

Background: Adult-onset Still’s Disease (AOSD) is a rare and complex autoinflammatory condition distinguished by recurrent fever, arthritis, and a characteristic salmon-colored rash. Notably, fever of unknown origin (FUO) is the initial presentation in 60–65% of AOSD cases. The diagnosis of AOSD requires the exclusion of other potential causes.
Objectives: This study prospectively assessed the utility of our previously developed algorithm in differentiating AOSD from other causes of fever in patients with FUO [1].
Methods: This study included 42 consecutive patients admitted to the Hacettepe University Department of Internal Medicine for evaluation of FUO between January 2023 and December 2024. Five patients with inconclusive final diagnoses were excluded. To differentiate AOSD from other FUO etiologies, we applied the Hacettepe FUO algorithm published in 2019 [1]. At admission, all patients were classified according to this algorithm using clinical features (arthralgia, sore throat) and fundamental laboratory parameters (ferritin level, neutrophil count).
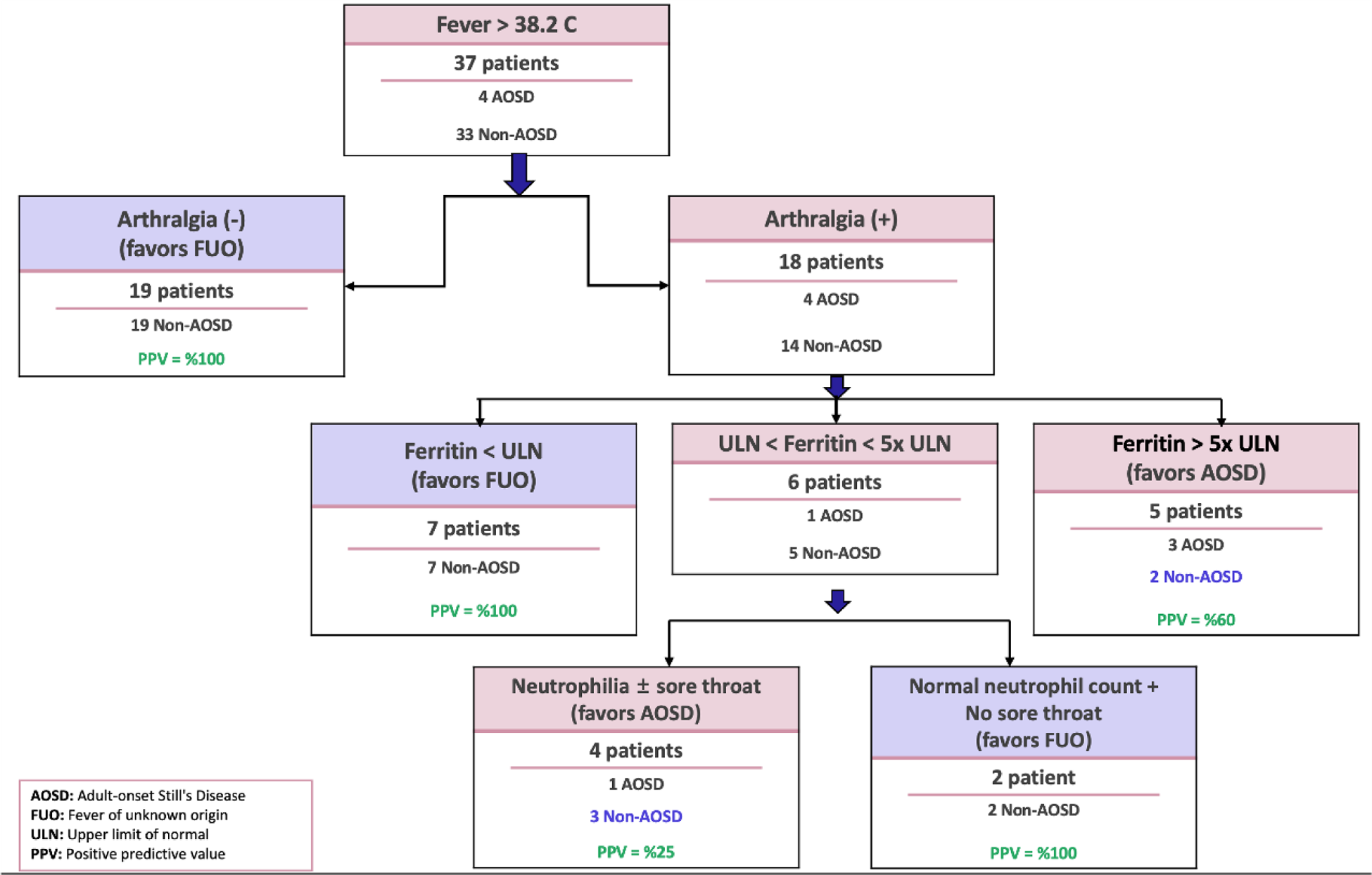
Results: Thirty-seven FUO patients (23 female) were included in the study. According to the algorithm, 9/37 (24.3%) patients were assigned to AOSD and 28/37 (75.7%) to FUO. Among the 9 patients assigned to the AOSD arm of the algorithm, only four (44.4%) ultimately received a diagnosis of AOSD. The final diagnoses differed in five cases: two patients were diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), one with sarcoidosis, one with Castleman disease, and one with anti-synthetase syndrome. Additionally, two patients were concurrently diagnosed with macrophage activation syndrome (MAS). In the non-AOSD arm of the algorithm, comprising 28 patients, none were ultimately diagnosed with AOSD. The algorithm provided three distinct pathways at different stages (Figure 1): a. Fever (+)/arthralgia (-) (n=19): Diagnoses included primary hemophagocytic syndrome, EBV infection, parvovirus infection, tuberculosis (in two patients), osteomyelitis, Coxiella endocarditis, infectious vasculitis, drug-associated ANCA vasculitis, VEXAS, diffuse panbronchiolitis & anti-glomerular basement membrane disease, recurrent panniculitis with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, anaplastic T-cell lymphoma, Hodgkin’s disease, acute myeloid leukemia, sarcoidosis, SLE, and hypothalamic dysfunction. b. Fever (+)/arthralgia (+)/ferritin below the upper limit (n=7): Diagnoses included granulomatosis with polyangiitis, SLE, sarcoidosis, seronegative arthritis, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, deep tissue infection in the lumbar region, and rapidly progressive avascular necrosis. c. Fever (+)/arthralgia (+)/ferritin between the upper limit and five times the upper limit/no neutrophilia or sore throat (n=2): Mesothelioma and drug fever. The algorithm demonstrated a sensitivity of 100%, specificity of 84.9%, positive predictive value of 44.4%, and negative predictive value of 100% in distinguishing AOSD from other causes of FUO.
Conclusion: The Hacettepe FUO algorithm was developed to differentiate AOSD from other potential causes of FUO based on retrospective data. Over the past two years, it has been prospectively applied to all patients hospitalized in the Internal Medicine clinic and referred to our department for FUO evaluation. Among 37 patients with confirmed final diagnoses, 44.4% of those categorized in the AOSD arm of the algorithm were ultimately diagnosed with AOSD. The algorithm showed limitations in diagnosing AOSD, particularly in the presence of rheumatological conditions and complications such as MAS. However, the key challenge in AOSD diagnosis remains proper exclusion. Importantly, when AOSD was excluded through the algorithm, an alternative cause of FUO (such as infection or malignancy) was identified in every case. These preliminary findings underscore the algorithm’s effectiveness in reliably excluding AOSD.
REFERENCES: [1] Bilgin E, et al. Clin Rheumatol. 2019;38(6):1699-706.
The distributions and final diagnoses of patients according to the Hacettepe FUO Algorithm
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (