

Background: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a heterogenous disease characterised by autoimmunity, vasculopathy, and fibrosis. The leading cause of mortality in SSc is interstitial lung disease (ILD).
Objectives: This study aimed to characterize the peripheral immunome associated with progressive ILD in SSc. Our findings will shed light into the pathogenesis of ILD in SSc. Furthermore, our findings will provide an opportunity to develop potential theragnostic tool to evaluate progressive ILD in SSc.
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were collected from SSc patients (n=10 progressive ILD, n=10 stable ILD). Progressive ILD was defined by relative decline in forced vital capacity of 10% or more from baseline, or a relative decline of 5% to <10% accompanied by either worsening respiratory symptoms or increased fibrosis on high-resolution computed tomography. Single-cell proteomic data was acquired using mass cytometry (CyTOF), with a panel of 77 unique markers. The CyTOF data was analysed using the Extended Polydimensional Immunome Characterization (EPIC) platform, which is an unsupervised machine learning algorithm to characterize immune cell subset perturbations. Using cell frequencies of the identified cell subsets, we built multiple logistic regression models to classify progressive and stable ILD. Lastly, a correlation network between nodes was constructed for active SSc and inactive SSc by performing pairwise correlations between each node pair (absolute correlation coefficient cut off > 0.6).
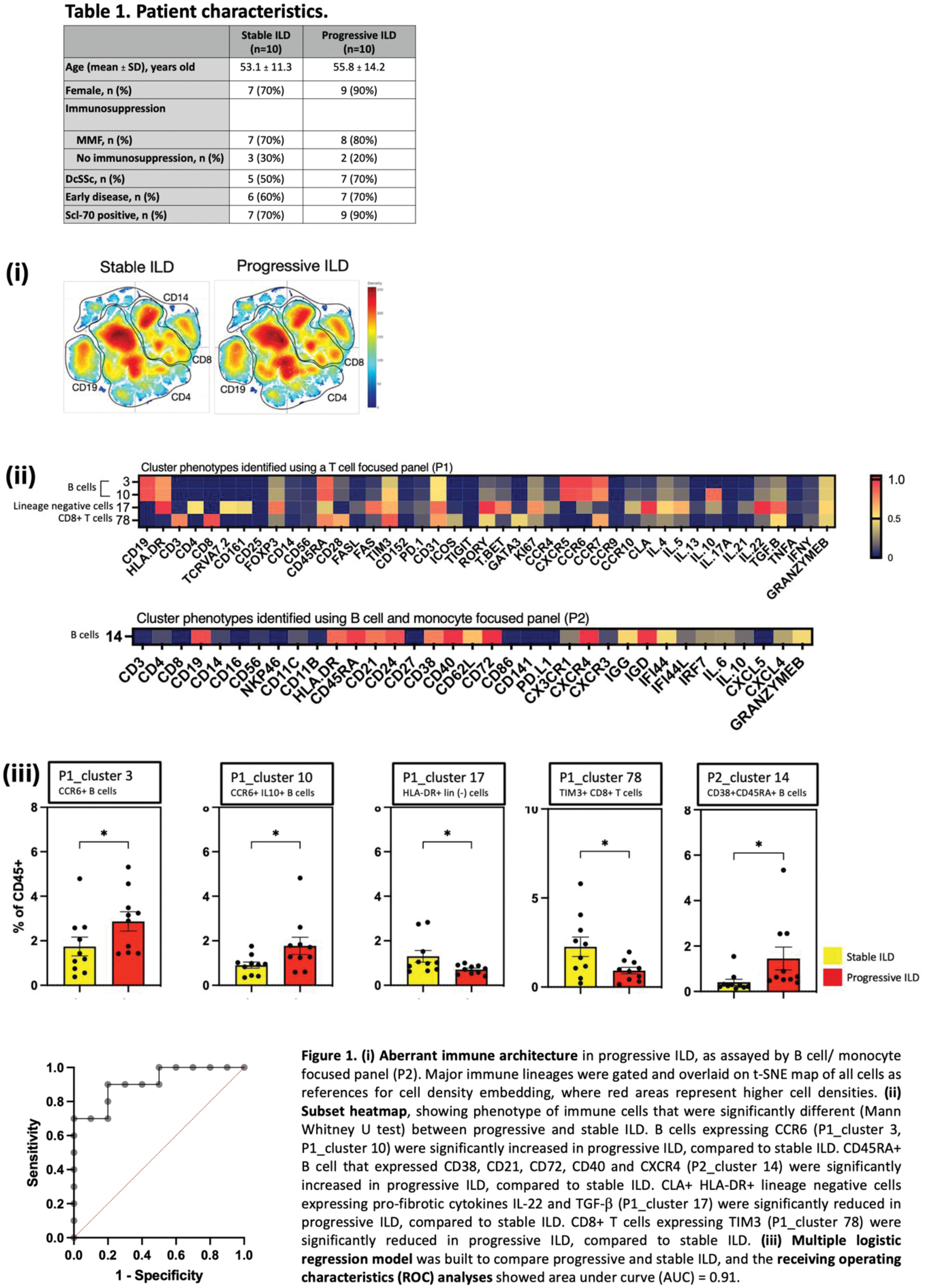
Results: Patient characteristics were summarized in Table 1. Dysregulations in various immune cell lineages were observed in the peripheral immunome of progressive ILD, as compared to stable ILD (Figure 1(A)). CCR6+ naïve B cells and immature B cells were increased in progressive ILD, while CLA+HLA-DR+ lineage negative cells expressing pro-fibrotic cytokines and CD8 T cell subsets expressing immune checkpoints were decreased in progressive ILD, compared to stable ILD (Figure 1(B)). By using cell frequencies of the identified immune cell subsets, we built a multiple logistic regression model and the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis showed an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.91 (95% CI: 0.78-1, P=0.0019, with negative predictive power: 89% and positive predictive power: 82% (Figure 1(C)). Immune cell network from SSc patients with stable ILD showed more negatively connected edges compared to network from SSc patients with progressive ILD. In addition, progressive ILD was characterized by decreased centralization and higher modularity, as compared to stable ILD, suggesting reorganization in the immune cell network and homeostasis.
Conclusion: We identified dysregulated immune cell subsets with distinct expression of activation markers, immune checkpoints, and chemokine receptors, suggesting perturbed immune cell trafficking and regulatory mechanisms in progressive ILD. Immune cell network analyses suggested a shift in the immune network architecture, marked by fewer negatively connected edges in progressive ILD, suggesting impaired peripheral immune tolerance in progressive ILD. Future studies to investigate their functional significance would shed light into the disease pathogenesis. The identified immune signatures could potentially be used as theragnostic tools to evaluate ILD status in SSc.
REFERENCES: [1] Nat Biotechnol. 2020 Jun;38(6):679-684.
Acknowledgements: This study was supported by the Reverie Rheumatology Research Fund and SYSMIC (BMRC/IAFPP/H24J4a0019). Noviani M held NMRC Research Training Fellowship (MOH-RTF23jan-0002) and NMRC Clinician Scientist Resident Seed Funding (MOH-CSSDFD23janB-0001). Low AHL held a National Medical Research Council Clinical Scientist Award (grant number: MOH-CSAINV19may-0005). SA held NMRC (NMRC/OFLCG/002/2018, CIRG19may0052), MOH-STaR19nov-0002, Duke-NUS and SingHealth AMC core; National Research Foundation Singapore, and the Agency for Science Technology and Research (A*STAR) Singapore (H22P0M0003).
Disclosure of Interests: Maria Noviani Boehringer Ingelheim, Pavanish Kumar: None declared, Vasuki Ranjani Chellamuthu: None declared, Ahmad Lajam: None declared, Alfred Chia: None declared, Katherine Nay Yaung: None declared, Martin Wasser: None declared, Joo Guan Yeo: None declared, Andrea Low Novartis, Boehringer Ingelheim, Johnson & Johnson, Boehringer Ingelheim, Boehringer Ingelheim, Johnson & Johnson, Salvatore Albani: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (