

Background: A majority of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) display autoantibodies targeting IgG Fc (rheumatoid factor, RF), and/or post-translationally modified proteins including anti-citrullinated (ACPA), anti-carbamylated (anti-Carb), and anti-acetylated (anti-Acet) protein antibodies. ACPA are highly specific for RA and are important clinical biomarkers. However, the targets and etiological and clinical relevance of ACPA fine-specificity patterns remains enigmatic. ACPA multi-reactivity by binding to small citrulline- (cit) containing peptide epitopes across antigens, as well as their cross-reactivity with Carb and Acet, provides a challenge when interpreting patient reactivities.
In this collaborative effort we use the next generation peptide array for improved and more granular ACPA fine-specificity profiling in combination with anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP2) and RF measurements for complete autoantibody profiling of RA patients.
Objectives: To explore the relationship and prevalence of autoantibodies in RA to enhance the definition of patient subsets.
Methods: Autoantibodies were measured in 6907 RA patients from five harmonized Scandinavian cohorts: ARCTIC (N=212), NOR-DMARD (N=302), ULRABIT (N=174), DANBIO/DRB (N=2324) and SRQb (N=3895) (1). Smoking status was available for 3214 patients and disease duration from RA diagnosis for 2654. IgM, IgG, and IgA RF and IgG, IgA anti-CCP2 analyses were performed by FEIA (fluoroenzyme immunoassay). ACPA fine-specificities were screened using a custom-made multiplex solid phase microarray platform. The analysis included one Carb peptide, three Acet peptides, 15 cit-peptides with single citrulline motifs and four original multi-citrulline peptides. Array peptide cutoff for positivity was established by using 700 healthy control samples. Comparisons were made using Fisher’s exact test expressed as odds ratios (OR).
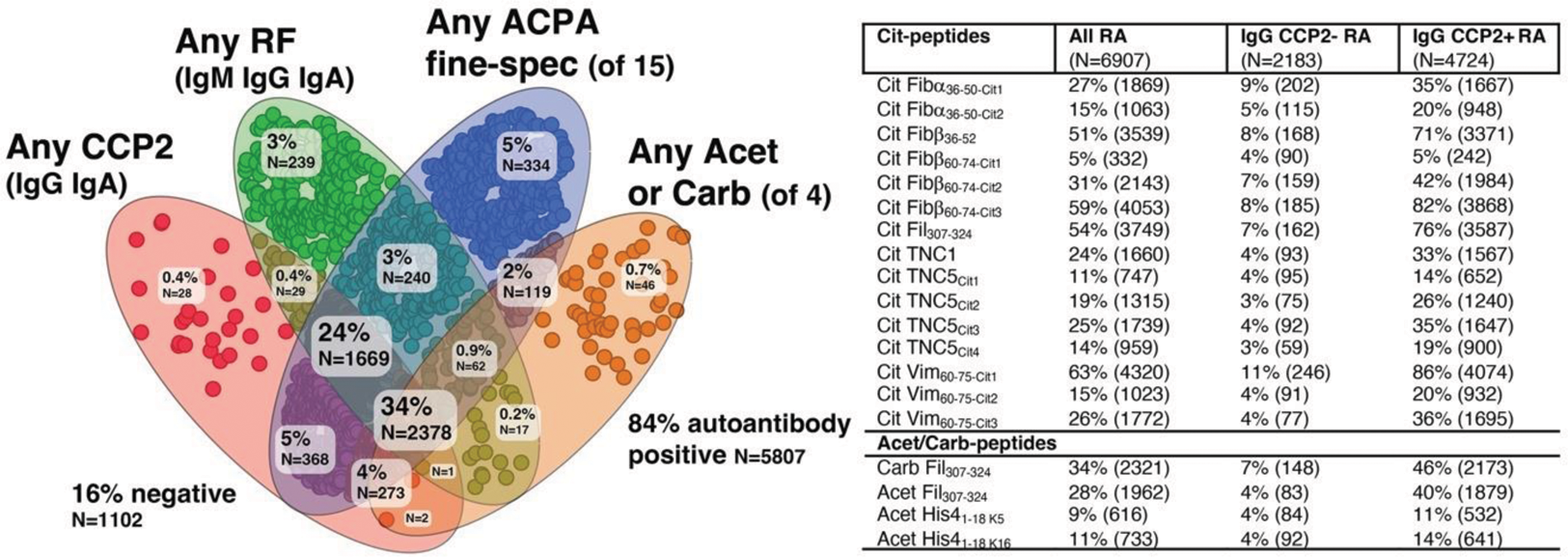
Results: In total, 75% of the patients were considered seropositive based on IgG CCP2 and IgM RF, but 84% of patients were autoantibody positive when all tests were included (see Figure 1).
The reactivity patterns in four peptide families (Cit Fibα 36-50 , Cit Fibβ 60-74, Cit TNC5, and Cit Vim 60-75 ) showed differential patterns for single-cit peptides when comparing the original multi-cit peptide with equivalent single-cit peptides, supporting serum dominance of certain fine-specificities and recognition of cit-motifs rather than long peptides. In all peptide families, the single cit peptides together captured more patients than the original peptide with multiple citrulline. Four cit-peptides stood out with a high frequency of positivity, Cit Fibβ 36-52 (51%) Cit Fibβ 60-74-Cit3 (59%) Cit Fil 307-324 (54%) Cit Vim 60-75-Cit1 (63%); when combined these captured 97% of IgG CCP2+ patients and 22% of IgG CCP2-.
Further, 42% of all patients were positive for IgG anti-Carb or Acet peptides (Carb Fil 307-324 , Acet Fil 307-324 , Acet His4 1-18 K5 , or Acet His4 1-18 K16 ) of which most were also IgG Cit positive (97%).
When stratified by smoking status, IgA autoantibodies were more common in smokers. For instance, IgG+ IgA+ CCP2 double pos vs. IgG+ IgA- CCP2 (71% smokers vs. 58%, OR: 1.8 [95% CI 1.5-2.1]), and IgM+ IgA+ RF double pos vs. IgM+ IgA- RF (74% smokers vs. 57%, OR: 2.1 [95% CI 1.7-2.5]).
There was no significant difference between new onset (<3 months duration), early (3-24 months) or established (>24 months) CCP2+ RA in terms of fine-specificities. While there was a considerable overlap between distinct ACPA fine-specificities, both their frequencies and levels could be used to define patient subsets with different autoantibody profiles.
Conclusion: New knowledge about the recognition motifs of anti-citrulline antibodies provides an opportunity to re-evaluate the role and biology of ACPA fine-specificities, their internal relation, and association with risk factors, which can be used for improved subsetting of patients.
REFERENCES: [1] Westerlind et al RMD Open 2023 Sep;9(3):e003027.
Acknowledgements: This project was supported by Vinnova, Innovationsfonden Denmark and The Research Council of Norway, under the frame of Nordforsk (Grant agreement no. 90825, Project NORA) and by The Swedish Research Council, Innovationsfonden Denmark, the Federal Ministry of Education and Research in Germany and The Research Council of Norway, under the frame of ERA PerMed (Project ScandRA)
Disclosure of Interests: Johan Askling Agreements between Karolinska Institutet (with JA as PI) and Abbvie, BMS, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi, mainly for the national safety monitoring of rheumatology immunomodulators in Sweden (ARTIS), Caroline Grönwall: None declared, Helga Westerlind: None declared, Linda Mathsson-Alm Employed by Thermo Fisher Scientific, Isabel Gehring Employed by Thermo Fisher Scientific, Joe Sexton: None declared, Siri Lillegraven: None declared, Espen Haavardsholm: None declared, Merete Lund Hetland: None declared, Hilde Berner Hammer Honoraria for lectures: Novartis, AbbVie, Lilly, UCB, Bente Glintborg Research grants: AbbVie, Sandoz, BMS