

Background: Recently, the incidence of late-onset Still’s disease has been increasing, but its clinical and immunologic characteristics are still unclear.
Objectives: Recently, the incidence of old patients with adult Still’s disease has been increasing, but its clinical and immunological characteristics are still unclear.
Methods: We reviewed consecutive patients with adult Still’s disease diagnosed based on Yamaguchi criteria at Keio University Hospital between April 2012 and June 2024. Patients were divided into two groups, young-onset and late-onset, with a cut-off age of the onset of 65 years. We compared clinical characteristics and peripheral blood immunophenotypes between the two groups.
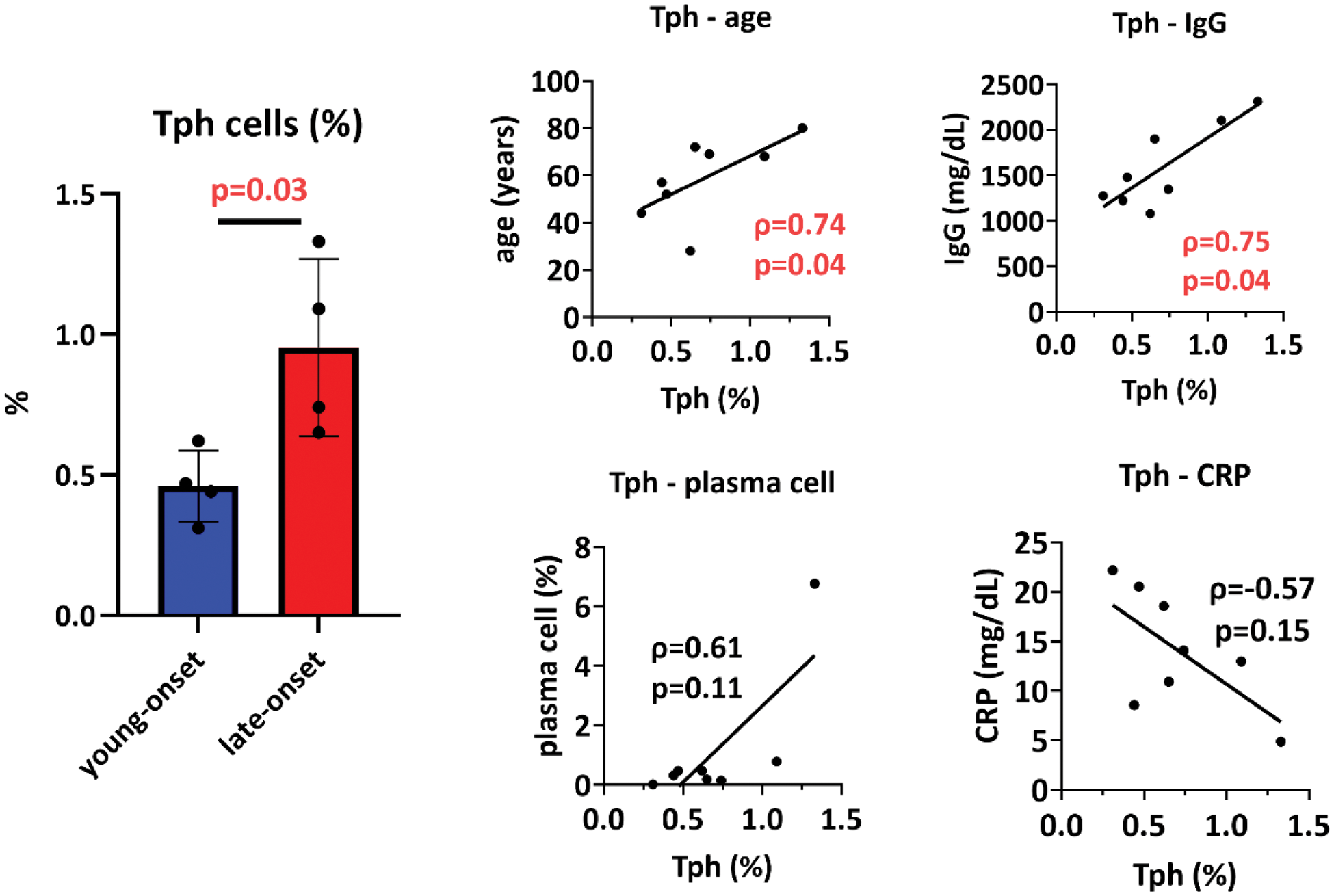
Results: Of the 113 patients with adult Still’s disease, 20 (17.6%) were late-onset. The median age was 40 and 72 years, and the proportion of the female was 71% and 70% in the young-onset and late-onset groups, respectively. At the time of diagnosis, the proportion of patients with sore throat (71% vs 40%, p=0.02), typical rash (69% vs 40%, p=0.02), and splenomegaly (54% vs 21%, p=0.01) was significantly lower in the late-onset group than in the young-onset group, whereas those with serositis (11% vs 70%, p<0.001) and interstitial pneumonia (5% vs 26%, p=0.01) was significantly higher in the late-onset group. Peripheral blood immunophenotyping was performed in 5 in the young-onset group and 4 in the late-onset group. The proportion of T peripheral helper (Tph) cells among all lymphocytes was significantly higher in the late-onset group (0.45% vs. 0.92%, p=0.03). The percentage of Tph cells was positively correlated with age (ρ=0.74, p=0.04), serum IgG (ρ=0.75, p=0.04), and percentage of plasma cells (ρ=0.61, p=0.11), and tended to be inversely correlated with C-reactive protein (ρ=-0.57, p=0.15).
Conclusion: The distribution of affected organs and the features of immune cells in the peripheral blood were different in late-onset patients compared to young-onset patients. Increased Tph cells in late-onset patients may contribute to the differences in the pathophysiology of adult Still’s disease.
REFERENCES: NIL.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: Moe Fukuchi: None declared , Satoshi Takanashi: None declared , Kie Tanaka: None declared , Hiroya Tamai: None declared , Yasushi Kondo: None declared , Noriyasu Seki employed by Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Kenji Chiba employed by Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Keiko Yoshimoto: None declared , Yuko Kaneko: None declared .
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (