

Background: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) affects mainly women of child-bearing age, and is associated with worse pregnancy and disease outcomes during pregnancy. Physiologically, pregnancy is associated with an immunotolerance state, and in other rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) pregnancy is associated with a lower disease activity. The molecular mechanisms underlying immune differences between healthy, RA and SLE pregnancies are largely unknown.
Objectives: To prospectively study the circulating monocyte mRNA and miRNA from healthy, RA and SLE women before, during and immediately after pregnancy.
Methods: Patients with RA or SLE and age-matched controls were included in the study. EDTA-anticoagulated blood was drawn within 3 months before pregnancy, at the time of positive pregnancy test, month 3 and 6 of pregnancy, during delivery and 1 month and 3 of post-partum. Monocytes were sorted using CD14 magnetic sorting (Miltenyi). Total RNAs were extracted with a commercial kit (Qiagen) and the transcriptome obtained using paired-end sequencing with a new generation sequencer SOLID 5500 (Life technologies). Sequencing data was processed using the nf-core/rnaseq pipeline, version 3.10.1. Within this pipeline, STAR was used for sequence alignment, while Salmon was used for RNA quantification, resulting in an expression matrix. For miRNAs, mirdeep2 was used to generate the expression matrix. In subsequent steps, DESeq2 was used to study differential expression. For each condition (SLE, RA or control), visits in chronological order were considered as a continuous variable on which transcriptional patterns were explored. In addition, the patient ID was used as a covariate to control for individual variability in gene expression profiles. For enrichment analyses and regulator predictions, Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software was used to decipher the expression variations observed. To link miRNAs and downstream mRNA targets, a correlation analysis was performed between mRNA and miRNA signal of the same patients. A miRNA was predicted to negatively regulate a mRNA if it was negatively correlated with that transcript across samples, and predicted as such by miRTarBase.
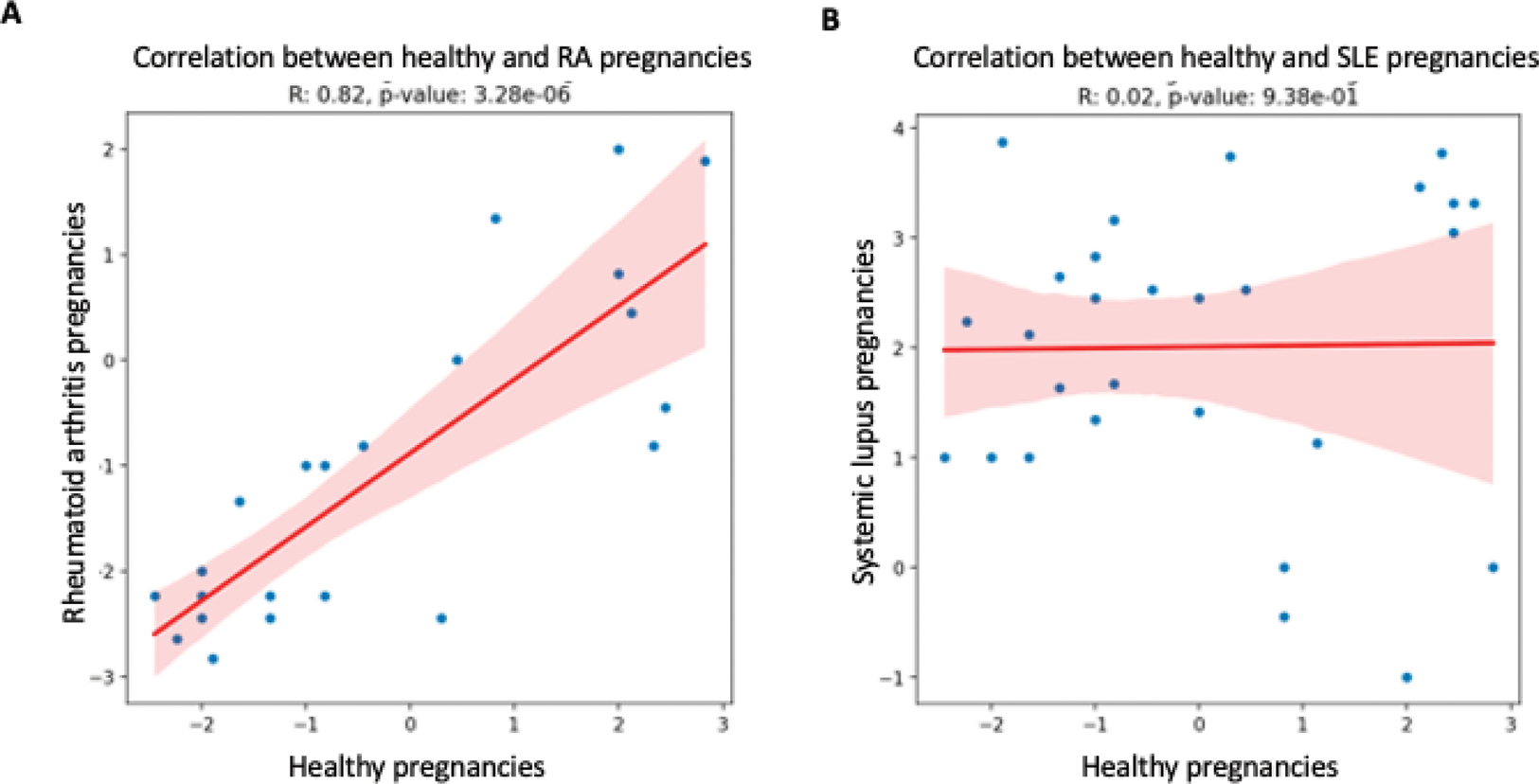
Results: Six patients with SLE, four with RA and five healthy donors were included. During the progression of RA pregnancies, the pathway enrichments highly correlated with the ones from healthy pregnancies (r = 0.82, p = 3.28 x10 -6 , Figure 1A). Conversely, the enrichments from SLE pregnancies did not correlate with healthy ones (r = 0.02, p = 0.94, Figure 1B), suggesting that SLE pregnancies have a distinct transcriptomic signature. Using pathway analysis we identified a downregulation of the interferon gamma, interleukin 1 and CD40L/CD40 pathways in both healthy and RA pregnancies during the progression of pregnancy. During SLE pregnancies, we identified an upregulation of pathways of interferon gamma, Interleukins 1, 6 and 8 and Tumor Necrosis factor. The upregulation of these inflammatory pathways remained significant after excluding visits with a clinical flare.
In contrast to healthy donors and RA patients, SLE patients were characterized by a significant downregulation of miRNAs 106a-5p and 148b-5p (adjusted p-value < 0.05) predicted to control cytokine-mediated signaling pathway and neutrophils activation/degranulation (adjusted p-values < 0.001 and < 0.01, respectively).
Conclusion: We identify that SLE pregnancies have a distinct monocyte transcriptomic signature which differs from healthy and RA pregnancies, that accompany increased risk of disease flares and adverse pregnancy events. Furthermore, our data suggest that miRNA may participate to this pro-inflammatory signature, which opens the way for a better understanding of SLE pregnancy and the development of biomarkers of adverse pregnancy events.
REFERENCES: NIL.
correlation of enriched pathways between healthy and RA (A) and healthy and SLE (B) pregnancies.
Acknowledgements: This project was founded by the l‘ANR PRCI “SPIRALE“ and by l‘ITI Transplantex. The DRCI of the HUS for promoting the study. MS is supported by ATIP-AVENIR, INSERM, Fondation Bettencourt-Schueller, FOREUM Early Career Grant and Fondation Arthritis.
Disclosure of Interests: Eloi Schmauch: None declared, Philippe Georgel: None declared, Raphael Carapito: None declared, Angélique Pichot: None declared, Ghada Alsaleh: None declared, Nicodème Paul: None declared, Anne Molitor: None declared, Catherine Mutter: None declared, Jacques-Eric Gottenberg: None declared, Renaud Felten: None declared, Séiamak Bahram: None declared, Jean SIBILIA: None declared, Marc SCHERLINGER Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, BMS, Fresenius Kabi, Galapagos, GSK, Nordic Pharma, Novartis, Sandoz., Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, BMS, Fresenius Kabi, Galapagos, GSK, Nordic Pharma, Novartis, Sandoz.