

Background: The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is a biomarker of residual inflammation and is an independent predictor of MACE and thrombosis events. 2 Its changes correlate with changes in the levels of CRP, serum amyloid, fibrinogen, haptoglobin, and lipoprotein(a). 1 IL-1 inhibitors, IL-6 receptor inhibitors and TNF inhibitors can reduce NLR. 2-4 It was recently shown that direct blockade of IL-6 also reduced this biomarker in high CV risk patients. 1 However, there are no similar investigations for olokizumab (OKZ), which directly binds to IL-6.
Objectives: To investigate the effect of OKZ in doses of 64mg every two weeks (q2w) or every 4 weeks (q4w) on NLR in patients with RA previously enrolled in the CREDO program. To determine correlations between NLR changes and RA activity indicators changes.
Methods: Post hoc analysis phase 3 studies (NCT02760368, NCT02760407, NCT02760433).
Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio was calculated by dividing the absolute number of neutrophils (ANC) by absolute number of lymphocytes (ALC) in the venous blood (NLR=ANC/ALC). Baseline parameters and their changes were analyzed in four groups: OKZ q2w, OKZ q4w, adalimumab group (ADA) and placebo group (PBO) all at background of MTX. A Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to evaluate the statistical significance between baseline parameters and after 12 and 24 weeks of therapy. Pearson correlation analysis was used to determine the relationship between NLR, ANC, ALC changes and the main indices of RA activity. A p-value <0.050 was considered statistically significant.
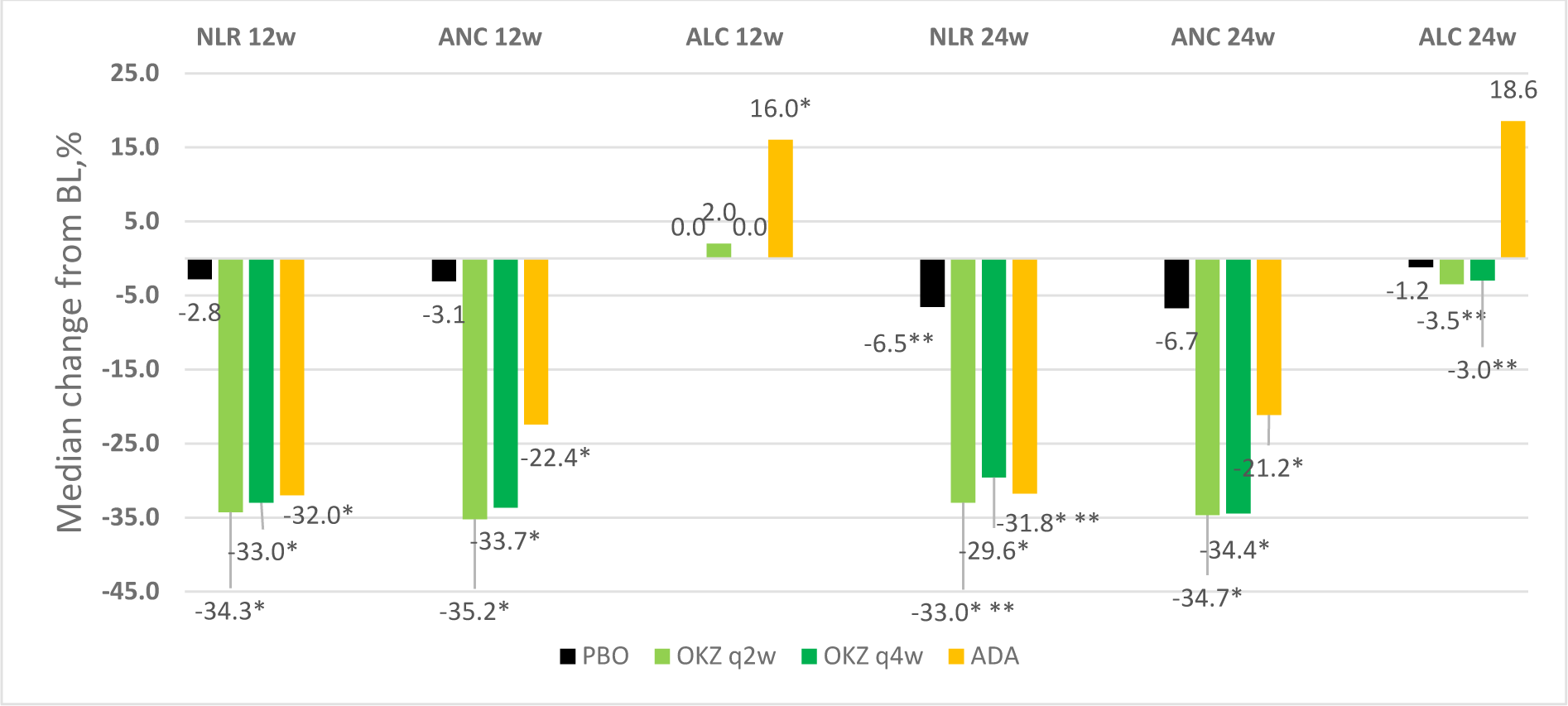
Results: NLR, ANK, ALC were studied in 4 groups of patients: OKZ q2w (n=745), OKZ q4w (n=777), ADA (n=462), PBO (n=454). The baseline levels of ANC and ALC were comparable in all four groups. NLR baseline level in the appropriate groups Me[Q1,Q3]: 3.12[2.24; 4.44], 3.21[2.33; 4.37], 3.21[2.35; 4.48], 3.21[2.44; 4.77]. NLR decrease had been recorded in all active therapy groups, respectively 34.3%, 33.0%, 32.0% (vs BL p < 0.001) after 12 weeks of therapy. NLR decrease was minimal in the placebo group (2.8%, vs BL p>0.05). After 24 weeks of therapy, the NLR decrease had been 33.0%, 29.6%, 31.8% in the active therapy groups (vs BL p<0.001), 6.5% in the placebo group (p<0.001). The NLR reduction occurred due to ANC decrease, with unchanged ALC in the OKZ groups. In ADA group ANC decreased less, but ALC increased (Figure 1). Correlation analysis revealed a positive weak relationship between changes in DAS28, CRP, ESR and ΔANC, ΔNLR, and a negative correlation with ΔALC. CDAI changes were not associated with changes of hematological parameters (Table 1).
Note: *-p<0,001 vs PBO, **- p<0.001 vs 12w
Pearson Coefficient Correlation. Change from Baseline at Week 12
| OKZ q2w | OKZ q4w | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔDAS28 | ΔCRP | ΔESR | ΔCDAI | ΔDAS28 | ΔCRP | ΔESR | ΔCDAI | ||
| ΔANC | 0.08* | 0.23* | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.16* | 0.11* | 0.08* | 0.12* | |
| ΔALC | -0.05 | -0.22* | -0.12* | 0.02 | -0.07 | -0.05 | 0 | -0.06 | |
| ΔNLR | 0.10* | 0.30* | 0.13* | 0.03 | 0.15* | 0.18* | 0.04 | 0.1* | |
| Pearson Coefficient Correlation. Change from Baseline at Week 24 | |||||||||
| ΔDAS28 | ΔCRP | ΔESR | ΔCDAI | ΔDAS28 | ΔCRP | ΔESR | ΔCDAI | ||
| ΔANC | 0.18* | 0.26* | 0.09* | 0.14* | 0.14* | 0.20* | 0.10* | 0.09 | |
| ΔALC | -0.06 | -0.12* | -0.08* | 0.02 | -0.06 | -0.07* | -0.03 | -0.03 | |
| ΔNLR | 0.14* | 0.24* | 0.12* | 0.08 | 0.14* | 0.24* | 0.12* | 0.09 | |
Note: * - p< 0.050
Conclusion: Post hoc analysis of CREDO 1-3 showed an association of direct IL-6 blockade by olokizumab and NLR decrease, which was connected with the neutrophil component reduction. NLR changes correlated with changes in RA activity indices and laboratory parameters.
REFERENCES: [1] Adamstein NH, Cornel JH, Davidson M, et al. JAMA Cardiol. 2023;8(2):177-181. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2022.4277
[2] Adamstein NH, MacFadyen JG, Rose LM, et al. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(9):896-903. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa1034
[3] Broch K, Anstensrud AK, Woxholt S, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77(15):1845-1855. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2021.02.049
[4] Sen R, Kim E, Napier RJ, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023;75(2):232-241. doi:10.1002/art.42333
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: Eugen Feist Abbvie, BMS, Galapagos, Lilly, Novartis, Medac, Pfizer, R-Pharm, Alina Egorova R-Pharm, Evgeny Alekseev JSC “R-Pham.”