

Background: Despite its clinical relevance, the immunopathogenesis of non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA) remains poorly defined, particularly in comparison to radiographic axSpA (r-axSpA). Emerging evidence underscores the role of cells involved in innate immunity, including granulocytes [1] and very rare subpopulations such as mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells [2], in the pathogenesis of axSpA, either by regulating or exacerbating inflammation. Mass cytometry (CyTOF) enables the more precise identification of rare cells and in-depth characterization of leukocyte subpopulations.
Objectives: To characterize the phenotypic and functional profile of all circulating leukocytes, including granulocytes, in nr-axSpA, using mass cytometry and to compare them with those in r-axSpA and healthy controls.
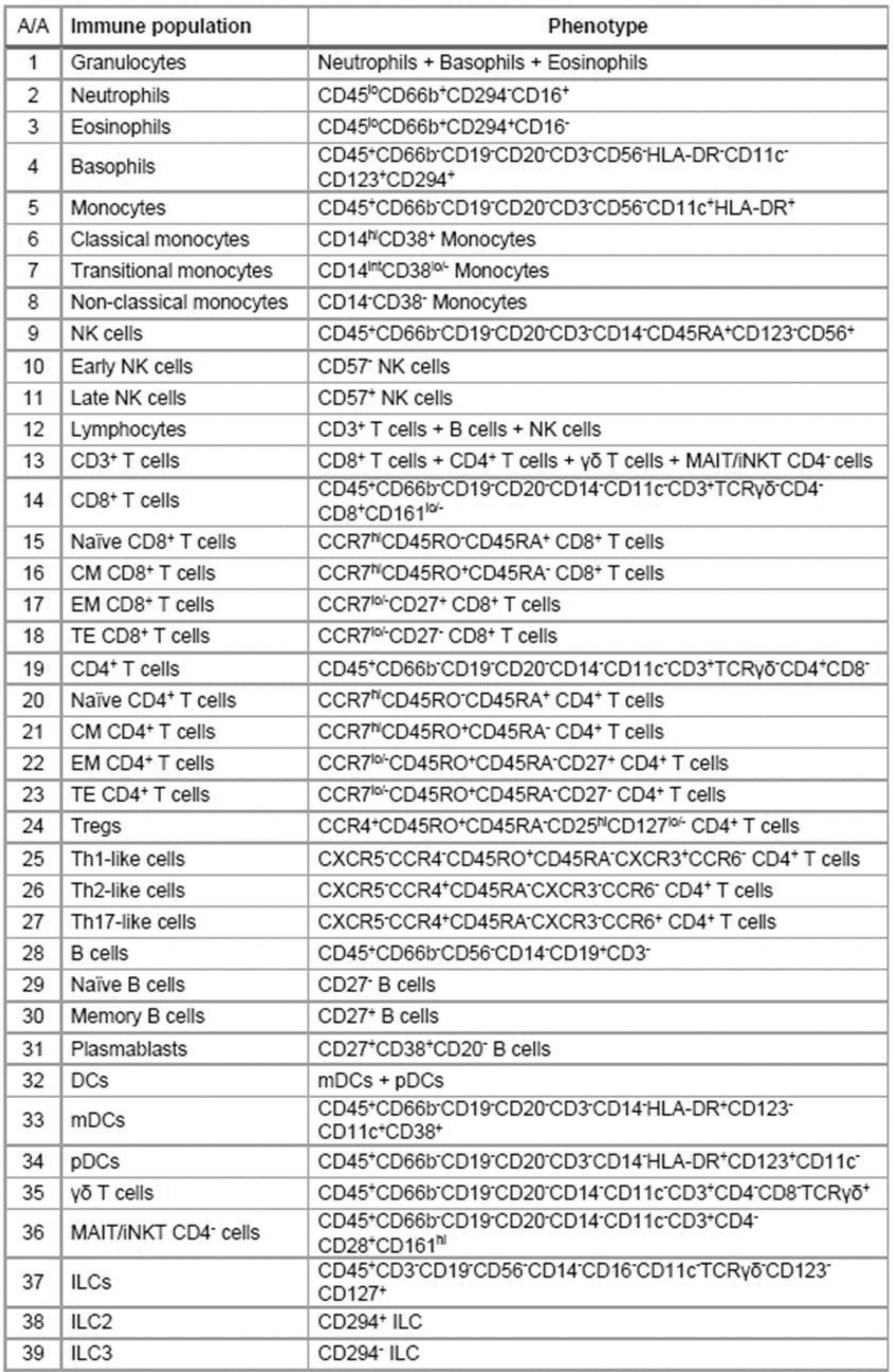
Methods: Fresh peripheral blood samples from treatment-naïve patients (nr-axSpA; n=8, median (range) age: 29 (23-51), 38% females, mean disease duration: 42 months, and r-axSpA; n=7, median (range) age: 51 (38-65), 43% females, mean disease duration: 183 months) with active disease, and healthy controls (HC; n=7, median (range) age: 34 (25-56), 57% females) were stained using a panel of metal-conjugated antibodies against 40 proteins, including 5 chemokine receptors and 10 functional markers (IL-17A, IL-4, IL-10, CTLA-4, CD69, CD107a, perforin, granzyme B, PD-1, PD-L1) and were analyzed by a 3 rd generation Helios mass cytometer. Frequencies (%) of 39 leukocyte subpopulations and subtypes (Figure 1), as well as their expression of functional markers (reported as frequencies and median intensity), were investigated.
Results: Nr-axSpA patients exhibited elevated frequencies of granulocytes (p=0.034) and CD3+ T cells (p=0.047) and reduced NK cell frequencies (p<0.001) compared to HC, being similar though to r-axSpA. When compared to r-axSpA, nr-axSpA demonstrated higher γδ T cell frequencies (p=0.004) but lower total CD4+ T (p=0.032) and Th-17-like (CXCR5 - CCR4 + CD45RA - CXCR3 - CCR6 + CD4 + T cells; p=0.040) cell frequencies, suggesting a potential shift from innate to adaptive immune dominance in r-axSpA compared to nr-axSpA. No significant differences were detected in other leukocyte subpopulations and subtypes examined. Investigation of chemokine receptor expression revealed reduced frequencies of CXCR3 + MAIT/iNKT (p=0.025) and CXCR3 + γδ T cells (p=0.031) in nr-axSpA compared to HC, with the respective frequencies being numerically even lower in r-axSpA, possibly reflecting enhanced chemokine-driven migration of these cells into sites of inflammation. Moreover, functional marker analysis revealed reduced frequencies of cytotoxic perforin + MAIT/iNKT cells in nr-axSpA compared to HC (p=0.028), albeit similar to r-axSpA. Within MAIT/iNKT cells, activated CD69 + cell frequencies were lower in nr-axSpA compared to r-axSpA (p=0.048), but similar to HC. Interestingly, no significant difference was observed between groups in the frequencies or median expression of the other functional markers, including IL-17A, a critical player in axSpA pathogenesis (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Our findings highlight distinct immune signatures in nr-axSpA. While nr-axSpA and r-axSpA exhibit broadly similar immune profiles, the adaptive branch appears to be more established in r-axSpA, which is not observed in nr-axSpA. These results underscore the immune heterogeneity between nr-axSpA and r-axSpA and align with the understanding that nr-axSpA may represent an earlier and/or incomplete disease stage.
REFERENCES: [1] Ramming A, Angeli M, Schütz C, et al, OP0213 Ly6G+CXCR2-CD101- GRANULOCYTES REGULATE INFLAMMATION IN AXIAL SPONDYLOARTHRITIS Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2024;83:108-109.
[2] Gracey E, Qaiyum Z, Almaghlouth I, et alI, L-7 primes IL-17 in mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells, which contribute to the Th17-axis in ankylosing spondylitis sAnnals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2016;75:2124-2132.
Circulating leukocyte subpopulations and subtypes investigated by mass cytometry.
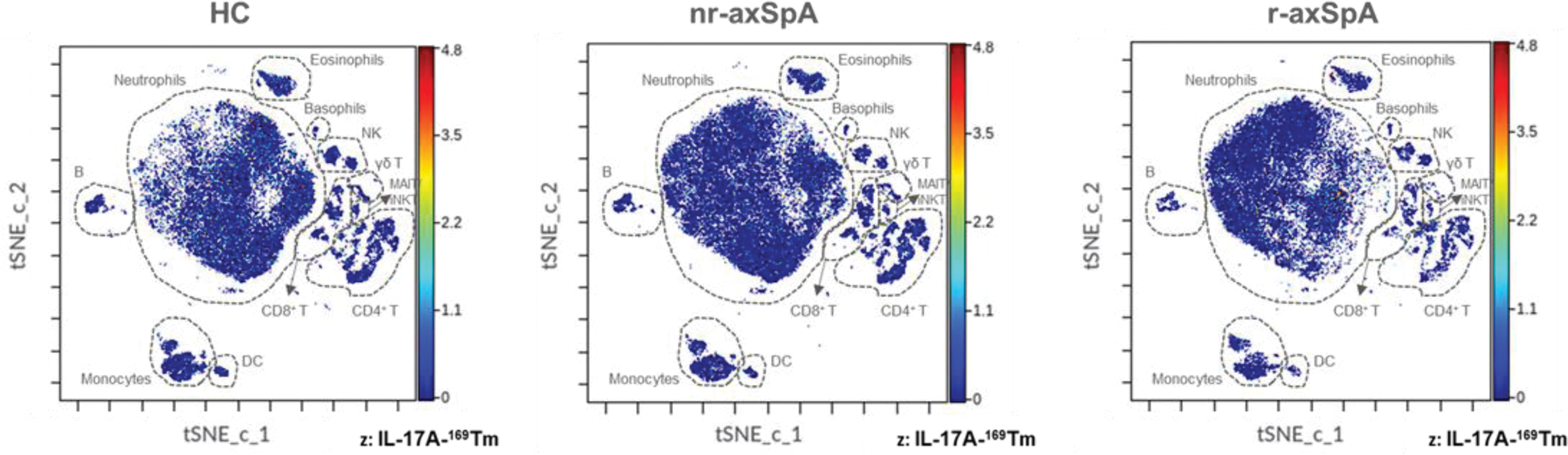
CyTOF analysis shows similar IL-17A expression in all circulating leukocytes across groups. tSNE plots showing live single cells in HC, nr-axSpA and r-axSpA patients. The primary leukocyte populations are circled with a dotted line on the tSNE plot. Each dot represents a cell and is colored according to IL-17A intensity on a spectrum heat scale (red = high intensity; blue = low intensity). Arcsine-transformed color scales report the raw values of the IL-17A’s intensity.
REFERENCES: NIL.
Acknowledgements: We acknowledge the support of this work by the project “The Greek Research Infrastructure for Personalised Medicine (pMedGR)” (MIS 5002802) which is implemented under the Action “Reinforcement of the Research and Innovation Infrastructure”, funded by the Operational Programme “Competitiveness, Entrepreneurship and Innovation” (NSRF 2014-2020) and co-financed by Greece and the European Union (European Regional Development Fund).
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (