

Background: The management of spondyloarthritis. (SpA) includes controlling disease activity as well as comorbidities such as metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome can be associated with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) or even steatohepatitis (MASH). The IL-23/TH17 axis plays a central role in the pathophysiology of SpA, but it is also implicated in hepatic steatosis and its progression to fibrosis.
Objectives: This study aims to evaluate, in an adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) rat model, the presence of hepatic inflammation and fibrosis at different stage of arthritis and to assess the effect of early treatment with anti-IL-17A.
Methods: Arthritis was induced in 6-weeks-old male Lewis rats by a subcutaneous injection at the base of the tail with 1.2 mg of inactivated Mycobacterium butyricum suspended in Freund’s incomplete adjuvant (AIA groups) at Day 0. At different stages of arthritis (Day 4 post-induction: preclinical phase; Day 11: arthritis onset; Day 30: acute phase; Day 90: resolution phase), intrahepatic inflammation was assessed by measuring mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNFα, IL-6, IL-17A, IL-23p19, IL-33) using RT-qPCR (delta-delta Ct method, relative expression normalized to GAPDH), and by detecting T lymphocytes (CD3+) and helper T lymphocytes (CD4+) using immunohistochemistry. Fibrosis was evaluated by hepatic TGFβ mRNA expression (RT-qPCR), serum AST/ALT ratio, and histology with picrosirius red staining. The same analyses were performed in non-arthritic control rats and AIA rats treated with secukinumab (20 mg/kg intraperitoneally every three days).
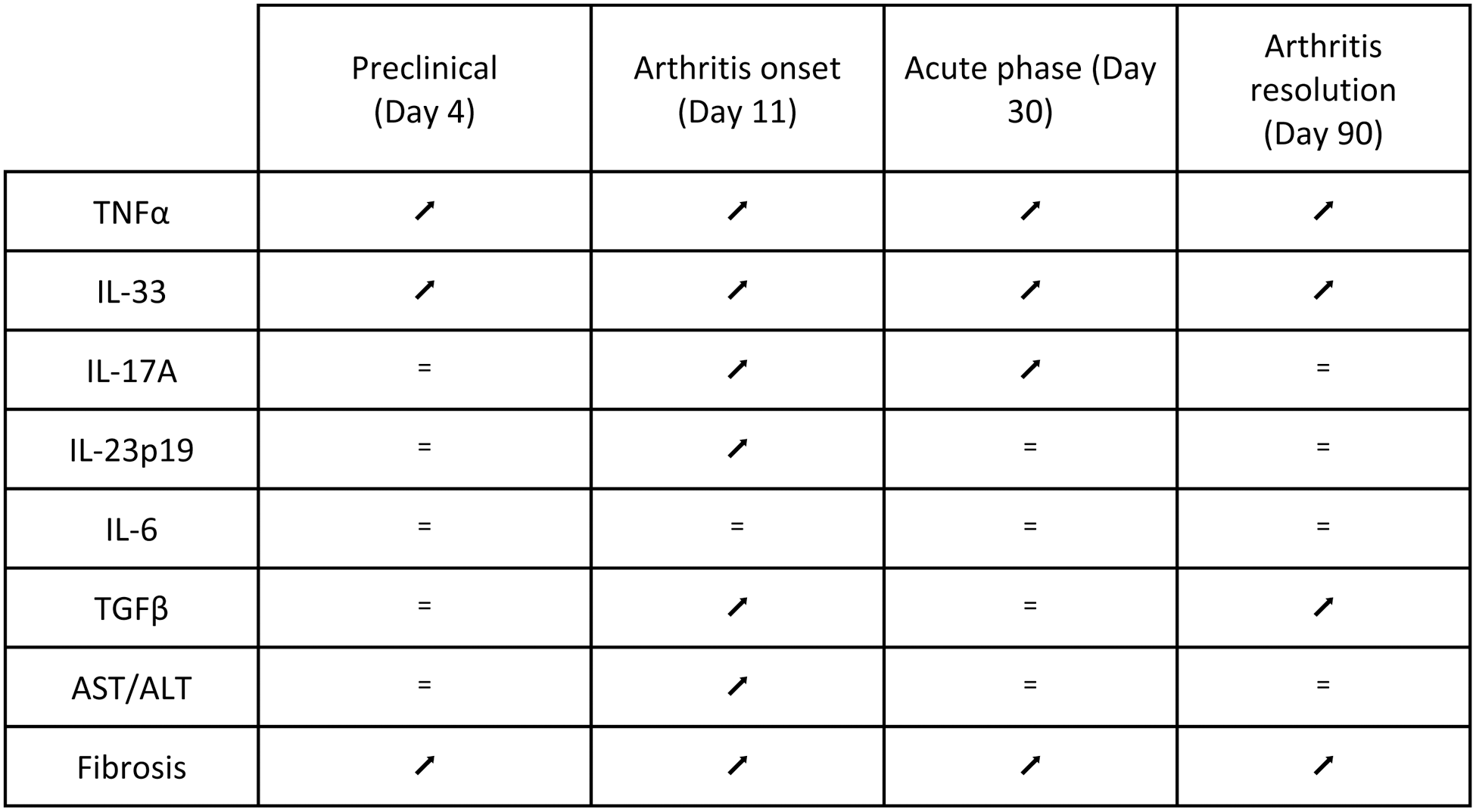
Results: Compared to controls, AIA rats exhibited early and sustained hepatic inflammation. At preclinical stage, overexpression of TNFα and IL-33 was observed, with additional overexpression of IL-17A and IL-23p19 beginning at arthritis onset (p < 0.015). During the acute phase, TNFα, IL-33, and IL-17A remained overexpressed, while only TNFα and IL-33 were still overexpressed at the resolution phase. Hepatic fibrosis was histologically present at all stages (p < 0.05), supported by overexpression of TGFβ at Day 11 (p < 0.001), Day 30 (p = 0.06, NS), and Day 90 (p < 0.001). However, the AST/ALT ratio was significantly elevated only during arthritis onset (Day 11, p < 0.0001).
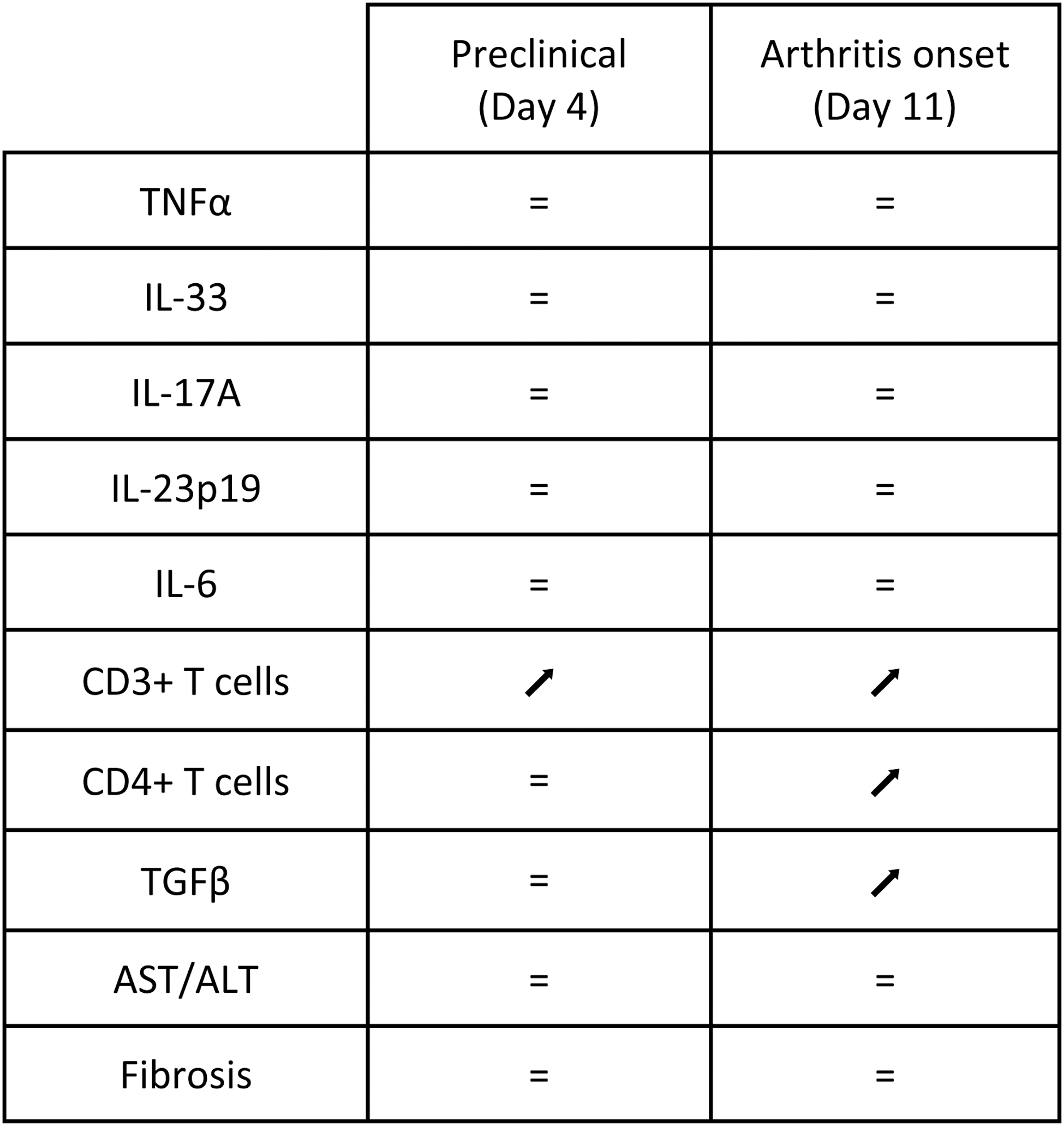
Preventive treatment with secukinumab did not alter hepatic pro-inflammatory cytokine genes expression in AIA rats. However, secukinumab increased hepatic CD3+ and CD4+ T cell counts on Day 11 (p < 0.05) and TGFβ mRNA expression (p < 0.01) compared to untreated AIA rats.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate early hepatic inflammation and fibrosis in a murine model of reactive arthritis. Preventive administration of anti-IL-17 did not reduce these abnormalities but instead partially exacerbated them. These findings do not support a major role for IL-17 in initiating hepatic abnormalities associated with SpA but encourage further investigation into the roles of other cytokines, particularly TNFα and IL-33, in their pathophysiology.
REFERENCES: NIL.
RT-qPCR, biochemical, and histological results for AIA groups compared to control groups.
RT-qPCR, biochemical, and histological results for AIA-SK groups compared to AIA-NT groups.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (