

Background: Lupus nephritis (LN) is a severe manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus, characterised by kidney inflammation and damage. Since the current standard therapy, typically consisting of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) plus glucocorticoids, is often insufficient to control disease activity, increased rate of complete renal response (CRR) attainment is a major unmet need. To achieve this goal, depletion of B cells is a compelling strategy given their key role in LN pathogenesis. Obinutuzumab, a recombinant, monoclonal, humanised and glycoengineered type II CD20 antibody, with more potent depletion B-cell capabilities than type I anti-CD20s, was found to be effective in the Phase II NOBILITY (NCT02550652) study of LN, demonstrating a pharmacodynamic effect of profound peripheral B-cell depletion (including naïve, memory and plasmablast/plasma subsets), resulting in reduced serum anti-double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibodies and increases in complement C3 and C4 levels. A confirmatory Phase III study (REGENCY, NCT04221477) of obinutuzumab plus standard therapy in patients with active LN demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in Week 76 CRR and an acceptable safety profile.
Objectives: Exploratory analyses of peripheral B-cell populations and serological markers, including complement components (C3, C4) and anti-dsDNA antibodies, were performed to further confirm the pharmacodynamic effects of obinutuzumab in patients enrolled in the Phase III REGENCY study.
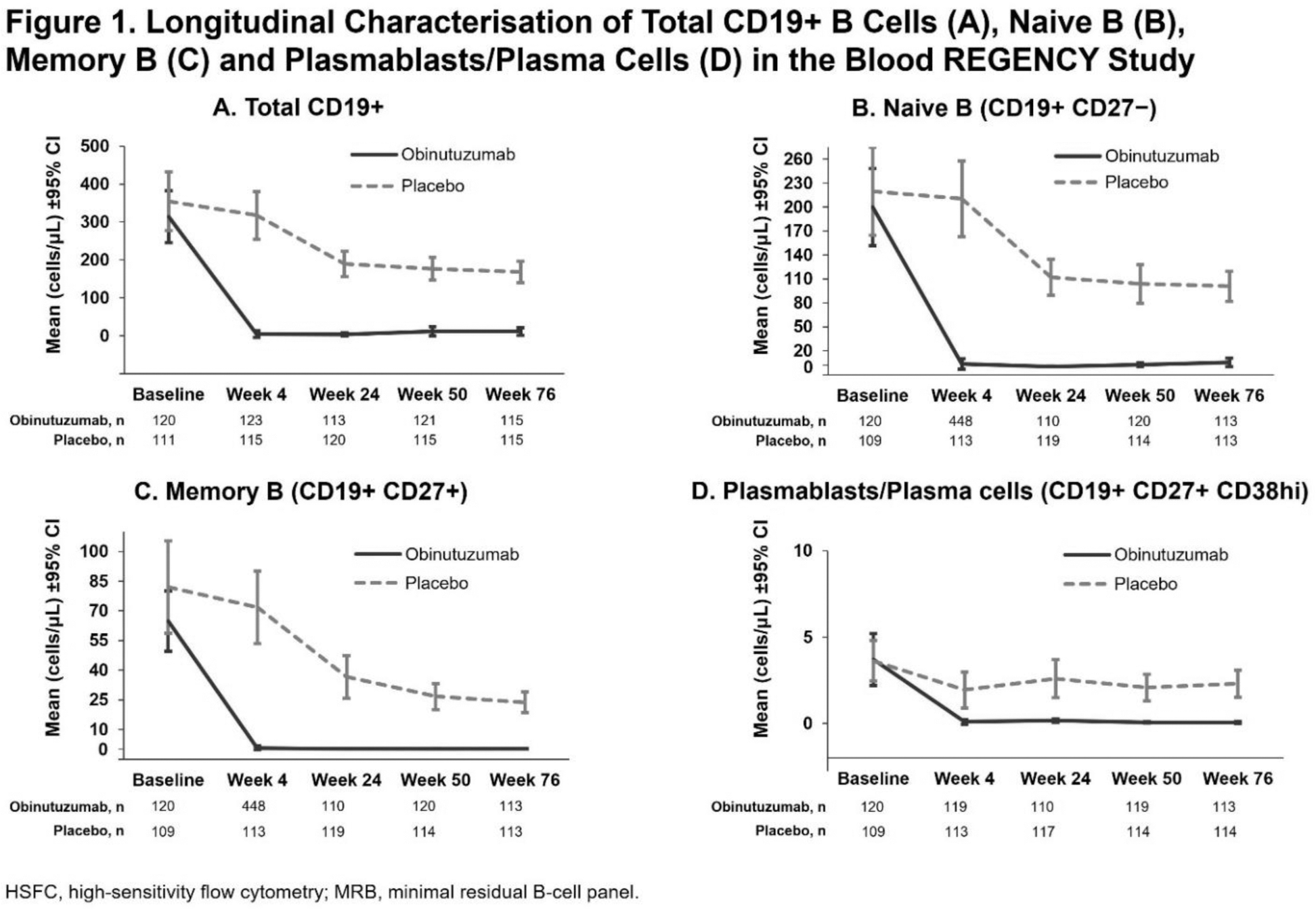
Methods: Adults with biopsy-proven active proliferative LN were randomised 1:1 to placebo or obinutuzumab in addition to standard therapy with MMF plus glucocorticoids. The primary endpoint at Week 76 was CRR (urine protein-to-creatinine ratio <0.5 g/g, estimated glomerular filtration rate ≥85% of baseline and no intercurrent events: rescue therapy, treatment failure, death or early study withdrawal). Peripheral B cells and B-cell subsets were assessed at a central laboratory using validated high-sensitivity flow cytometry (HSFC) assays minimal residual B-cell panel (MRB)1.1 and BCP2.2, respectively. Details of the markers used to define the subsets are displayed on Figure 1. The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) of CD19+ B cells by MRB1.1 is 0.441 cells/μL. Complement components and anti-dsDNA antibody levels were measured at a central laboratory by nephelometry and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, respectively. Peripheral B-cell and serum biomarker assessments were performed on the safety-evaluable and efficacy-evaluable population, respectively, from samples drawn at Weeks 0, 4, 12, 24, 50 and 76.
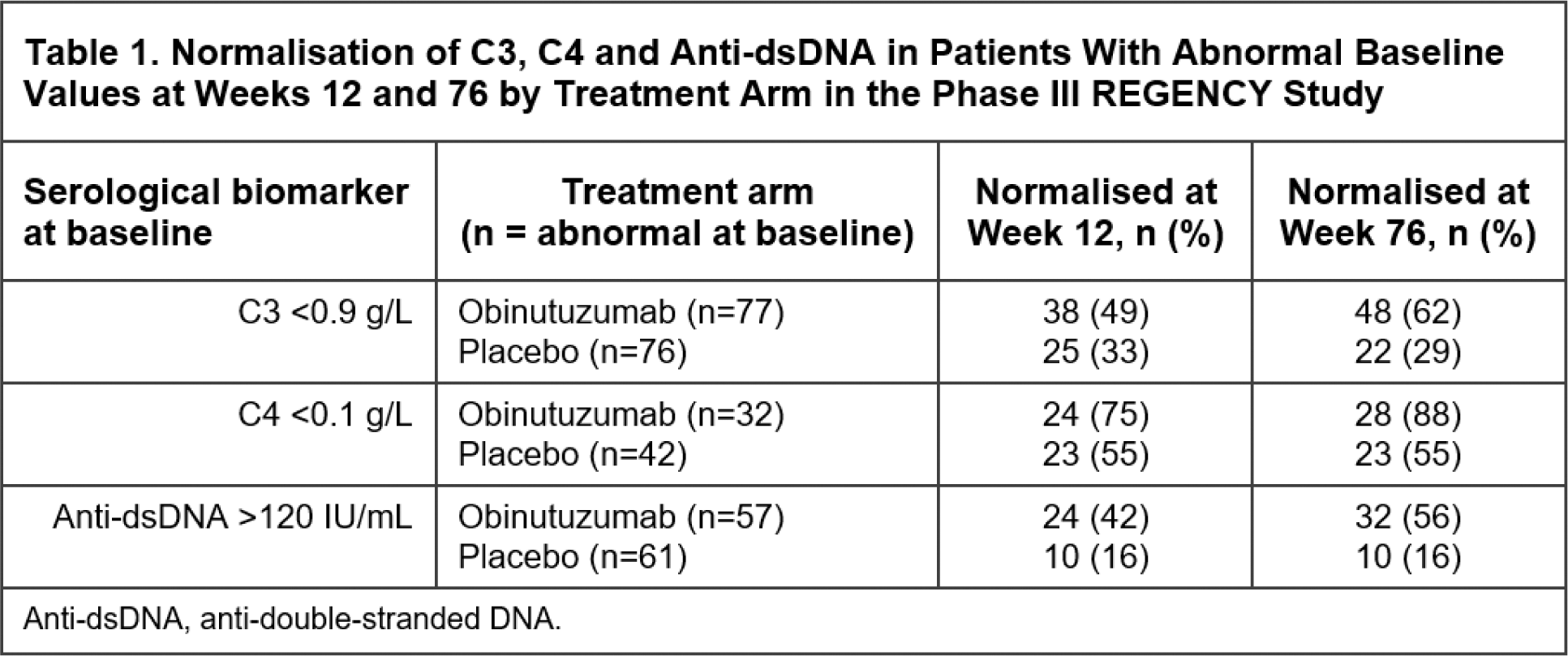
Results: At baseline, biomarker levels were generally comparable between the two arms and no patients had B-cell levels below the LLOQ by MRB1.1. At Week 4, the first post-treatment timepoint for peripheral B-cell assessment by HSFC, the mean total CD19+ B-cell levels were greatly reduced in the obinutuzumab group (mean cells/μL [SD]: 4.7 [45.6], −99.8 median % change from baseline) compared with placebo group (mean cells/μL [SD]: 317.8 [338.5], −4.2 median % change) and remained low relative to placebo at every timepoint tested through Week 76 (Figure 1A). Similar substantial decreases in circulating B-cell subsets, including naïve, memory and plasmablast/plasma cells, were observed in the obinutuzumab group relative to placebo from Week 4 through Week 76 (Figure 1B–D). In all patients, treatment with obinutuzumab also resulted in greater reductions in anti-dsDNA antibody levels and increases in complement C3 and C4 relative to placebo. Furthermore, amongst patients with abnormal baseline serologies, higher normalisation rates for C3 (43% versus 14%), C4 (70% versus 39%) and anti-dsDNA antibody levels (45% versus 11%) were observed at Week 12 in the obinutuzumab versus placebo arms, and these normalisation rates were sustained or further improved through Week 76, with normalisation rates of 62% versus 29% for C3, 88% versus 55% for C4 and 56% versus 16% for anti-dsDNA antibody levels at Week 76 (Table 1).
Conclusion: Obinutuzumab plus standard therapy induced rapid and sustained depletion of total peripheral CD19+ B cells, including potentially pathogenic subsets such as memory B cells and plasmablasts/plasma cells, in patients with active LN. Concurrent with B-cell depletion, obinutuzumab demonstrated improvements in serological markers of disease activity, such as greater increases in serum C3 and C4 levels, and reductions in anti-dsDNA antibody levels over placebo in all patients. Furthermore, amongst the subset of patients with abnormal baseline values for these markers, obinutuzumab led to earlier and greater normalisation rates compared with placebo. Along with the results from the NOBILITY study, these data support the mechanistic hypothesis that deep B-cell depletion with obinutuzumab contributes to the improved clinical responses observed in LN, reinforcing its potential as a new treatment option for patients with LN.
REFERENCES: NIL.
Acknowledgements: Funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. Editorial assistance was provided by Nucleus Global, an Inizio company, and funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
Disclosure of Interests: Richard A. Furie consulting fees from GlaxoSmithKline and Genentech, Inc., research support from GlaxoSmithKline and Genentech, Inc., Ioannis Parodis consulting fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Aurinia, BMS, Eli Lilly, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Otsuka and UCB, research support from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Aurinia, BMS, Eli Lilly, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Otsuka and UCB, Rachel Jones consulting fees from F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, GlaxoSmithKline and CSL Vifor, research support from F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, GlaxoSmithKline and CSL Vifor, Liz Lightstone consulting fees from F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Alexion, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Kezar, Novartis, Otsuka and Pfizer, Olivia Hwang shareholder of F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, employee of Genentech, Inc, Amelia Au-Yeung shareholder of F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, employee of Genentech, Inc., Imran Hassan employee of F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Huiyan (Ashley) Mao shareholder of F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, employee of F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, William F. Pendergraft III shareholder of F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, employee of Genentech, Inc., Jay P. Garg shareholder of F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, employee of Genentech, Inc., Harini Raghu shareholder of F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, employee of Genentech, Inc., Brad H. Rovin consulting fees from F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd/Genentech, Inc.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (