

Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease, where response to treatment (RT) is the main management goal. Therefore, predicting RT is fundamental, and warrants further study of predictor variables that are related to RT.
Objectives: The aim of the present study is to identify predictor variables of RT in patients with RA, through artificial intelligence (AI) models in a specialized RA Center.
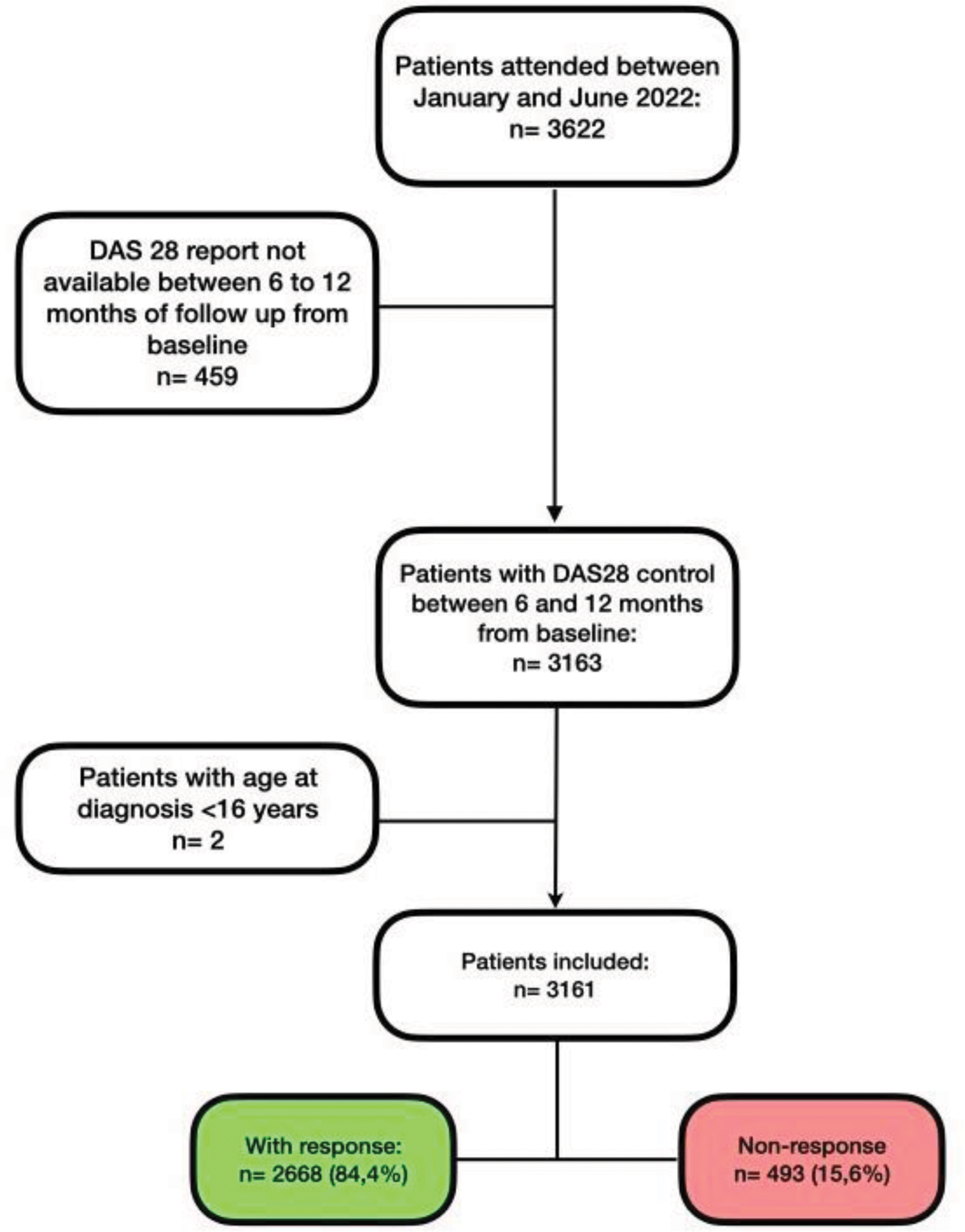
Methods: Retrospective cohort study, was conducted in adult RA patients attended between January and June 2022. Baseline was obtained from patient’s last consultation. Follow-up data related to RT was taken from 6-12 months after the baseline. The response variable is divided as responder and non-responder. Responder is an individual who achieves DAS28 <3.2 at the end of the follow-up period or decreases ≥ 0.6 compared to baseline regardless of the initial DAS28 value. 25 input variables were pre-selected for modeling. Data were divided into training (80%, n = 2528) and test (20%, n = 633). Predictive models were generated by machine learning (ML), by Python programming language, using the training dataset. Five models with the highest performance scores were selected. The selected models were: Gradient Boosting Classifier (gbc), Random Forest Classifier (rf), Extra Trees Classifier (et), Light Gradient Boosting Machine (lightgbm) and Extreme Gradient Boosting (xgboost). Explainability in Artificial Intelligence (XAI) techniques were used to identify the most relevant clinical features, using the SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) method. All quantitative variables were explained using the median and interquartile range, while absolute and relative frequencies were used for qualitative variables. Stata18 and Python 3.10.12 were used for data analysis.
Results: A total of 3161 patients with RA were included. Median age was 65 years (Interquartile range [IQR] 57 - 72). 82.7% were female. Disease duration was 8.3 years (IQR 4.9 - 11.3). 75.9% (2216/2918) were positive for Rheumatoid factor and 73.6% (2060/2798) were positive for anti-CCP. The median value of baseline DAS28 was 2.1 (IQR 2.1 - 2.8). The median follow-up time from baseline and closest control was 8.6 months (IQR 7.9 - 9.6). Methotrexate was the most commonly prescribed conventional synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic drug (csDMARD) in 63.5% of patients. 23.6% patients were under biological disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) treatment. Of the total number of patients, 2668 (84.4%) were classified as responders, and 493 (15.6%) as non-responders. At baseline 30% of non-responder’s patients were in moderate and high disease activity. (Figure 1).
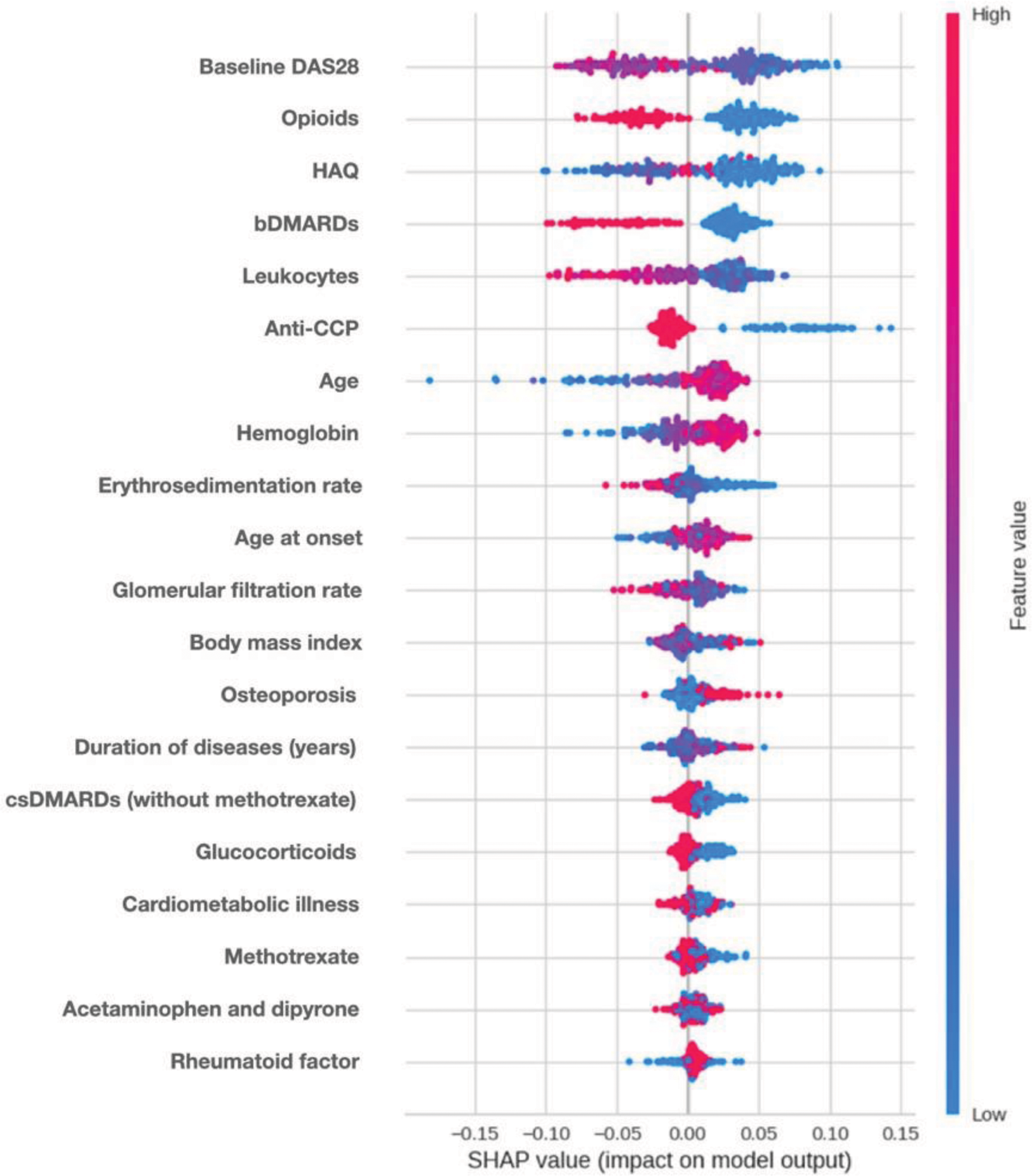
Similar performance was observed for all the ML models evaluated. In the cross-validation, an accuracy of 0.65 was recorded for all models. The et model showed a higher sensitivity (0.841). Regarding treatment prediction with SHAP method, it was observed that low values of baseline DAS28 were positively associated with RT, while high values were negatively related to RT. Second important result was the use of opioids, showing an association between the use of these therapies, and lack of RT. Low values of Multidimensional Health Assessment Questionnaire (MDHAQ), leukocyte count, and Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, located in third, fifth and ninth place in importance, were positively related to RT. Other relevant findings were that use of bDMARDs and the presence of anti-CCP are related to an increase in the probability of non-RT, which may be secondary to the level of severity of the disease (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Application of AI models in patients with RA allows the use of large amounts of data to predict the RT when patient come at the first time to the consultation. This enables to think of targeted approaches taking into account variables of non-response to treatment. The severity of the disease may be influenced by the presence of anti-CCP positivity, and the use of biologic therapies, since these therapies are used when disease control is not achieved with conventional therapies (Confounding by indication).
REFERENCES: NIL.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.