

Background: Radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (r-axSpA) is a chronic inflammatory rheumatic disease, linked to increased mortality primarily due to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Traditional risk factors, as well as chronic inflammation influence the risk of CVD. The coronary artery calcification score (CAC score) is an established instrument that identifies calcification in the coronary arteries and can be used in risk prediction for CVD. However, the knowledge of CAC score in patients with r-axSpA is limited.
Objectives: This study aims to explore risk factors for an increase in the CAC score among patients with r-axSpA and to compare the CAC score between patients with r-axSpA and matched controls recruited from the general population.
Methods: Patients with r-axSpA (modified NY criteria) in southwestern Sweden were recruited to a cohort study as previously described [1]. This report is based on the 13 year follow-up evaluation, where measures of clinical disease activity (the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score with CRP (ASDAS), the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI)), physical function (the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (BASFI)), back mobility (the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index (BASMI)), and r-axSpA-related radiographic spinal changes (the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spinal Score (mSASSS))) was evaluated along with blood lipid profile, biomarkers of inflammation and health history. In addition, the first recorded C-reactive protein (CRP) concentration each year since inclusion deemed unrelated to acute infection, was collected and a historical time-averaged CRP was calculated. For each patient, four controls matched on sex, age and geographic location were collected from the Swedish CArdioPulmonary bioImage Study (SCAPIS) [2], a study that invited randomly selected participants from the Swedish population registry, (n = 30154, 50-64 years old). Patients with r-axSpA, in the same age-span as the controls, and controls were examined with computed tomography of the heart and the calcium content in each coronary artery was measured to produce right coronary artery score, circumflex coronary artery score, left main and left anterior descending coronary artery score and a total CAC score according to the Agatston method [3]. To investigate possible trends in medians, Jonckheere-Terpstra test was used. To test distributions in categorical variables, Fishers Exact test and Fisher-Freeman-Halton tests were used. For comparison of continuous variables between two groups, Mann Whitney U-test was used.
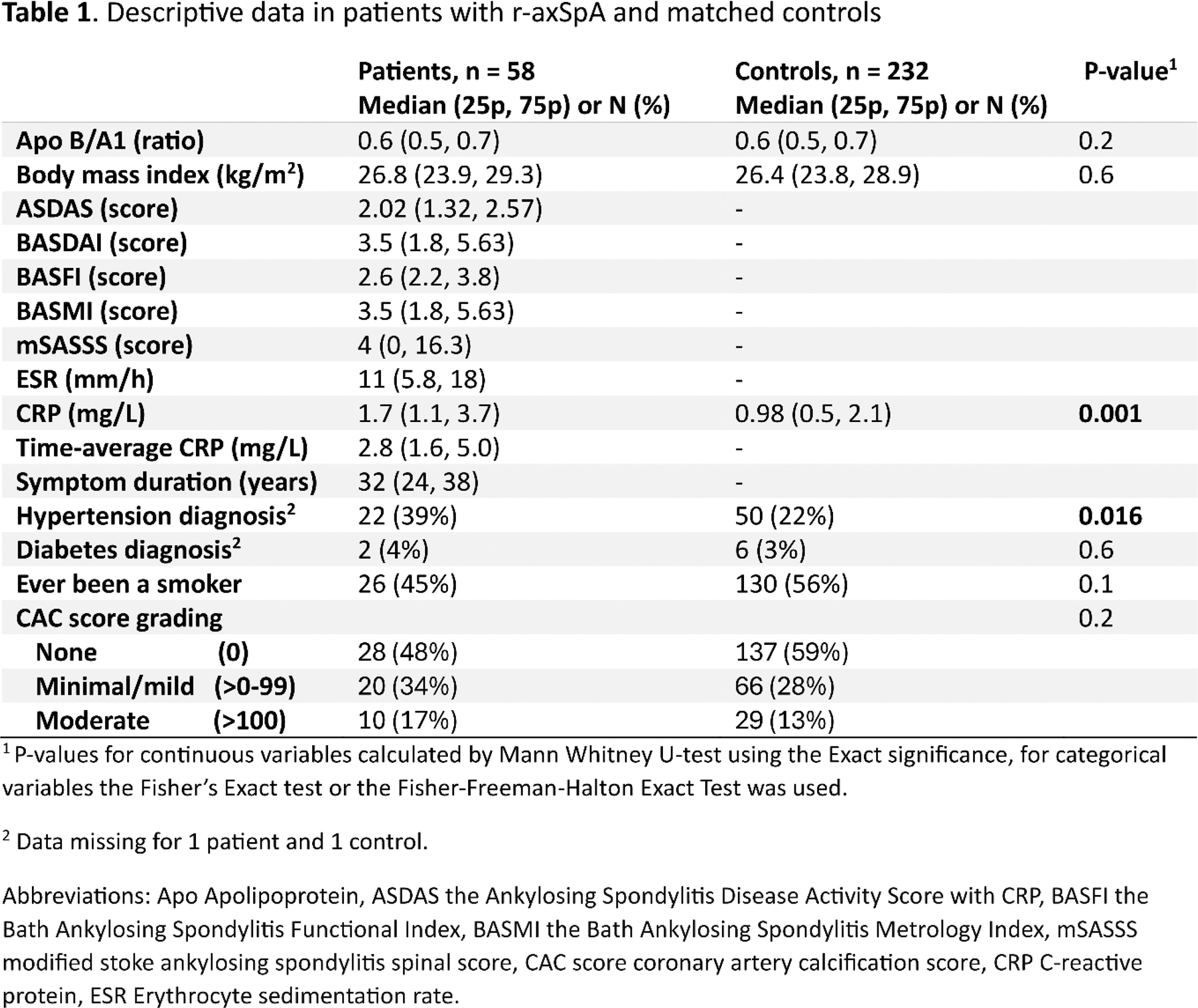
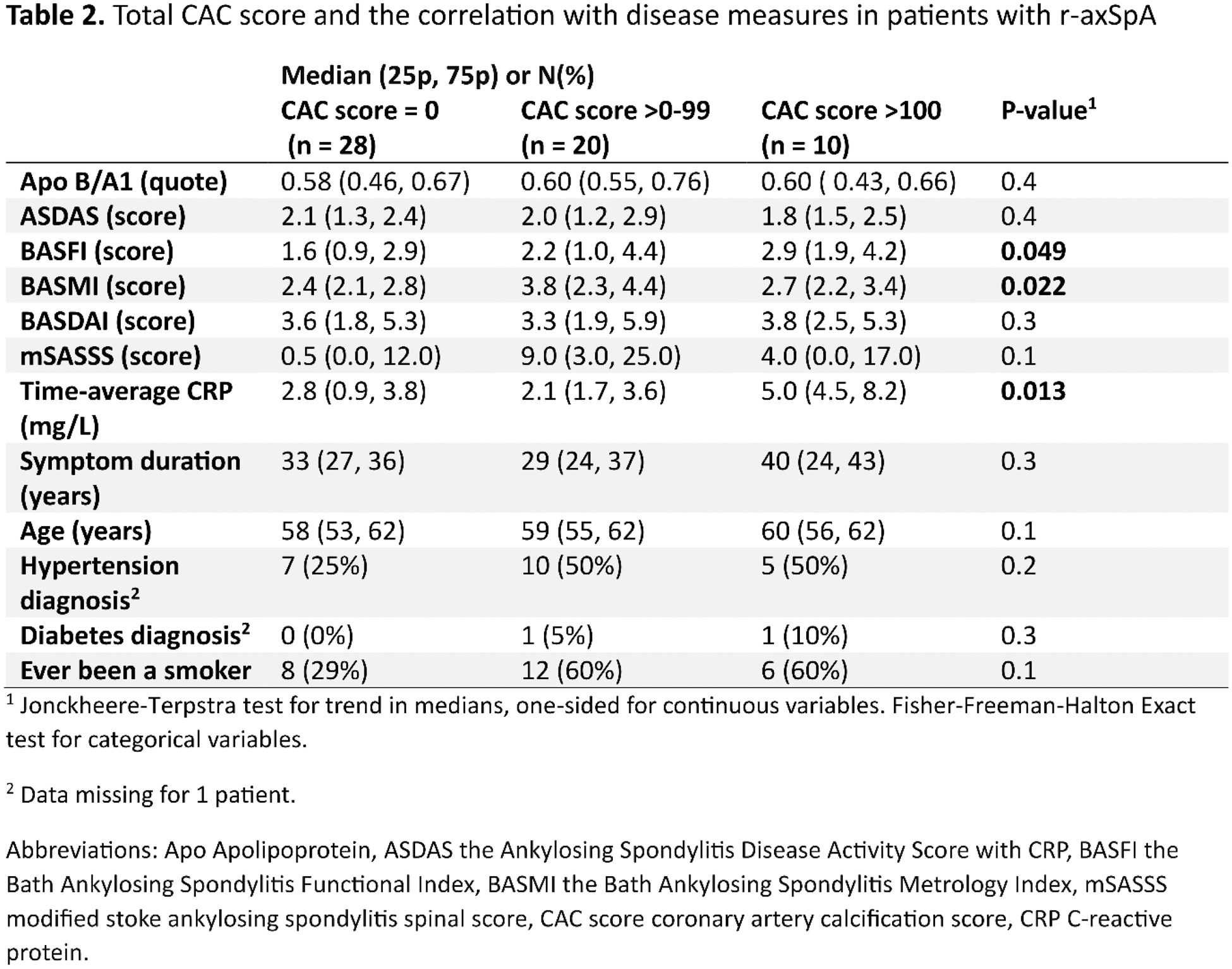
Results: In total 58 patients with CAC score and 232 matched controls were included, 48% of participants were females, mean age was 58 years and 83% of the patients were HLA-B27 positive. Among the patients, 17% were treated with csDMARDs and 38% with bDMARDs and 29% used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs at least twice per week. Patients with r-axSpA had similar total CAC score compared to controls (Table 1). Within patients with r-axSpA, the time-averaged CRP, the BASFI and BASMI score were significantly correlated with the CAC score (Table 2).
Conclusion: Chronic inflammation appears to accelerate coronary calcification and thereby predicate CVD development in patients with r-axSpA, possibly indicating the importance of efficient treatment to reduce systemic inflammation. Furthermore, spinal immobility and functional limitations were related to coronary calcification, which warrants further investigation. While the CAC score was higher among patients compared to controls, no significant differences were detected, however, the number of patients were relatively low which calls for an interpretation with caution.
REFERENCES: [1] Klingberg E, et al. Arthritis research & therapy. 2012;14(3):R108.
[2] Bergström G, et al. J Intern Med. 2015;278(6):645-59.
[3] Agatston AS, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990;15(4):827-32.
Acknowledgements: We would like to thank research nurses Anneli Lund and Marie-Louise Andersson for their work with the study and thank all participating patients.
Disclosure of Interests: Erik Hulander: None declared, Anna Deminger: None declared, Sofia Enegren: None declared, Magnus Hallström: None declared, Caroline Feldthusen: None declared, Erika Fagman: None declared, Oskar Angerås: None declared, Tatiana Zverkova Sandstrom: None declared, Mats Geijer Abbvie, UCB, Helena Forsblad-d’Elia: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (