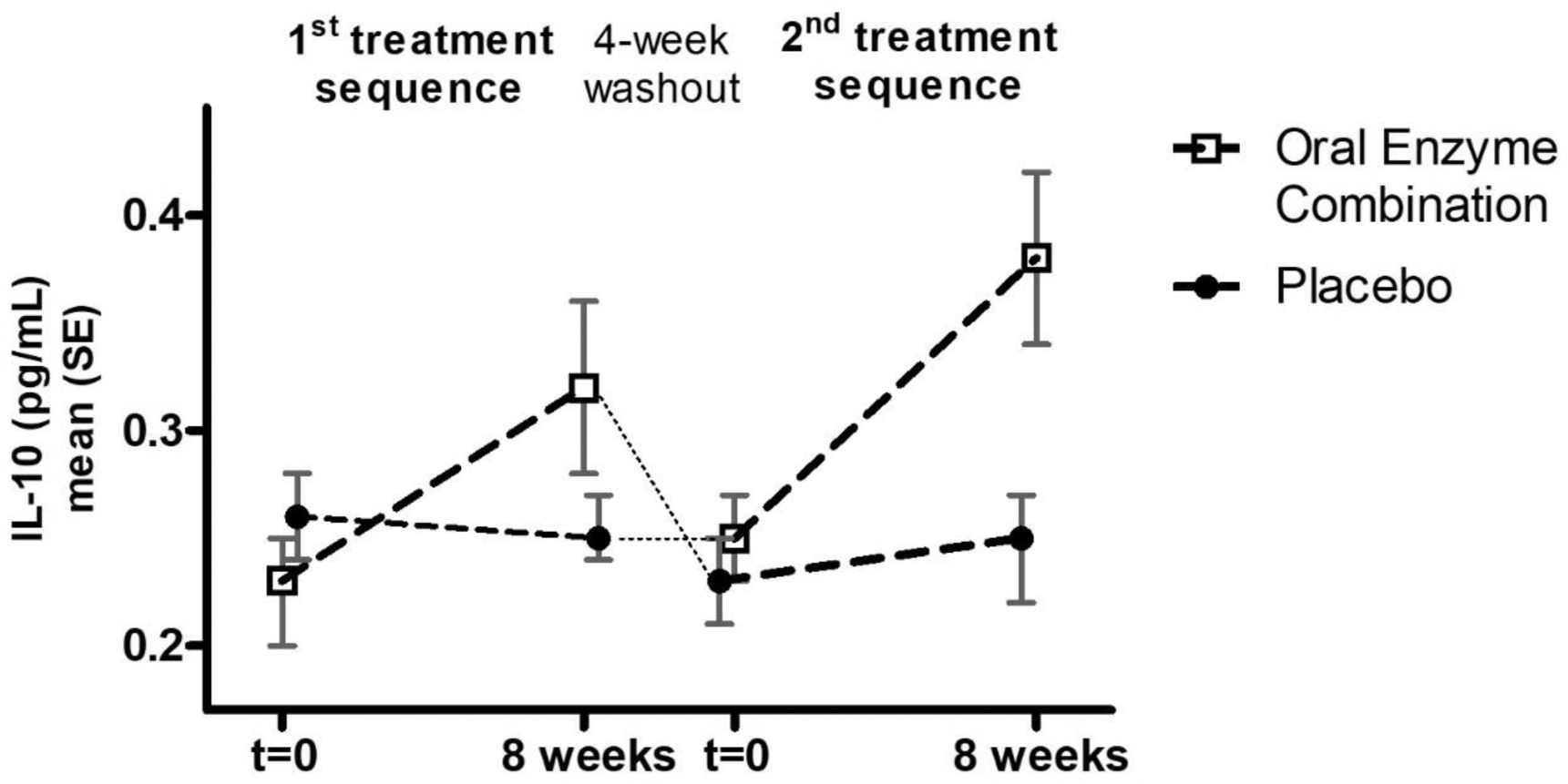
Results: A total of 56 patients were screened at 5 sites in Belgium, of whom 45 were randomized (n=24 women, mean age/BMI 63 years/27.4 kg/m 2 , VAS pain at rest/walking 38.3/56.9, KOOS global score 48.7) and 43 participants completed both study sequences (April 2021 - Oct 2022), representing the mITT population. A significant difference in the change from baseline between OEC and PBO geometric means (G mean ) of IL-10 (Figure 1) was observed (BL OEC/PBO 0.240/0.245 pg/mL; G mean (95% CI) OEC/PBO 138% (118%, 162%); p<0.001) (Figure 1). Similarly, A2M levels (BL OEC/PBO 1.60/1.68 g/L) increased significantly with OEC (G mean (95% CI) OEC/PBO 103% (100%, 105%); p=0.038). The urinary cartilage biomarker CTX-II (BL OEC/PBO 485/495 ng/mL) was significantly reduced with OEC (G mean (95% CI) OEC/PBO 88% (79%, 99%); p=0.038), whereas serum collagen markers remained unchanged. OEC significantly improved the KOOS subdomain scores “Symptoms” (p=0.026) and “Pain” (p=0.046), but not total or other KOOS subscores as compared to PBO. Adverse events were overall balanced between groups, and no clinically relevant changes in clinical biology and hemorheological parameters were observed in either group.
Conclusion: This is the first clinical study rigorously exploring the underlying mechanisms of action of OEC in OA. OEC significantly increased IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine, and reduced CTX-II level, a marker of cartilage degradation. Together with the reduction of OA symptoms, these findings suggest that OEC could have disease-modifying potential in knee OA. Future clinical research could leverage MRI to evaluate long-term symptomatic and structural effects of OEC in appropriate OA populations.
REFERENCES: NIL.
IL-10 trajectories with OEC or placebo during 1 st and 2 nd 8-week treatment sequence.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: Yves Henrotin Wobenzym, Tilman, Artialis, Kiomed Pharma, Grunenthal, Genquine, Allegro, Expanscience, Nestlé, Tilman, Expanscience, Heel, Valérie Badot: None declared, Siddhartha Lieten: None declared, Didier Urbin-Choffray: None declared, Carl Brabant: None declared, Jean-Emile Dubuc: None declared, Stefanie Rau Nestlé Health Science, Odd Erik Johansen Nestlé Health Science, Maximilian Eynatten Nestlé Health Science.