

Background: Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are at an elevated risk for cardiovascular (CV) events compared to the general population. One method for assessing CV risk is the measurement of non-HDL cholesterol (Non-HDL-C), a biomarker that has demonstrated reliability in identifying coronary artery disease and increased carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT). As such, non-HDL cholesterol could serve as a valuable index for managing CV risk in patients with PsA.
Objectives: To associate the levels of Non-HDL-C and the presence of carotid plaque (CP) in patients with PsA.
Methods: A cross-sectional, descriptive, comparative study was conducted. Patients aged 30 to 75 with PsA who met the 2006 CASPAR Classification criteria were included. Those with CV disease history were excluded. Carotid ultrasound was performed on all participants and CP was defined as a diffuse carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) ≥1.2 mm or focal thickness ≥0.8 mm. Non-HDL-C was calculated by subtracting HDL cholesterol levels from total cholesterol. Patients will be categorized into two groups: those with levels >130 mg/dl will be classified as high, and those with levels <130 mg/dl as low. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was employed to determine normality. Comparisons with Chi-square and Student’s T- or Mann Whitney’s U-test, accordingly. A p-value of ≤0.05 was considered statistically significant.
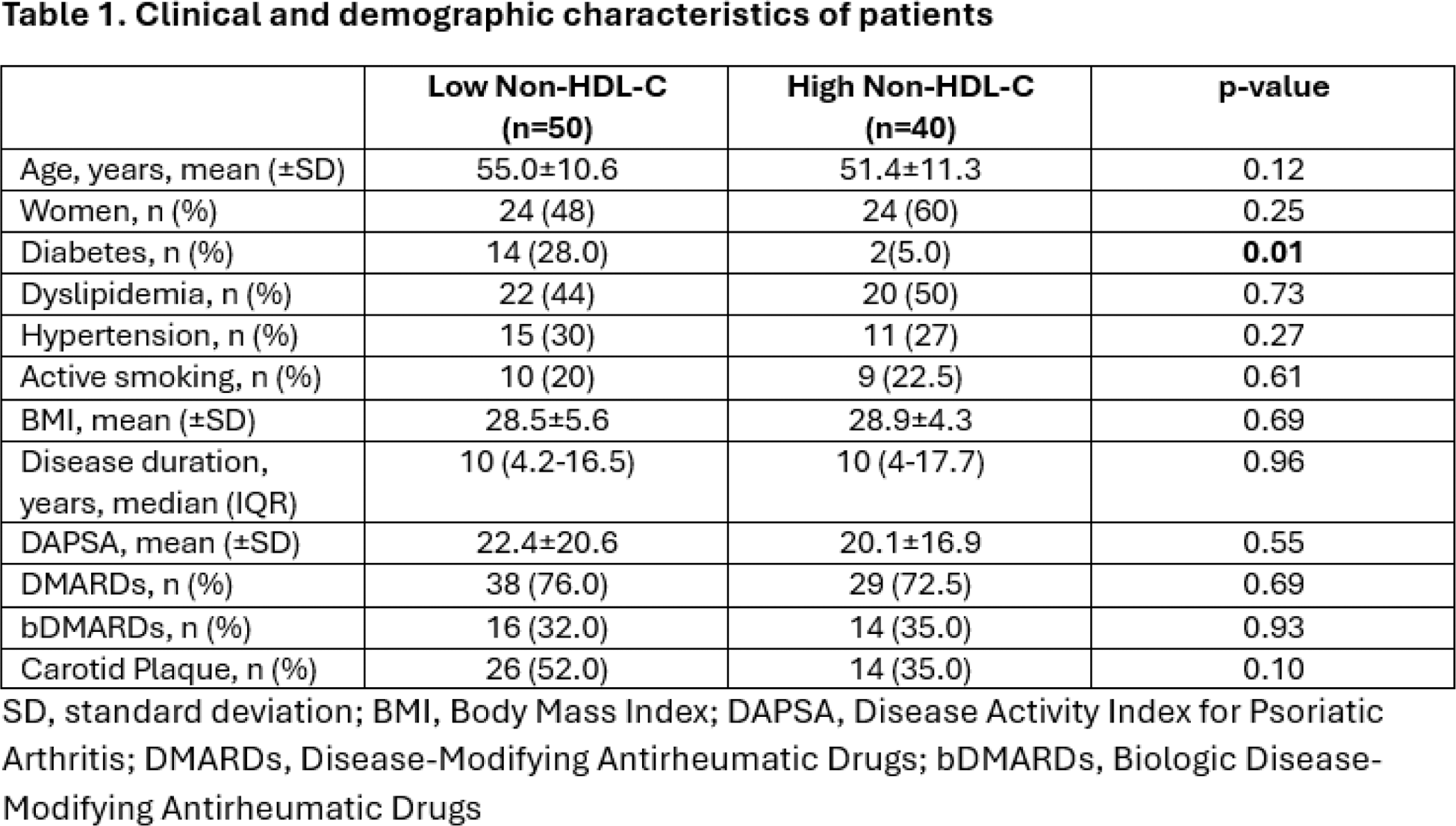
Results: A total of 90 patients with PsA were recruited (Table 1): 40 with high levels of Non-HDL-C and 50 with low levels of Non-HDL-C. The mean age of the patients was 53.4±11.1 years. CV comorbidities were similar between both groups, with no statistical significance found, except for diabetes (p=0.01). CP was detected in 44.4% of the total sample; however, although patients with low Non-HDL-C had the highest prevalence (n=26, 32%), no statistical significance was observed.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that Non-HDL-C levels do not show a significant association with the presence of CP in patients with PsA. Further research with larger cohorts are essential to gain a deeper understanding of the relationship between lipid profiles and CV risk assessment in PsA patients.
REFERENCES: [1] Yun YM. Apolipoprotein B, Non-HDL Cholesterol, and LDL Cholesterol as Markers for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment. Ann Lab Med. 2023 May 1;43(3):221-222. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.43.3.221. Epub 2022 Dec 22. PMID: 36544332; PMCID: PMC9791017.
[2] Aggarwal DJ, Kathariya MG, Verma DPK. LDL-C, NON-HDL-C and APO-B for cardiovascular risk assessment: Looking for the ideal marker. Indian Heart J. 2021 Sep-Oct;73(5):544-548. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2021.07.013. Epub 2021 Jul 31. PMID: 34627566; PMCID: PMC8514398.
[3] Sniderman AD, Williams K, Contois JH, et al. A meta-analysis of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and apolipoprotein B as markers of cardiovascular risk. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2011 May;4(3):337-345. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.110.959247.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (