

Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapies used to treat cancer can induce immune-related adverse events (irAEs). Previously we identified a clonal CD38 hi cytotoxic CD8 T cell population specifically expanded in ICI-arthritis over rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis, indicating an irAE specific T cell response[1]. Fulminant ICI-myocarditis is a life-threatening condition that requires rapid recognition and multi-disciplinary care.
Objectives: Whether CD38 hi cytotoxic CD8 T cell population facilitates ICI-myocarditis recognition and therapeutic response remains unclear.
Methods: We compared T cells from the peripheral blood of 3 ICI-arthritis and 3 ICI-myocarditis patients induced by anti-PD-1 therapy. Detailed immunophenotyping, transcriptomic features and TCR clonotypes were examined using high-dimensional flow cytometry and single cell sequence to identify significantly altered populations.
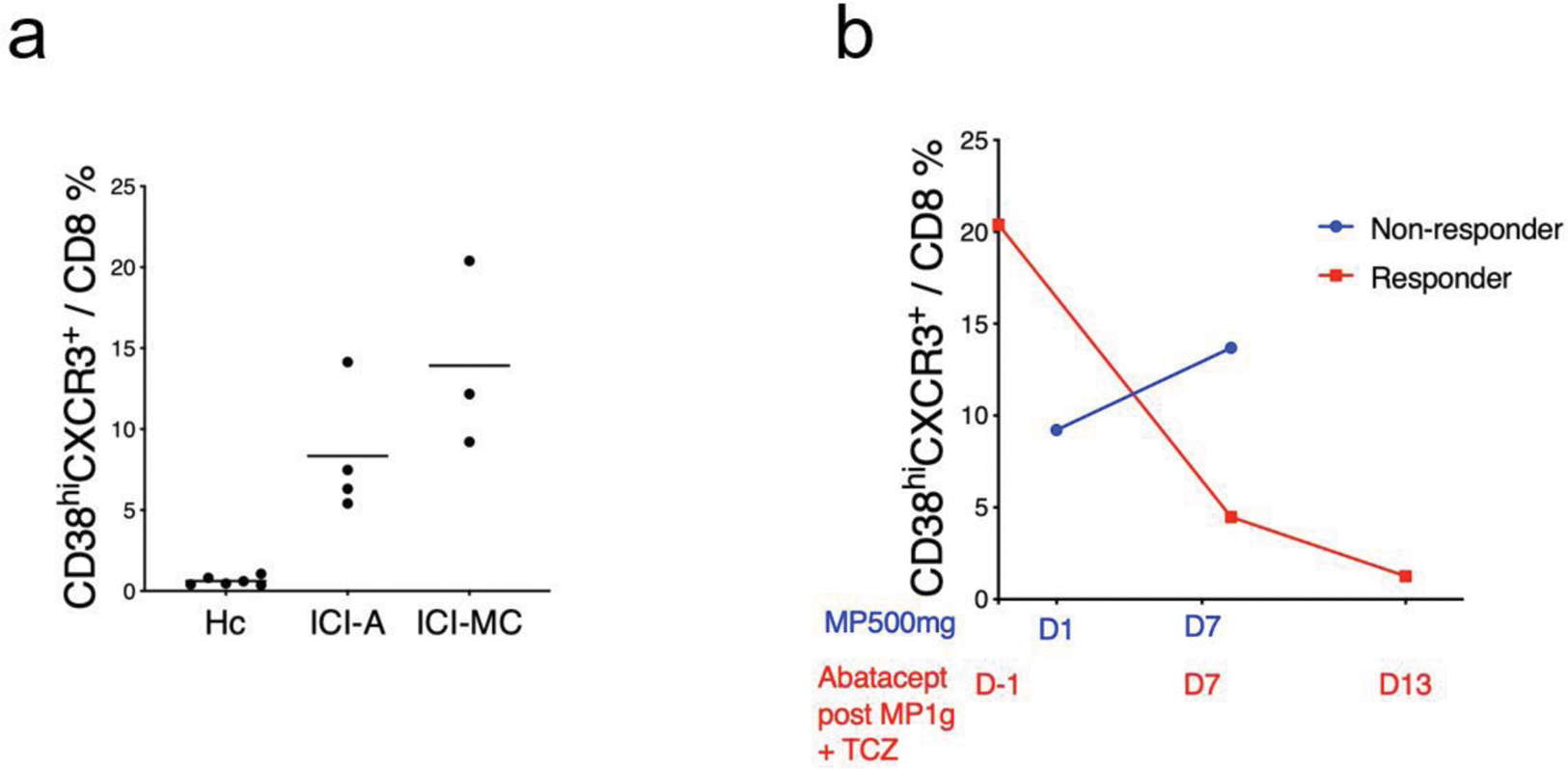
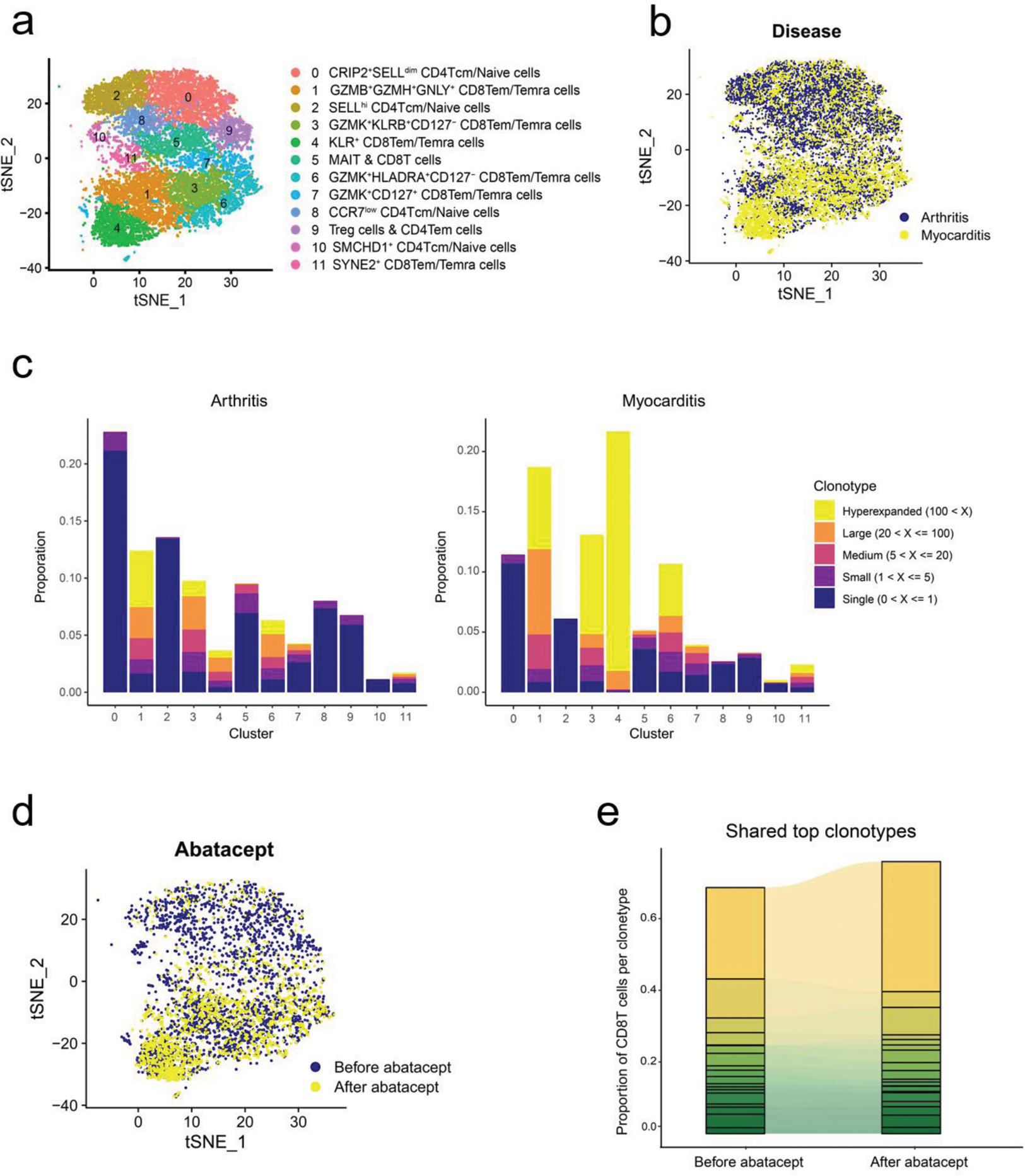
Results: High-dimensional flow cytometry showed that the frequency of CD38 hi CD127 - CXCR3 + CD8 T cells increased in the blood of ICI-myocarditis over ICI-arthritis and healthy control (Figure 1a). Patients with fulminant ICI-myocarditis who did not respond to high dose methyprednisone showed persistently elevated frequency of this population. A tailored dosing of abatacept was applied based on the frequency of CD38 hi CD8 T cells and the degree of CD80 blockade, and successfully rescued clinically fulminant ICI-myocarditis, sparing the responder from subsequent immunosuppressants and pacemaker implantation (Figure 1b). Single cell transcriptomic and antigen receptor repertoire analyses revealed more prominent clonal expansion of CD38-related CD8 T cell (C3+C6) population in the blood of ICI-myocarditis patients over ICI-arthritis (Figure 2a-c), and abatacept altered the composition and clonality of CD8 T cells (Figure 2d-e). Interestedly, KIR+ CD8T cells[2] were clonally expanded in myocarditis, especially after abatacept treatment (Figure 2b, d and e).
Conclusion: The frequency and clonality of CD38 hi CD8 T cells and KIR + CD8 T cells indicate disease severity and therapeutic response in ICI-myocarditis. Analyzing these populations may provide personalized treatment strategy for life-threatening irAEs.
REFERENCES: [1] Wang R, Singaraju A, Marks KE, et al. Clonally expanded CD38(hi) cytotoxic CD8 T cells define the T cell infiltrate in checkpoint inhibitor-associated arthritis. Sci Immunol. 2023;8(85):eadd1591. doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.add1591.
[2] Li J, Zaslavsky M, Su Y, et al. KIR + CD8 + T cells suppress pathogenic T cells and are active in autoimmune diseases and COVID-19. Science. 2022;376(6590):eabi9591. doi.org/doi:10.1126/science.abi9591.
a. The percentage of CD38 hi CD127 - CXCR3 + CD8 T cells in the blood of ICI-myocarditis, ICI-arthritis and healthy control. b. The percentage of CD38 hi CD127 - CXCR3 + CD8 T cells after treatment. MP, methyprednisone. TCZ, tocilizumab.
tSNE plot of T cell clusters (a) and two diseases (b). c. Clonality of T cell clusters. d. tSNE plot of paired before and after abatacept treatment. e. The CD8 T cell proportion of shared 19 top clonotypes between paired before and after abatacept treatment patient.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.