

Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is one of the most common systemic autoimmune diseases, affecting approximately 0.5-1% of the global population [1]. MicroRNAs (miRNA) play a critical role in regulating immune responses, immune cell development, and autoimmunity, suggesting their involvement in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases like RA, Sjögren’s syndrome, and systemic lupus erythematosus [2, 3]. Moreover, miRNA-223 is overexpressed in RA synovial tissue, and its silencing has been shown to reduce disease severity in experimental arthritis models [4].
Objectives: To determine whether serum levels of miRNA-223 and miRNA-146a could serve as diagnostic biomarkers for RA, correlate with disease activity, and potentially reflect treatment response.
Methods: Serum levels of miRNA-146a and miRNA-223 were measured in 60 RA patients and 30 healthy controls. Disease activity was assessed using the Disease Activity Score 28 (DAS28). Patients were stratified into two groups based on their treatment regimen: 30 patients on conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs) and 30 patients on biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs). The expression levels of miRNA-146a and miRNA-223 were assessed by real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
Results: In patients with RA, there was a significant overexpression of miRNA-146a compared to healthy controls (p<0.05). The Area Under the Curve (AUC) for miRNA-146a in serum was 0.679 (95% Confidence Interval: 0.572-0.774, p<0.001), indicating its diagnostic potential (Table 1).
Predictive Values of miRNA-146a and miRNA 223 for RA
| AUC (95% CI) | Cut-off According to the Youden’s Index | p-value | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRNA-146a | 0.679 (0.572-0.774) | 28.47 | 0.001 | 66.67 | 70 |
| miRNA-223 | 0.588 (0.479-0.691) | 28.92 | 0.155 | 51.67 | 70 |
AUC: Area Under the Curve; miRNA: microRNA
ROC curve analysis revealed that miRNA-146a had a sensitivity of 66.67% and specificity of 70% (Figure 1). Both miRNA-146a and miRNA-223 levels were found to be highest in patients with high disease activity, and their elevated levels were strongly associated with elevated CRP and DAS28 scores, both of which are indicators of systemic inflammation and disease activity in RA.
miRNA-146a and miR-223 exhibited upregulation in RA; however, the increase in miRNA-223 was not statistically significant. 1A. ROC analyses linked miRNA-146a and RA with a sensitivity of 66,67% and specificity of 70% 1B. ROC analyses linked miRNA-223 and RA with a sensitivity of 51.67% and specificity of 70%.
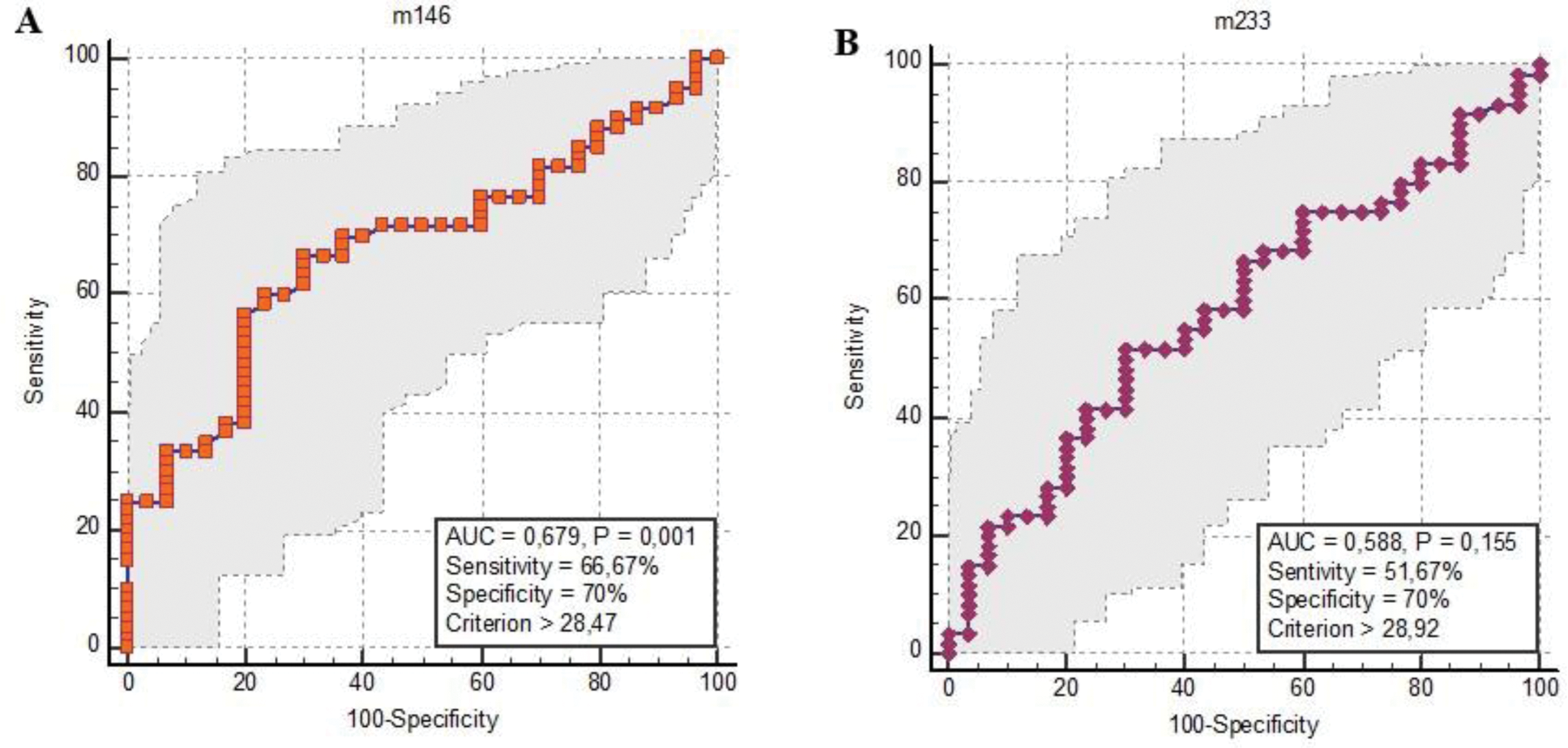
Conclusion: The high specificity of miR-146a upregulation in RA patients highlights its importance in RA pathogenesis. Additionally, the correlation of miRNA-223 and miR-146a with CRP levels, tender joints, and DAS28 scores underscores their potential as reliable biomarkers for disease activity in RA. Future large-scale, multi-center studies are needed to further investigate their roles and evaluate the feasibility of targeting these miRNAs for therapeutic interventions.
REFERENCES: [1] Almutairi K, Nossent J, Preen D, Keen H, Inderjeeth C. The global prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis based on a systematic review. Rheumatol Int. 2021;41(5):863-77.
[2] Pauley KM, Cha S, Chan EK. MicroRNA in autoimmunity and autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun. 2009;32(3-4):189-94.
[3] Alevizos I, Alexander S, Turner RJ, Illei GG. MicroRNA expression profiles as biomarkers of minor salivary gland inflammation and dysfunction in Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(2):535-44.
[4] Li YT, Chen SY, Wang CR, Liu MF, Lin CC, Jou IM, et al. Brief report: amelioration of collagen-induced arthritis in mice by lentivirus-mediated silencing of microRNA-223. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(10):3240-5.
Acknowledgements: The present study is supported by the Firat University Coordinatorship of Scientific Research Projects (No: TF.16.05).
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (