

Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by synovial angiogenesis, especially in patients with prolonged disease duration and high activity [1]. Angiogenesis is essential for the development of the rheumatoid pannus that is driving joint destruction. Integrin αvβ3 expression is upregulated in active angiogenesis sites, such as in RA synovium [2]. Moreover, studies showed that αvβ3 antagonists inhibit synovial angiogenesis and reduce inflammation in preclinical arthritis models. Non-invasive Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging with αvβ3-targeted tracers to visualize angiogenesis has shown promise for early diagnosis, disease staging, and monitoring treatment response, hence positioning αvβ3 as a valuable biomarker for RA [3, 4]. [ 18 F]Fluciclatide, an RGD (arginine-glycine-aspartic acid)-based peptide PET tracer with high affinity for integrin αvβ3, has shown potential in cancer imaging, particularly for assessing tumor vasculature [5]. Its potential in the context of RA remains to be elucidated.
Objectives: To investigate the expression of integrin αvβ3 in the synovium of Antigen-Induced Arthritis (AIA) rats and evaluate the potential of integrin αvβ3 as a target for PET imaging of angiogenesis using [ 18 F]Fluciclatide.
Methods: Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining was performed to assess integrin αvβ3 expression in tissue sections of knee joints from AIA rats [6] using a polyclonal αvβ3 antibody. Arthritis was induced in one knee, with the contralateral knee serving as a control, and healthy knees from non-arthritic rats served as negative controls. QuPath software quantified the proportion of positively stained cells in IHC-stained sections, comparing arthritic, contralateral, and healthy knees (mean ± SEM). Biodistribution of [ 18 F]Fluciclatide was conducted in AIA rats (n=4). Rats were euthanized at 30 minutes, organs were dissected and weighed, and radioactivity (CPM) was measured. Tracer uptake was calculated as %ID/gram. Dynamic PET with [ 18 F]Fluciclatide (1-15 MBq injected) was performed on AIA rats (n=4) for 1 hour post-injection, followed by whole-body computed tomography (CT) scanning to localize tracer uptake. A blocking study was performed by injecting an excess amount of Cilengitide (20mg/Kg BW) 15 min prior to the injection of [ 18 F]Fluciclatide in a separate group of rats (n=2). Cilengitide is a cyclic RGD peptide targeting integrin αvβ3 with an affinity of 0.61 nM [7]. This blocking study was conducted to assess the specificity of the uptake of the tracer. SUV mean values were calculated for both arthritic and control knees, with and without Cilengitide blockade.
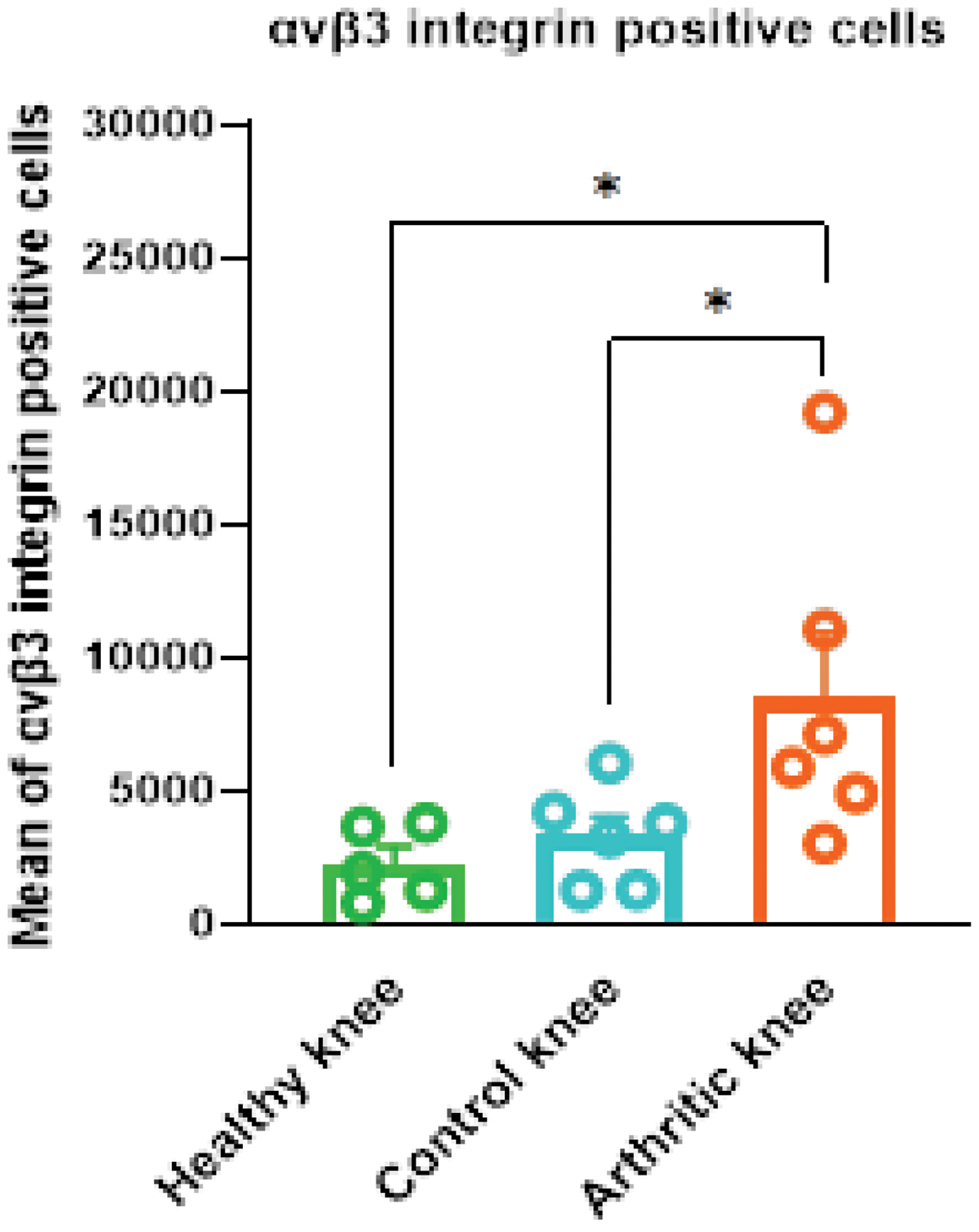
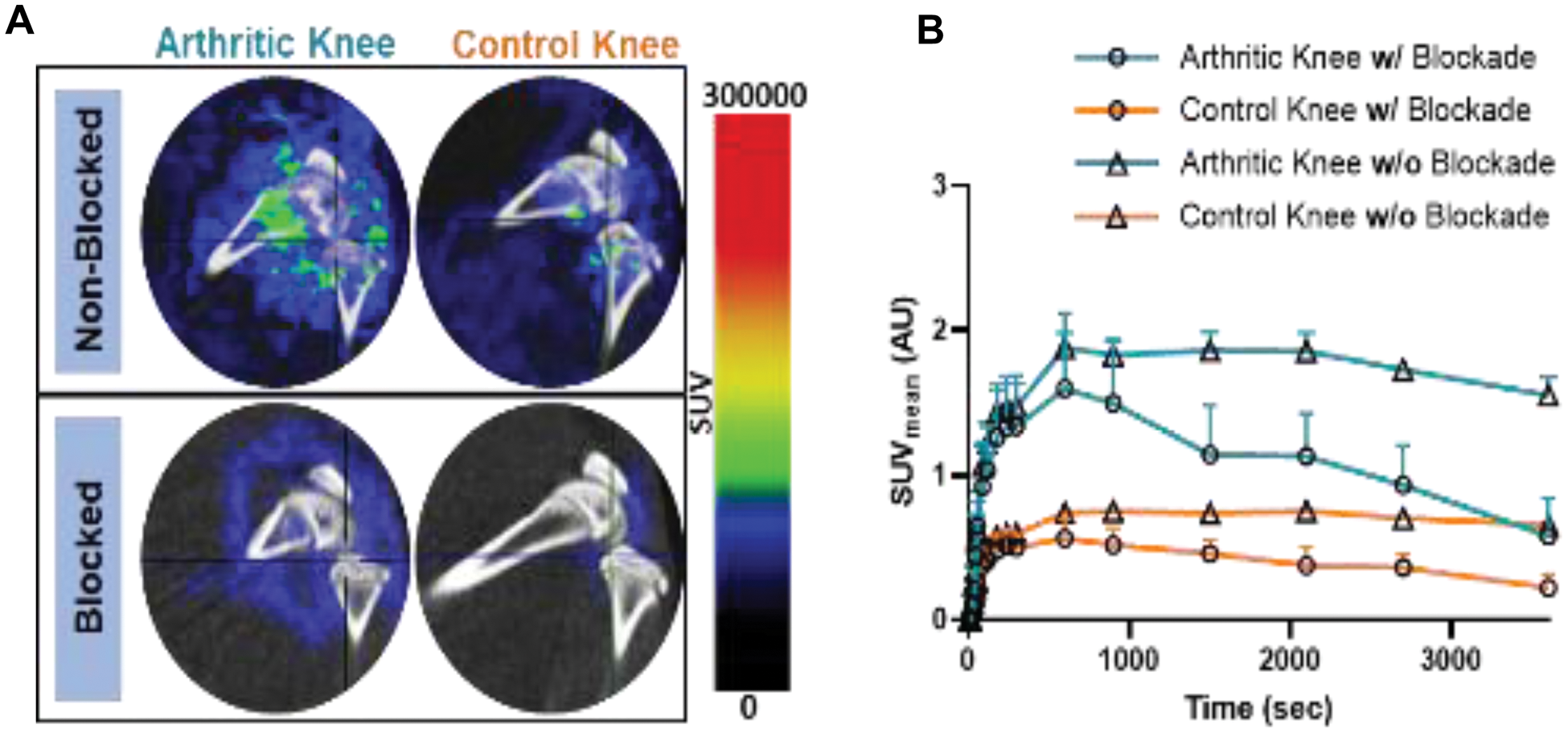
Results: IHC staining revealed significant integrin αvβ3 expression in arthritic knee tissues compared to control knees from AIA rats and healthy rats. Quantitative analysis confirmed an increase in expression in the arthritic tissues (p < 0.05; Figure 1). Biodistribution studies of [ 18 F]Fluciclatide showed higher tracer uptake in the arthritic knees (0.3 ± 0.02 %ID/gram) compared to the control knees (0.2 ± 0.02 %ID/gram) (p < 0.05). The primary excretion route was via the urinary tract, with high tracer uptake also observed in the gastrointestinal tract. Furthermore, the uptake in peri-articular tissues such as muscle, bone, and blood was lower than in the knee joints, ensuring clear visualization of the inflamed knee. PET demonstrated approximately two-fold higher uptake in the synovium of arthritic knees compared to control knees, aligning with biodistribution data. Blocking with Cilengitide led to a marked reduction in tracer uptake, with SUV mean values decreasing by approximately 50% in the arthritic knees, confirming the specificity of the tracer binding to integrin αvβ3 (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Integrin αvβ3 is a promising target for non-invasive imaging of angiogenesis in RA. [ 18 F]-Fluciclatide PET-CT imaging effectively detected increased αvβ3 expression in arthritic synovium, supporting its potential for disease activity assessment and therapy evaluation.
REFERENCES: [1] Khodadust F, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(13):7 doi:10.3390/ijms23137071.
[2] Morshed A, et al. Molecules. 2019;24(8):1 doi:10.3390/molecules24081537.
[3] Notni J, et al. EJNMMI Res. 2019;9(1):8 doi:10.1186/s13550-019-0541-6.
[4] Zhu Z, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(6):1269-72. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204820.
[5] Sharma R, et al. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020;47(5):1239-5 doi:10.1007/s00259-019-04532-z.
[6] Chandrupatla DMSH, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2015:509295. doi:10.1155/2015/509295.
[7] Pan X, et al. Bioengineered. 2022;13(2):4557-72. doi:10.1080/21655979.2022.2029236.
Quantitative analysis of integrin αvβ3 expression is significantly higher in arthritic knee tissues compared to healthy controls. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (p < 0.05, Wilcoxon signed-rank test for control vs. arthritis, and Mann-Whitney U test for arthritis vs. healthy controls; N = 5-6/group).
Representative PET images (sagittal view) of the knee of AIA rats acquired over a 1-hour period using [ 18 F]Fluciclatide and SUV mean analysis of AIA rat knees. A ) PET-CT images of the arthritic and control knees of AIA rats, showing the knees with and without blockade by Cilengitide. B ) SUV mean time-activity curves of [ 18 F]Fluciclatide for the arthritic (orange) and control (blue) knees of AIA rats, with and without blockade. Data were analyzed using vivoQuant software, where the synovium area was delineated from the bones for SUV mean measurement, ensuring accurate assessment of tracer uptake in the synovial tissue. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. N = 4 for the non-blockade group and N = 2 for blockade group.
Acknowledgements: This project received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie Grant Agreement No. 847551.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (