

Background: Monogenic lupus is a rare form of lupus caused by pathogenic variations in single genes.
Objectives: This literature review aims to evaluate all available cases of monogenic lupus in the literature, identifying and summarizing the characteristic genotypic and clinical features of patients with this disorder.
Methods: Google Scholar, PubMed and Web of Science databases were reviewed, resulting in the identification of 1291 articles. After abstract and title evaluations, 271 articles were retrieved. Following the exclusion of duplicates, 182 articles remained for full-text evaluation. Ultimately, 91 articles were included in the study.
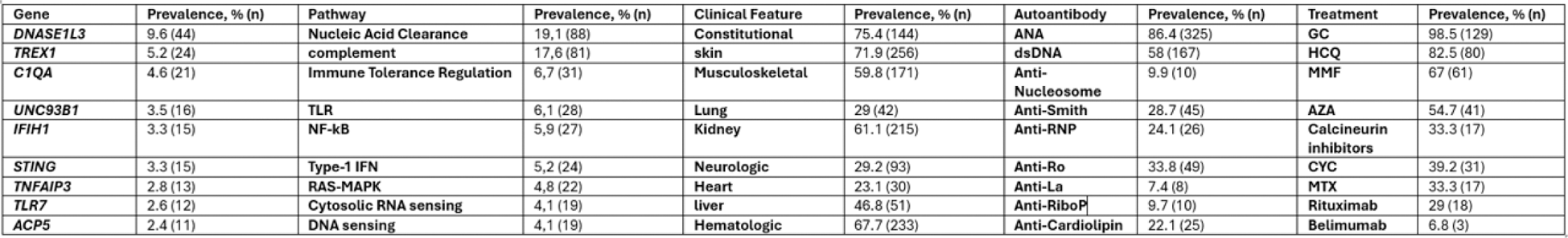
Results: This review identified 460 patients with monogenic lupus and 149 disease-causing genes. Clinical features, antibody profiles, treatment modalities, and the most commonly affected genes and pathways are summarized in the table. The mortality rate of patients with available data was %8.6 (11). Skin and neurologic involvement were more common, while kidney involvement was less common in females (%81.2 vs 64.6 p-value:0.003, %33.3 vs %19.8 p-value:0.03, %65.3 vs %78 p-value:0.032). Deceased patients exhibited increased rates of lung, hematological, neurological, and heart involvement (%20 vs %36.1 p-value:0.011, %100 vs %64 p-value:0.033, %66.7 vs %26.1 p-value:0.018, %100 vs %8.8 p-value:0.000, respectively) and decreased GC response rates (%28.6 vs %78 p-value:0.015). Musculoskeletal (MSK) involvement was associated with more frequent kidney, neurologic, and liver involvement (%67.5 vs %51.5 p-value:0.033, %33.3 vs %18.6 p-value:0.045, %62.5 vs %25 p-value:0.002). Additionally, patients with MSK involvement had higher rates of azathioprine (AZA) and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) use (%60.5 vs %28.6 p-value:0.019, %53.3 vs %18.8 p-value:0.031). Kidney involvement was associated with higher rates of hematologic and lung involvement, and increased ANA and Anti-dsDNA positivity rates (%76.8 vs %63.9 p-value:0.043, %37.8 vs %14.9 p-value:0.012, %94.2 vs %86.6 p-value:0.041, %69.3 vs %46.6 p-value:0.002, respectively). Furthermore, methotrexate (MTX), mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), and cyclophosphamide (CYC) were used more frequently in these patients (%50 vs %15.6 p-value:0.027, %80.9 vs %45.9 p-value:0.001, %65.7 vs %17.5 p-value:0.000).
Conclusion: Genes involved in nucleic acid clearance, complement activation, and immune tolerance regulation were the most frequently affected among these patients. Lung, heart, hematological, and neurological involvement, and unresponsiveness to GCs were associated with mortality. Patients exhibiting these features should be closely monitored and treated more aggressively.
REFERENCES: NIL.
Table 1.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (