

Background: The excess risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) compared to the general population is attributed to chronic inflammation. Identifying the underlying mechanisms and shared inflammatory pathways more precisely would enable tailored treatment.
Objectives: To identify genetic variants associated with the cardio-metabolic-inflammatory proteomic signature in patients with early, treatment-naïve RA and low CVD risk.
Methods: The Coronary Artery Disease Evaluation in RA (CADERA) study was a bolt-on to a RCT of patients with early, treatment-naïve RA and low CVD risk profile (maximum of 1 traditional CVD risk factor and no diabetes mellitus). Normalised expression of 334 proteins from 75 CADERA patients who underwent cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) was measured using the Olink Proximity Extension Immunoassay across Inflammation, Cardiovascular II, III and Cardiometabolic panels. Genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) data were generated using the Illumina Global Screening Array (GSA) and was imputed and checked for data quality using standard approaches. Proteins associated with CMR parameters were identified using Bayesian mixed effects linear regression. Protein quantitative trait locus (pQTL) analysis was then performed using linear regression models adjusted for age, gender, and systolic blood pressure. Cis -pQTLs were defined as SNPs within 1 Mb of the protein-encoding gene, and significance threshold was set at 1e-5. Due to sample size, trans -pQTLs were not considered in this analysis. Linkage disequilibrium (LD) clumping was performed using PLINK software to identify index SNPs defined as the most significant variant in LD (r2 <0.5) within a region of +/- 250 Kb.
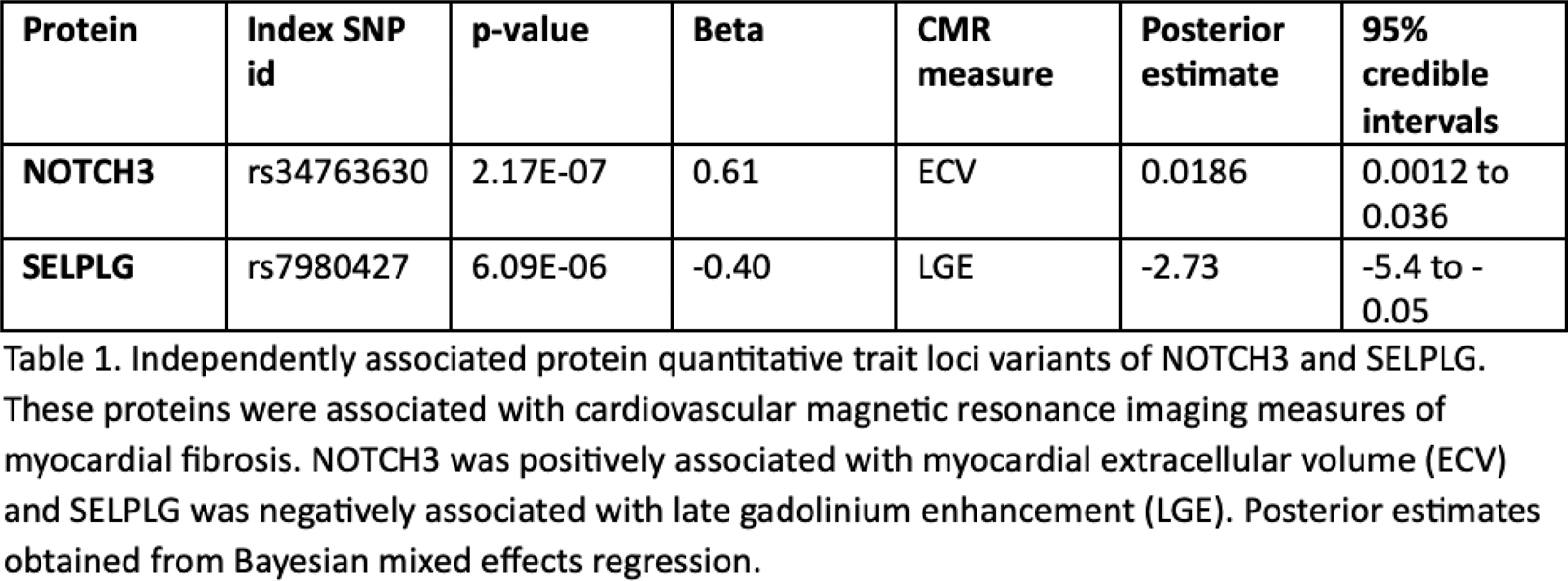
Results: Following quality control a total of 318 proteins and 5,971,781 SNPs were available for analysis in 75 CADERA patients. The median age was 51 years [inter-quartile range (IQR) 40 - 61] with 52/75 (69%) females, 40/75 (53%) current or ex-smokers, and median body mass index (BMI) 26.4kg/m2 (IQR 23.3 - 28). Participants had a median RA symptom duration of 21.9 weeks (IQR 14.4 - 32.7). Only 8/75 (10%) reported a history of hypertension, hypercholesteroaemia or family history of CVD. Fifty four out of 318 proteins were associated with CMR measures of myocardial fibrosis and/or vascular stiffness. Four hundred and sixty cis -pQTLs were identified for 20 out of the 318 proteins. LD clumping revealed 40 cis -pQTLs independently associated with these 20 proteins. Of these, NOTCH3 (rs34763630) and SELPLG (rs7980427) were associated with measures of myocardial fibrosis (NOTCH 3 = myocardial extracellular volume (ECV); SELPLG = late gadolinium enhancement) as detected on CMR (Table 1). No other protein with genetic support were associated with CMR measures.
Conclusion: This study for the first time, implicates genetic markers associated with two proteins as putative candidate biomarkers of CMR-identified myocardial fibrosis in new-onset RA that now warrant validation in an independent cohort.
REFERENCES: NIL.
Acknowledgements: AIM is supported by an Academic Clinical Fellowship awarded by the National Institute for Health Research as part of the Integrated Academic Training (IAT) programme.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.