

Background: Janus kinases inhibitors (JAKi) have proven effective in treating various inflammatory conditions, including rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs). Growing clinical experience with established indications and the emergence of new and generic JAKi may significantly shift global RMD treatment practices. This is evidenced by ongoing case reports and translational studies that highlight the broader use of JAKi and potential introduction of new indications. To guide future research, there is a need to establish clinical opinion on the evolution of JAKi use within current and broader indications given their expanded availability and upcoming generic forms.
Objectives: This study aimed to gain the unique perspectives of Rheumatologists in Europe, by consensus scoring and gaining clinical and scientific opinion on current and future JAKi utilization. This work aimed to determine European expert consensus on (1) current and (2) potential expanded future roles of JAKi in RMDs.
Methods: A four-round modified Delphi approach was used to achieve consensus on JAKi use in RMDs. A scoping review [1] on current use of JAKi in expanded indications informed the initial statements, which were further developed by a global team of experts comprising an academic committee (4 UK/US experts) and a steering committees (1 expert from each participating country). Panellists were recruited from France, Switzerland, UK and Ukraine in Europe. Eligibility criteria included fluency in English, being a medical doctor providing Rheumatology care, board certified Rheumatologist (or equivalent), ≥5 years Rheumatology clinical experience/or ≥5 publications, membership of a national or international Rheumatology association, and at least two years experience in prescribing JAKi for RMD or treating ≥5 patients with JAKi. In Ukraine, only fluency in English, clinical experience, and association membership were required. Panellists ranked 79 statements on a Likert scale of 1-9, provided feedback on statement stringency, and provided free text comments. Stable consensus or disagreement was defined as a median score of ≥7 or ≤3, respectively, from two consecutive rounds. All statements were presented in a at least two rounds, with amendments made based on panellist feedback and committee review.
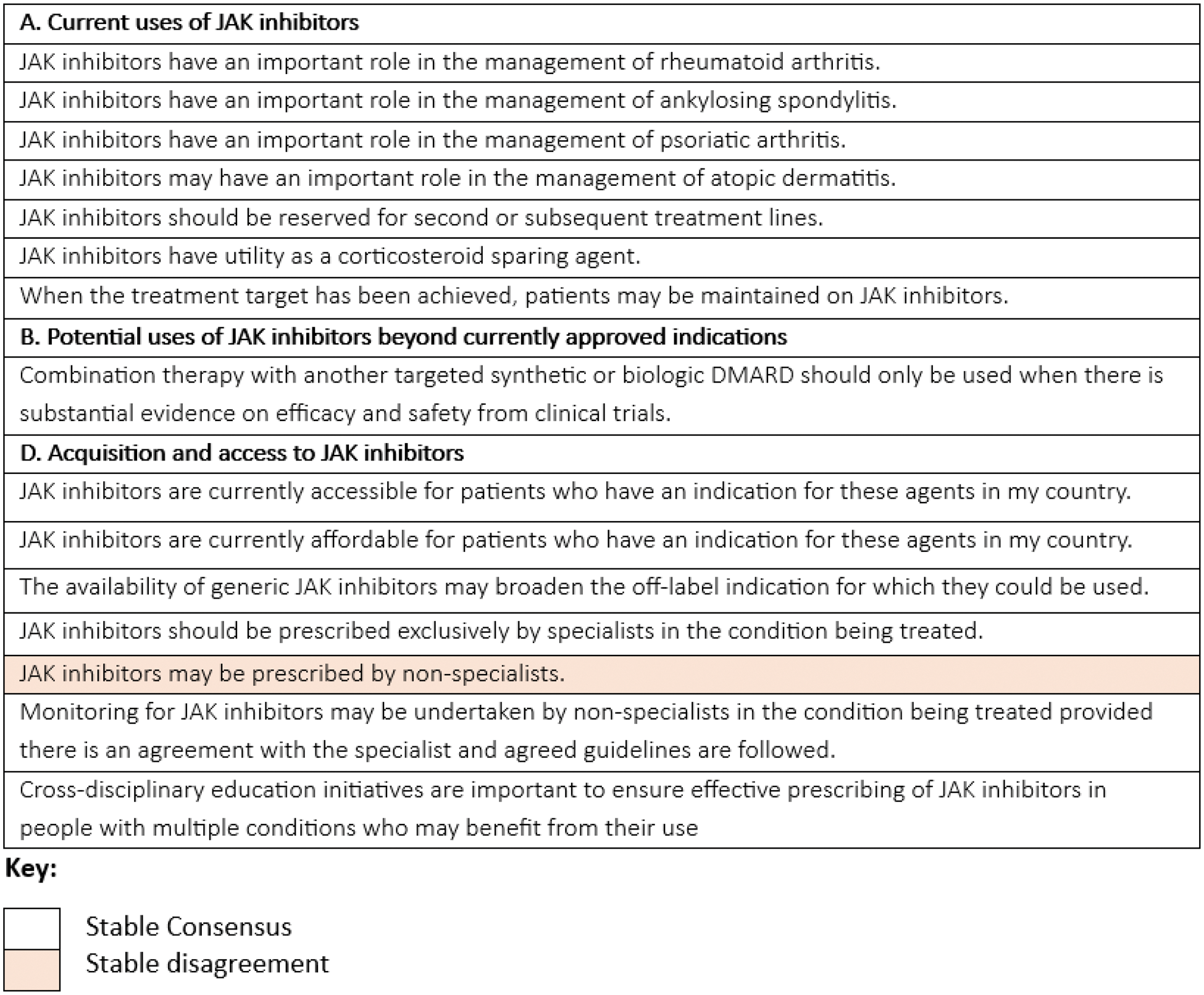
Results: A total of 40 panellists from Europe took part: France (n=11), Switzerland (n=11), the UK (n=10), and Ukraine (n=8), of whom 30, 30, 28 and 25 panellists took part in rounds 1-4, respectively. As shown in Table 1, 14 statements reached stable consensus, and 1 statement reached stable disagreement, categorised into the following groups: Current Uses of JAKi, Potential uses of JAKi beyond currently approved indications, or Acquisition and access to JAKi. No statements regarding TYK2 inhibitor use reached consensus. The majority of statements that reached consensus were established during the first two rounds. European panellists showed clear consensual agreement for the important role JAKi have in the management of numerous current indications including rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis and atopic dermatitis. However, no statements relating to any of the 12 additional indications highlighted in the scoping review [1], reached consensus. In contrast, panellists did highlight combination therapy with another targeted synthetic or biologic DMARD may potentially be considered, but only if substantial evidence on efficacy and safety is available from clinical trials. No consensus amongst European panellists was reached regarding JAKi use upon introduction of generic versions, but did agree that introduction of JAKi generics may increase their off-label use. JAKi were agreed to be accessible and affordable in Europe and should be exclusively prescribed by specialists.
Conclusion: This work highlights European opinion on the potential evolution of JAKi use in RMDs based on available literature evidence and expert opinion. Widely acknowledged was the significant role of JAK inhibitors in managing diseases for which they have approval. European clinicians were more hesitant at providing opinion on how the availability of generic JAKi may lead to their wider use as compared to clinicians outside of Europe. Whilst this study provides valuable insight into the current and potential future trends of JAKi use in RMDs, it does highlight numerous areas for further exploration. Addressing these gaps is essential for optimising the use of JAK inhibitors in the management of RMDs and beyond. This study was sponsored by Pfizer. Pfizer employees and academic authors designed the study, interpreted data, and wrote the abstract. Analytical and writing support was provided by Momentum data Ltd, funded by Pfizer.
REFERENCES: [1] Challoumas D, Simpson C, Arnold M, Mease P, Moots R, Ndosi M, Rutter Locher Z (2025). Janus-kinase inhibitor use in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases beyond licensed indications: A scoping review.
Autoimmunity
Reviews 24 (3);
Table 1. Statements which achieved stable consensus or stable disagreement regarding JAKi use in RMDs in Europe.
Acknowledgements: International steering committee and panellists who took part in the study.
Disclosure of Interests: Anna Barkaway Shareholder of Pfizer Ltd, Employee of Pfizer Ltd, Philip J. Mease Honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Consultant for AbbVie, Acelyrin, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squib, Cullinan Biotech, Eli Lilly, lnmagene, Janssen, Moonlake, Novartis, Pfizer, Takeda, UCB. Other: Genascence, Grants/research support from: AbbVie, Acelyrin, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squib, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Robert Moots Consultant for Pfizer, Grant from Novartis, Mwidimi Ndosi Consultant for Pfizer, Grants from Sanofi and Vifor Pharmaceuticals, Zoe Rutter-Locher Consultant for Pfizer, James Galloway Honoraria from Abbvie, Alfasigma, Gilead, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Consultant for Abbvie, Alfasigma, Janssen, Lilly, Pfizer, Jérôme Avouac Honoraria from Galapagos/Alfasigma, Lily, Pfizer, Abbvie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Sanofi, Chugai, Nordic Pharma, Medac, Novartis, Biogen, Fresenius Kabi, Celltrion, Janssen, Amgen, Consultant for Galapagos/Alfasigma, Lily, Pfizer, Abbvie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Nordic Pharma, Medac, Fresenius Kabi, Celltrion, Research grants from Galapagos/Alfasigma, Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Nordic Pharma, Novartis, Fresenius Kabi, Axel Finckh Honoraria from AbbVie, Eli-Lilly, Pfizer, Astra-Zeneca, Consultant for AbbVie, Astra-Zeneca, Pfizer, Research grants from AbbVie, Alfasigma, BMS, Eli-Lilly, Pfizer, Yelyzaveta Yehudina Consultant for Pfizer, Michael McLean Shareholder of Pfizer Ltd, Employee of Pfizer Ltd.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (