

Background: Patients with rheumatic diseases (RMD) have a lower pregnancy rate, with infertility being one of the main causes. The rate of assisted reproductive therapies (ART) and the factors associated with the need for ART in patients with RMD are not fully identified.
Objectives: our aim was to describe ART rate and factors related to the need of ART in patients with RMD.
Methods: Retrospective study of patients with RMD followed up in a specialized pregnancy clinic in Madrid, Spain. Patients with RMD who attended the clinic from December 2012 to January 2023 were included. After one year trying to conceive, patients were referred for ART. Each episode of pregnancy counseling was included as a case. Carriers of autoantibodies, anti-Ro and antiphospholipid (aPL) antibodies, without defined disease, were excluded. Factors associated with the need for ART (ART group) were compared with patients who did not require ART (no ART group). Categorical variables were described as proportions and/or percentages, while continuous variables were shown as mean and standard deviation (SD). The Mann-Whitney U test, Student t test and χ2 test were used to compare data (ART and non-ART groups), when appropriate. A multivariate logistic regression model was plotted to identify factors associated with the need of ART.
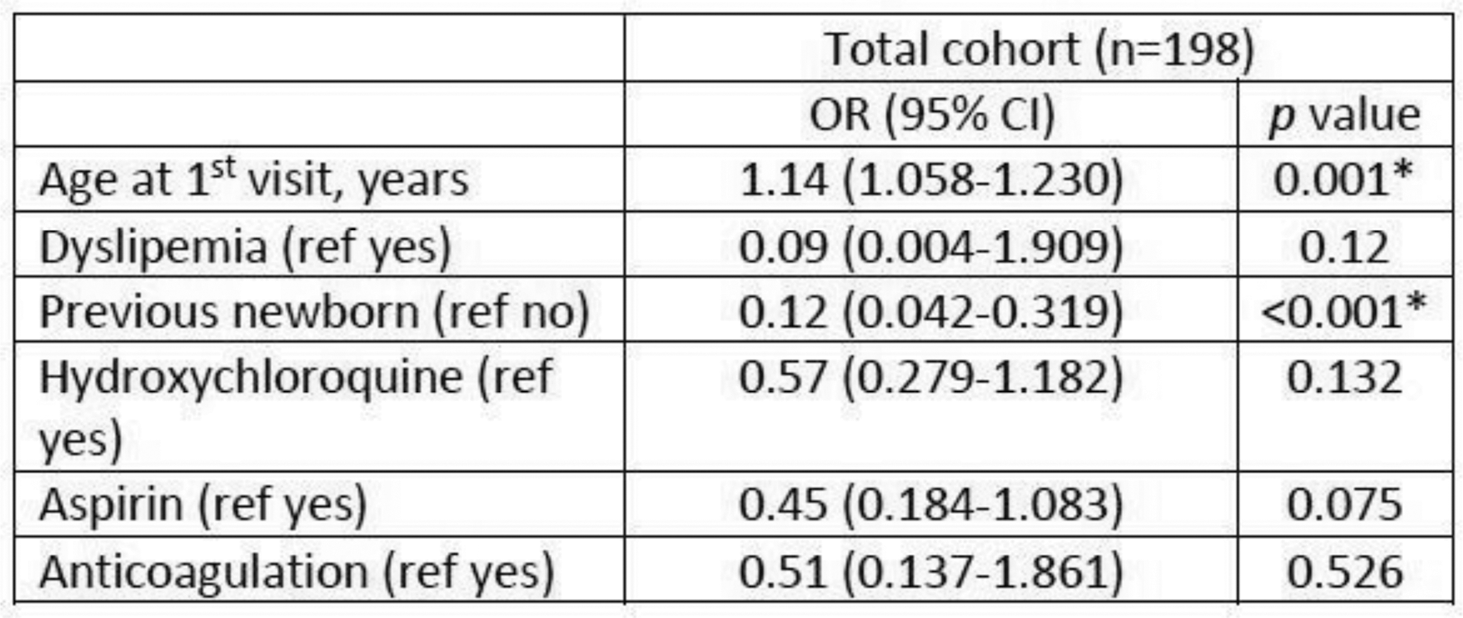
Results: 259 cases in 202 patients were included. Fifty-two cases, in 39 patients, of autoantibody carriers were excluded. Sixty-one of 259 (23.6%) cases required ART. The main characteristics and univariate analysis are reported in Table 1. The most frequent diagnosis was the combined RA-JIA group (28.6%). There was a low frequency of comorbidities, including previous nephritis, and 62.7% of the cases had never been pregnant. The patients who required ART were older, more frequently with dyslipidemia. A higher rate of patients in the non-ART group had previously delivered a newborn, but there was no difference from prior miscarriage. There were no differences regarding immunosuppressive treatment, but there was a higher prescription of hydroxychloroquine, aspirin, and heparin in the ART group. In the multivariate analysis (Table 2), older age was associated with the need for ART, while previous delivery of a newborn was the main protective factor for not needing ART.
198 (76.4%) cases became pregnant. The pregnancy rate was lower among the ART group (39/61, 63.9%) compared to the no ART group (159/198, 80.3%), p=0.008. Among the 61 (23.6%) cases who did not become pregnant, the main reason in the ART group was ART failure (9/21, 42.9%) and in the no ART group it was the interruption of the desire for pregnancy (17/39, 43.6%) and active disease (8/39, 20.5%), p= 0.03.
Conclusion: In our cohort, the ART rate was 23.5% and maternal age was the main factor associated with the need for ART, while a history of a previous newborn was associated with a lower risk of needing ART.
REFERENCES: NIL.
Table 1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
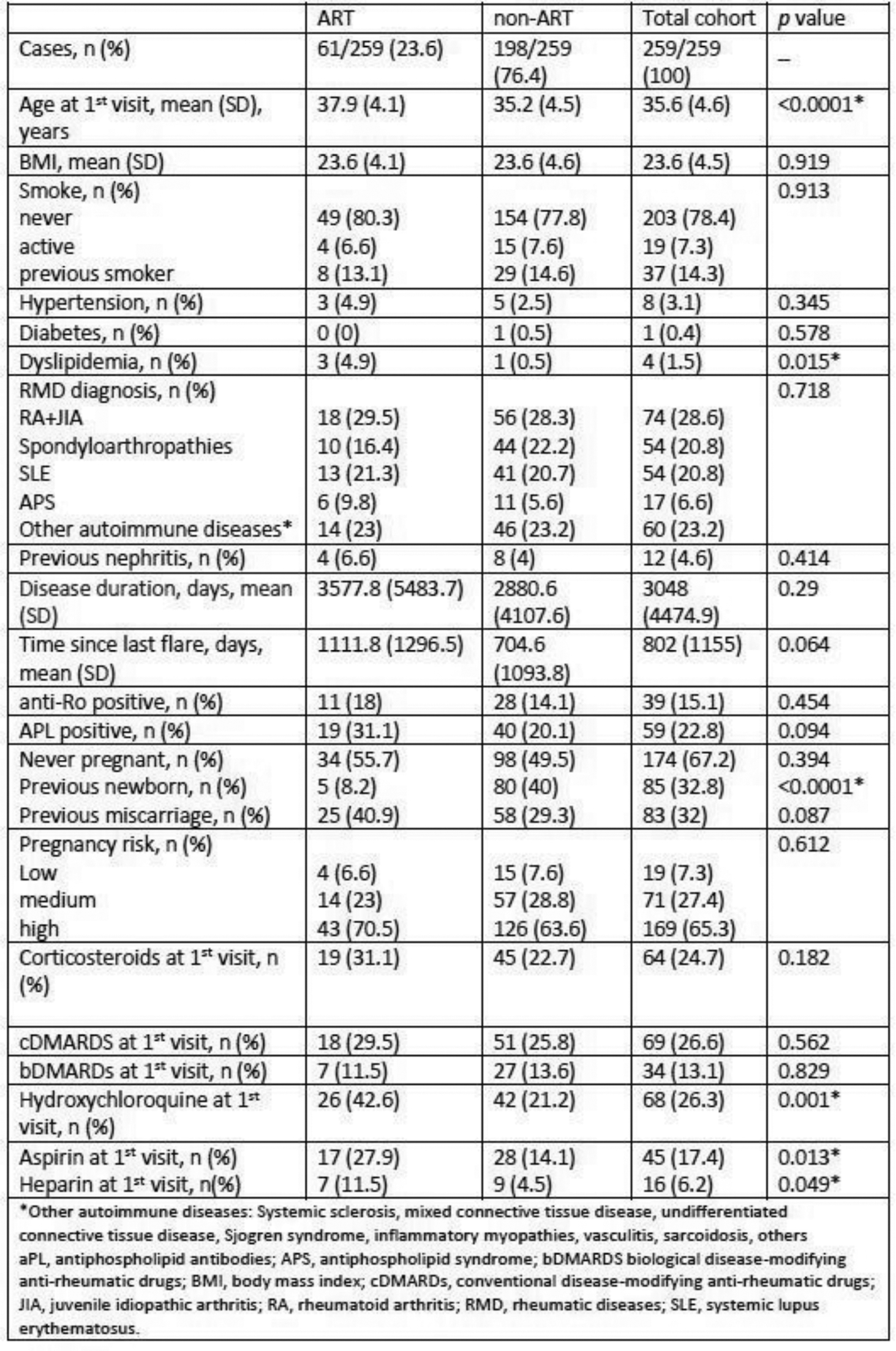
Table 2. Multivariate analysis
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.