

Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic inflammatory autoimmune disease, affecting 1% of the world population. The etiology of RA remains largely unknown. However, glycan antigens are involved in RA autoimmune pathogenesis and have appeared as possible diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in autoimmune diseases and cancers.
Objectives: This study addresses the diagnostic potential of circulating IgM or IgG antiglycan antibodies in RA versus healthy controls (HC) and whether antiglycan antibodies are associated with disease activity in early, treatment-naïve RA patients (eRA) and/or altered by treatment.
Methods: Plasma samples from newly diagnosed, treatment naïve and disease active eRA patients (OPERA trial, n=60) [1] and matched HC, (n=60) were analyzed for antibodies towards glycans on the NCFG v.2 microarray. This study investigated a randomly selected subpopulation of the OPERA trial where all patients included were above 18 years of age and met the American College of Rheumatology’s 1987 revised criteria for RA. The printing, binding, and scanning conditions have been described previously [2]. Briefly, diluted plasma (1:50) was applied to the slides at RT for 1 h, followed by a fluorescent-tagged anti-IgG antibody and anti-IgM. A positive signal was measured by the mean fluorescent intensity minus the background and reported as a relative fluorescence intensity (RFUs) of four printed replicates. The study was approved by the Regional Ethics Committee and the Danish Medical Agency. In accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, informed written consent was obtained from all participants.
Results: We observed that the total signal intensities (SI) of anti-IgG and anti-IgM antibodies recognizing glycans on the microarray were comparable between HC and eRA patients, furthermore the SI of IgG and IgM antibodies was not significant different between seropositive and seronegative RA. However, the anti-IgG SI between specific glycans differed between HC and eRA patients. The SI levels of IgGs recognizing chitin oligosaccharides (-4GlcNAcβ1-) n were significantly higher in eRA compared with HC (p<0.01). In particular, the SI levels of IgGs recognizing chitoheptose (C7) were elevated in eRA patients (4558 RFU, 95% CI [2976-6140]) compared with HC (2390 RFU, 95% CI [910-3869]), (p< 0.05). The levels of IgG binding to C7 positively correlated with joint pain (ρ=0.42, p<0.01) and disease activity (DAS28crp) (ρ=0.29, p<0.05) after 1 yr. A treat-to-target treatment strategy did not affect the SI levels of eRA IgG recognizing C7. The SI of IgM antibodies recognizing C7 was not different between HC and eRA patients.
Conclusion: This study shows that the plasma RFU levels of IgG binding to chitoheptose (C7) are elevated in eRA patients compared with HC. The levels correlated with both joint pain and disease activity after 1 yr. These observations indicate that IgG recognition of C7 may be of diagnostic and prognostic value in RA.
REFERENCES: [1] Hørslev-Petersen et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013.
[2] Heimburg-Molinaro et al. Curr Protoc Protein Sci. 2011.
Antigenic specificity of IgG and IgM glycan antibodies. Heatmap showing the relative intensity of the fluorophore-conjugated anti-human IgG and IgM antibodies binding with the individual glycan on the NCFG v.2 microarray. Healthy controls (HC, n=60) and early, treatment-naïve RA (RA, n=60). The red triangle displayed show increasing disease activity (DAS28CRP) in the RA patients.
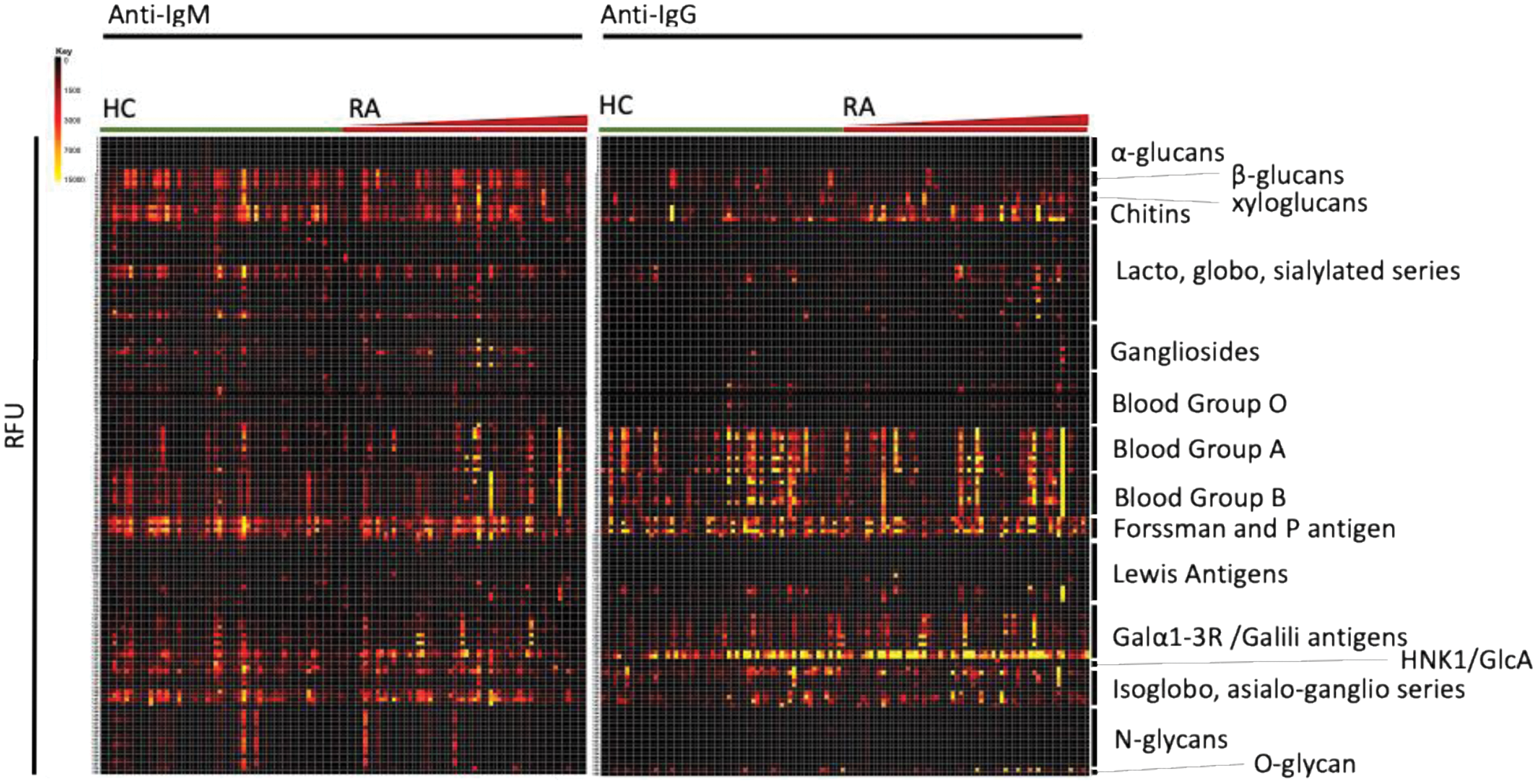
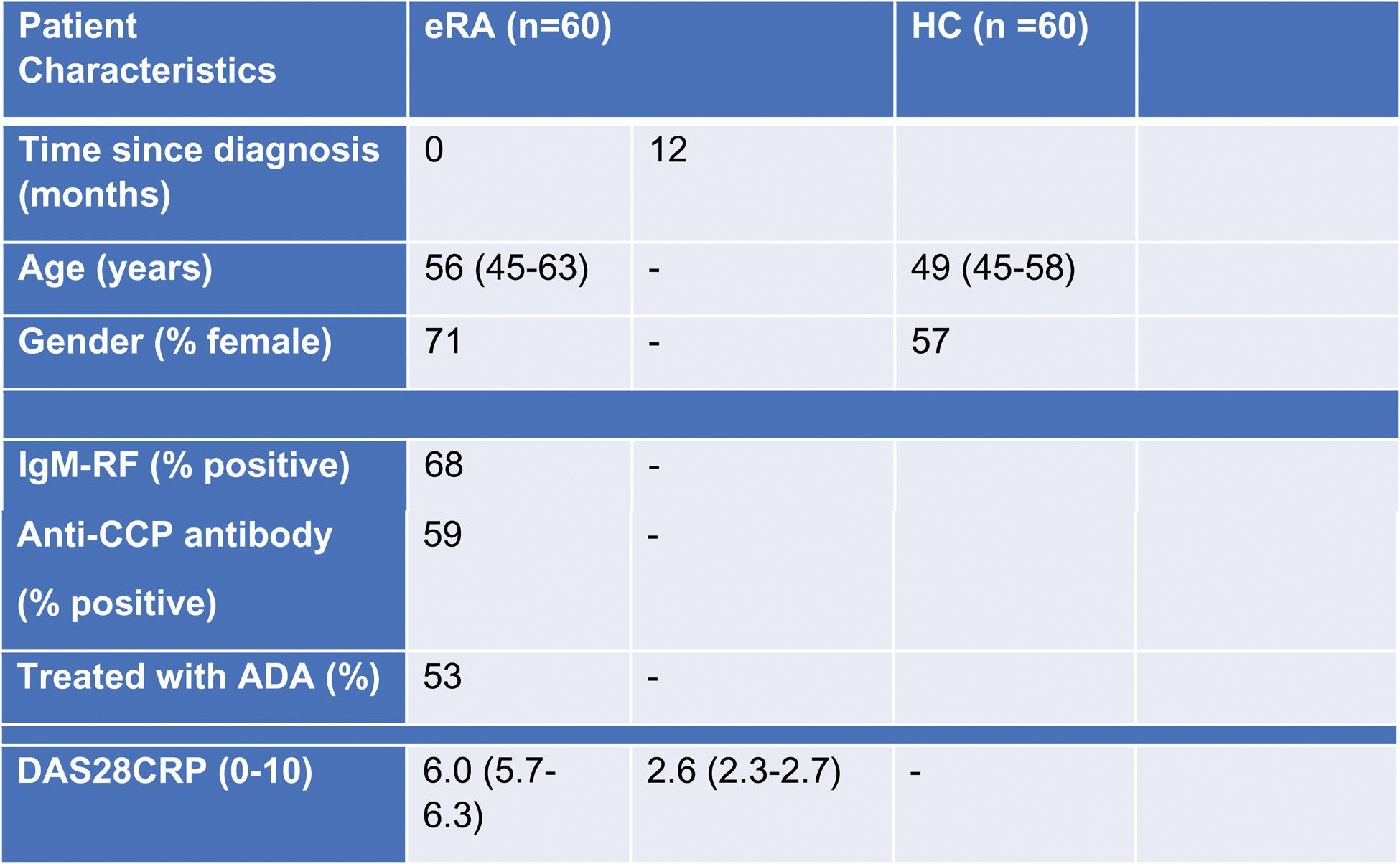
Table 1. Patient characteristics in treatment-naïve early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) ( n = 60) and healthy controls (HC) ( n = 60). Data are expressed as mean with (0.05, CI) unless otherwise indicated. ADA Adalimumab, CCP Cyclic citrullinated peptide, DAS28CRP disease activity score 28 based on C-reactive protein, IgM-RF IgM rheumatoid factor.
Acknowledgements: We thank medical doctors and nurses at the Danish Departments of Rheumatology, for helping to collect the patient samples. The authors kindly acknowledge a grant from the Danish Rheumatism Association (R188-A6589).
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (