

Background: The variability in treatment response in people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) warrants the prediction of patients at high risk of treatment failure. Identification of biomarkers linked to clinical remission in RA is currently a challenge. Metabolomics may help to identify such biomarkers as it allows for a comprehensive exploration of disease-related variations that extends beyond the genome and proteome.
Objectives: To identify serum metabolites associated with disease activity and therapeutic response in a large cohort of people with untreated early RA.
Methods: Data from 220 adults with untreated newly diagnosed RA, randomly selected from the Swedish arm of the NORD-STAR study cohort [1], were included. Participants were randomized at baseline into 4 arms of treatment: methotrexate combined with 1) prednisolone, 2) certolizumab, 3) abatacept, or 4) tocilizumab. Serum metabolites at baseline were measured using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Peak intensities data were annotated for a list of metabolites. Participants who achieved clinical disease activity index (CDAI) remission (CDAI≤ 2.8) at the 24-week follow-up were defined as responders. The analyses were performed using MetaboAnalyst 5 and R.
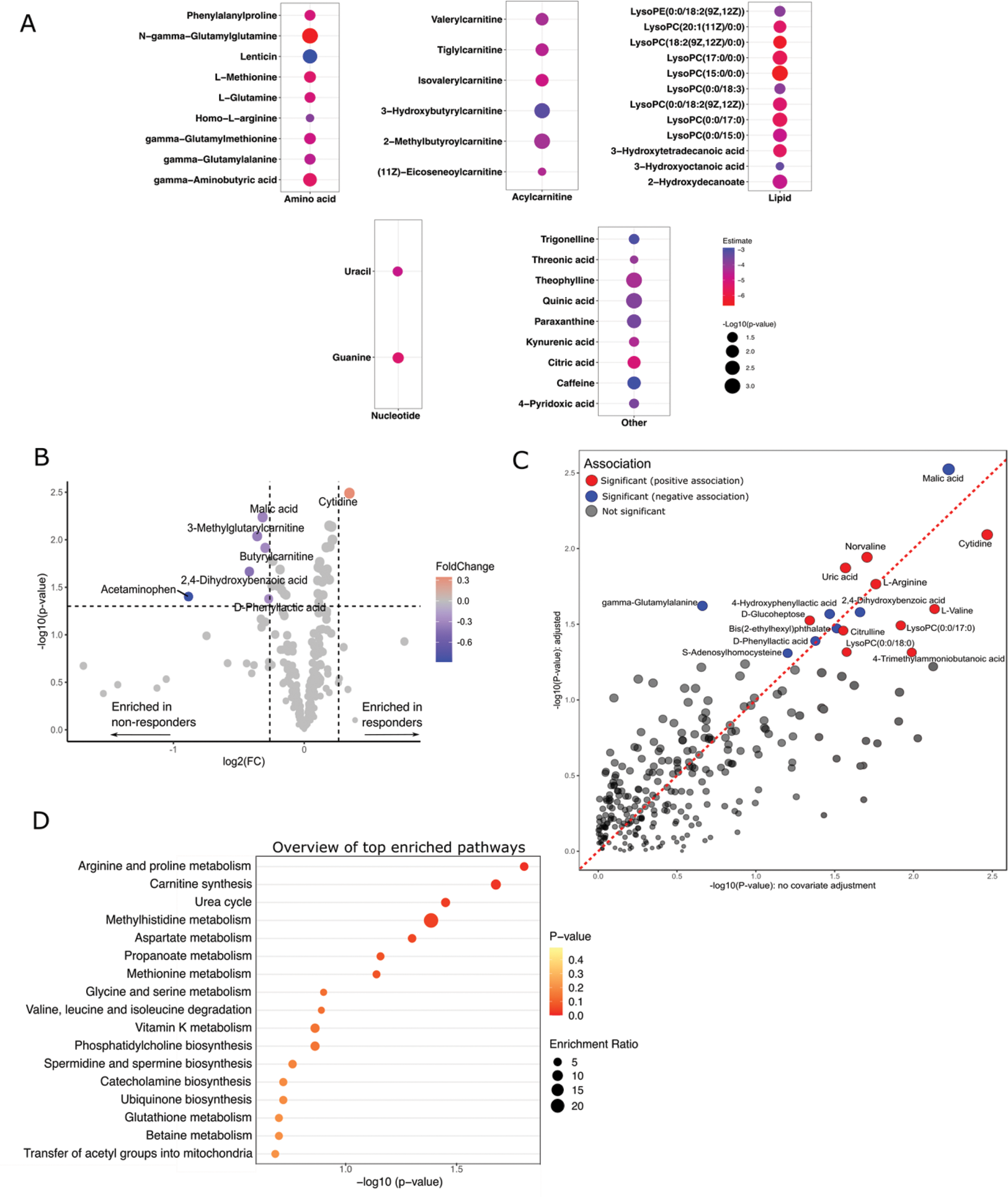
Results: A total of 278 putatively annotated metabolites were identified in serum samples. Multivariable regression analysis indicated 39 baseline metabolites significantly associated with CDAI at baseline, with only acetaminophen (paracetamol) showing a positive association. Of the 38 metabolites negatively associated with baseline CDAI, nine were amino acids, common biproducts of several metabolic pathways, and six were acylcarnitines, which are fatty-acid conjugates involved in lipid metabolism in mitochondria (Figure 1A). We then looked at the association between baseline metabolites and CDAI remission at the 24-week follow-up. Results from the univariate analysis combining the outcomes from t-test (p < 0.05) and fold-change (>1.2) analyses in a volcano plot, showed that cytidine was the only baseline metabolite being significantly upregulated in responders, while six other metabolites significantly downregulated in responders (Figure 1B). Generalized linear model adjusted for several baseline confounders showed 17 baseline metabolites significantly associated with CDAI remission including malic acid (β= -0.4, p = 0.003), cytidine (β= 0.4, p = 0.008), arginine (β= 0.3, p = 0.01), and citrulline (β= 0.2, p = 0.03) (Figure 1C). Pathway enrichment analysis indicated several metabolic pathways potentially associated with treatment response, including, among others, arginine and proline metabolism, carnitine synthesis and urea cycle (Figure 1D).
Conclusion: We showed a detailed serum metabolomics profiling of a large cohort of people with early RA and its association with disease activity and treatment response. Overall, levels of several amino acids and acylcarnitines were inversely associated with disease activity at baseline. Acylcarnitines are important markers of mitochondrial metabolism which is known to be impaired in both immune cells and joint fibroblasts in RA. Malic acid, arginine, citrulline, and cytidine levels were associated with CDAI remission at the 24-weeks follow-up. We have detected carnitine metabolism, arginine and proline metabolism and urea cycle as potentially associated with treatment response in early RA.
REFERENCE: [1] Hetland ML, et al. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2020;371:m4328.
A) Baseline metabolites significantly associated with baseline CDAI. B to D) Baseline metabolic profiles discriminating responders from non-responders; B) Volcano plot C) Multivariable linear regression model for association of baseline metabolites with CDAI remission at 24 weeks, adjusted for age, sex, anti–citrullinated protein antibody status, current smoking status, baseline Disease Activity Score with 28-C-reactive protein, and treatment randomization D) Pathway enrichment plot in relation to response to treatment.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: Tahzeeb Fatima: None declared, Georgios K. Vasileiadis: None declared, Ronald F. van Vollenhoven: None declared, Jon Lampa: None declared, Bjorn Gudbjornsson Consulting fee from Novartis and Lectures fees from Novartis and Nordic Pharma, Espen A Haavardsholm: None declared, Dan Nordström Reports personal consultancy fees from BMS, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB, personal study grant from MSD, outside current work., Gerdur Grondal: None declared, Kim Hørslev-Petersen: None declared, Kristina Lend: None declared, Marte S Heiberg: None declared, Merete Lund Hetland Research grants from AbbVie, iogen, BMS, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Janssen Biologics B.V, Lundbeck Foundation, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung Biopies, Sandoz, Novartis, Nordforsk to institution; payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Pfizer, Medac, Sandoz paid to institution; participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board from Abbvie paid to institution. Chaired the steering committee of the Danish Rheumatology Quality Registry (DANBIO, DRQ), which receives public funding from the hospital owners and funding from pharmaceutical companies. Co-chairs EuroSpA, which generates real-world evidence of treatment of psoriatic arthritis and axial spondylarthritis based on secondary data and is partly funded by Novartis., Michael Nurmohamed: None declared, Mikkel Østergaard Grants from Amgen, BMS, Merck, Celgene and Novartis to institution; consulting fees from Galapagos, Gilead, Hospira, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB; payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Abbvie, BMS, Eli-Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB; support for attending meetings and/or travel from UCB; participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board from Galapagos, Gilead, Hospira, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB., Till Uhlig Personal fees from Galapagos, Lilly, Pfizer, UCB outside the submitted work., Tuulikki Sokka-Isler Research grant from Amgen paid to the institution, honoraria from Nordic Pharma., Anna Rudin: None declared, Yuan Zhang: None declared, Cristina Maglio: None declared.