

Background: Tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2), a member of the Janus kinase (JAK) family, plays a key role in several inflammatory diseases driven by interleukin (IL)-12, IL-23, and/or Type I interferon signaling. Orthosteric, small molecule inhibitors of TYK2 can also bind other JAK family members, which complicates their therapeutic profile due to inhibition of JAK1/2/3 signaling. Allosteric inhibitors, which target the pseudokinase (JH2) domain of TYK2, show greatly improved selectivity, providing efficacy in immune disorders without concurrent JAK inhibition. Although there are allosteric TYK2 inhibitors in development for various autoimmune/autoinflammatory diseases, efficacy matching that of the anti-IL-23 monoclonal antibodies has not yet been achieved, and there remains a need for a more efficacious oral agent. Here we describe a new drug candidate, ATMW-DC, a novel, potent, and selective allosteric inhibitor of human TYK2, discovered using the AtomNet® artificial intelligence-enabled drug discovery platform.
Objectives: To determine the biochemical and cellular potency and selectivity of ATMW-DC and evaluate its efficacy in mouse models of psoriasis.
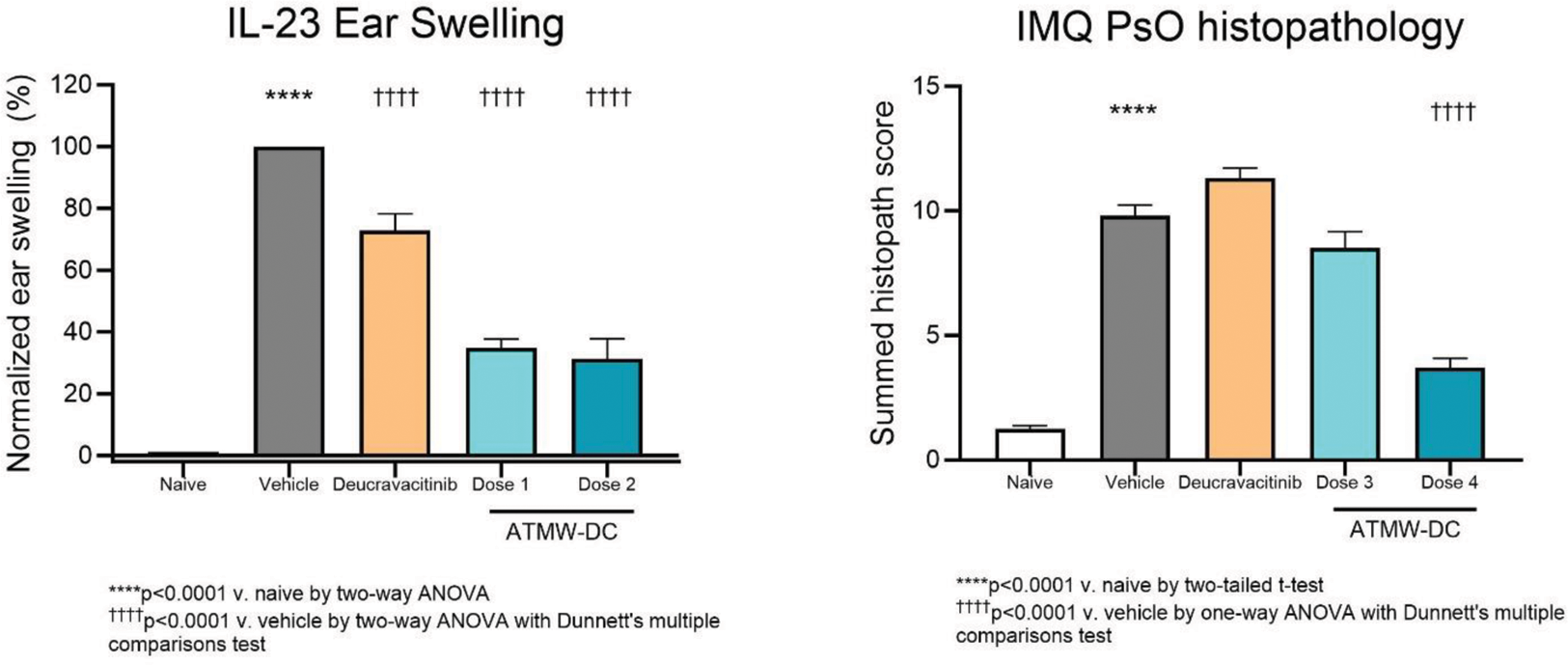
Methods: Potency and selectivity of ATMW-DC were determined in biochemical competition assays and cellular cytokine-induced STAT (signal transducer and activator of transcription) phosphorylation assays. ATMW-DC was evaluated in a mouse pharmacodynamic (PD) model, where ear swelling and IL-17A levels were measured after 4 days of subcutaneous IL-23 injection ± oral administration of ATMW-DC (Doses 1 and 2) or deucravacitinib (at a dose targeting clinically-relevant exposures). An acute model of psoriasis, based on imiquimod (IMQ)-induced skin inflammation, was used to evaluate efficacy of ATMW-DC (Doses 3 and 4) as compared to deucravacitinib via histological and clinical assessments and disease-relevant cytokine/chemokine levels in the skin (relative to naïve and vehicle-treated animals). ATMW-DC Doses 1 and 3 were selected to target the human whole blood IC 90 while Doses 2 and 4 targeted the IC 99 .
Results: ATMW-DC exhibited potency (TYK2-JH2 IC 50 = 12pM) and selectivity (≥350-fold for TYK2-JH2 over JAK1, JAK2, JAK3) for TYK2 in biochemical binding assays. Against a kinome panel, ATMW-DC demonstrated a high degree of selectivity with a partition index (P TYK2-JH2 ) of 0.98. In cellular cytokine assays, ATMW-DC inhibited IL-12-induced pSTAT4 (IC 50 = 18nM) with >460-fold selectivity over JAK1/2-signaling cytokines (IL-6/pSTAT3 IC 50 >8.5μM, GM-CSF/pSTAT5 IC 50 >8.3μM).
ATMW-DC showed dose-dependent inhibition of ear swelling (65-69%) and IL-17A cytokine levels (11-73%) in the IL-23-driven PD model. In the IMQ-induced mouse model of psoriasis, oral administration of ATMW-DC resulted in significant inhibition of inflammation, as measured by daily PASI summed scores (p<0.001), spleen weight (p<0.001), histopathology scores (p<0.001), and skin cytokine/chemokine levels (p<0.001 inhibition of IL-17A, GM-CSF, and TNF and p<0.05 for CCL3).
Conclusion: ATMW-DC is a novel, oral, allosteric inhibitor of TYK2, with potency and selectivity in biochemical and cellular assays. The in vitro profile and in vivo efficacy of ATMW-DC in both the IL-23 PD and IMQ mouse models also support its further development for the treatment of autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases driven by TYK2-mediated signaling pathways.
REFERENCES: NIL.
ATMW-DC demonstrates dose-dependent inhibition in mouse models of psoriasis
Acknowledgements: R. Hussein and P. Tsuruda contributed equally to this work
Disclosure of Interests: Razika Hussein Equity holder of Atomwise Inc., Employee of Atomwise Inc.
, Pamela Tsuruda Equity holder of Atomwise Inc., Employee of Atomwise Inc., Shahab Mortezaei Equity holder of Atomwise Inc., Employee of Atomwise Inc., Nicky Ferdyan Equity holder of Atomwise Inc., Employee of Atomwise Inc., Christopher Wegerski Equity holder of Atomwise Inc., Employee of Atomwise Inc., Karthik Srinivasan Equity holder of Atomwise Inc., Employee of Atomwise Inc., Gavin Hirst Equity holder of Atomwise Inc., Employee of Atomwise Inc., Neely Mozaffarian Equity holder of Atomwise Inc.; owns shares of Eli Lilly and Gilead, Employee of Atomwise Inc.