

Background: Anti-TNF-alpha and anti-IL-17 drugs are widely used in Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) and have shown good results in terms of both efficacy and safety [1]. However, a subset of patients may still experience residual pain due to central sensitization mechanisms typical of Fibromyalgia (FM). This leads to more complex disease management and less satisfactory therapeutic outcomes.
Objectives: The aim of our study is to evaluate the efficacy of anti-TNF-alpha and anti-IL-17 drugs in managing inflammatory and neuropathic pain, as well as fatigue, in patients diagnosed with PsA and concomitant FM.
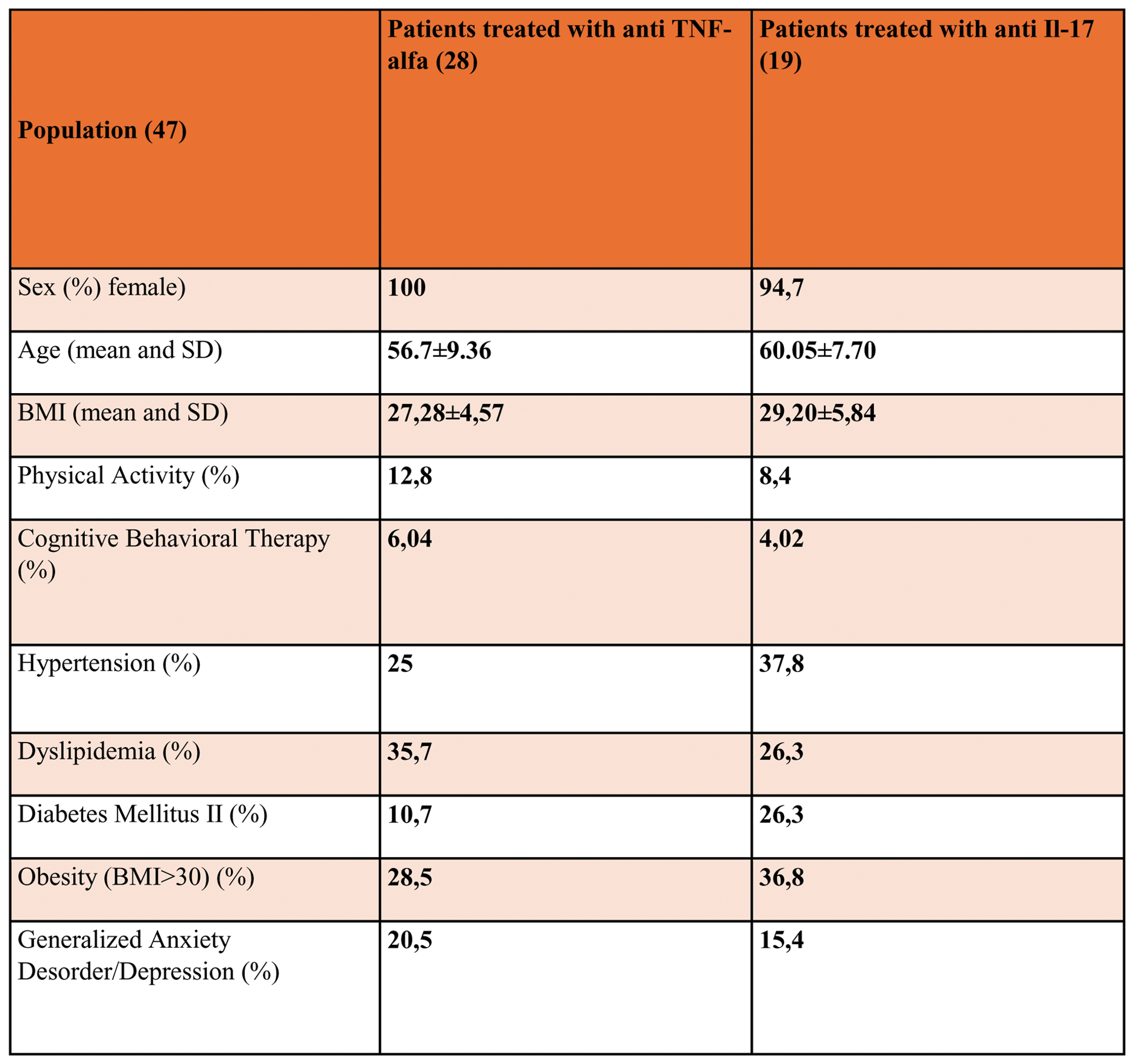
Methods: We enrolled 47 patients diagnosed with PsA (according to the CASPAR 2006 criteria) and FM (according to the ACR 2016 criteria) and treated with anti-TNF-alpha and anti-IL-17 drugs (Table 1). Disease activity was assessed using DAPSA, neuropathic pain using PDQ, subjective pain using VAS, and fatigue using FACIT. All data were collected at baseline and after 4 months of therapy. Statistical analysis was performed using the Wilcoxon test for paired samples and the Mann-Whitney U test for unpaired samples.
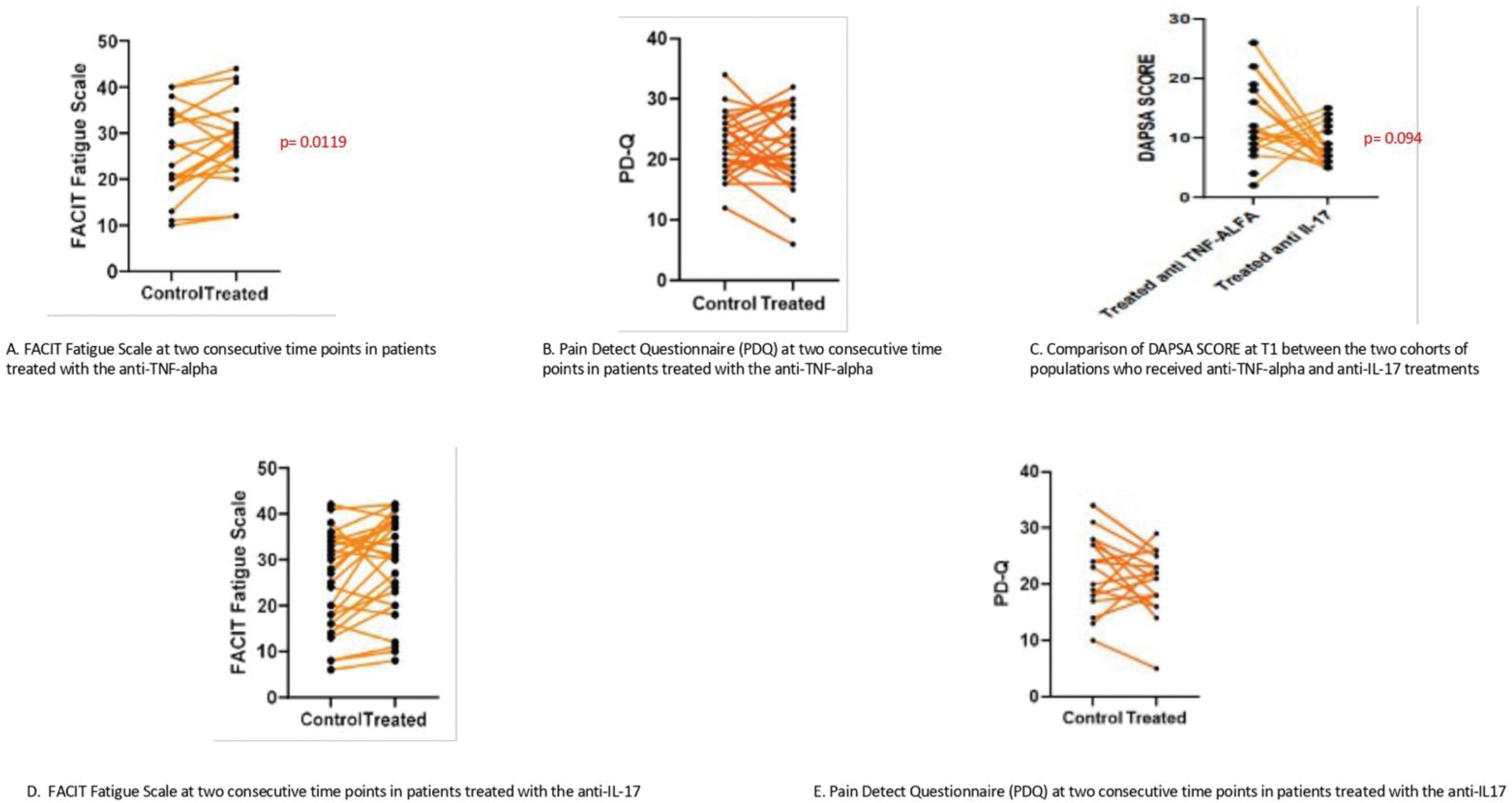
Results: Comparing the two patient groups, we observed that patients treated with Anti-TNF-alpha showed an improved fatigue (p=0.0119) (Figure 1 A) and reduced PDQ by 28.5% (Figure1 B). Patients treated with Anti-IL-17 achieved greater DAPSA reduction (p=0.0094) (Figure1 C) but had limited impact on fatigue and neuropathic pain (Figure1 D, E).
Conclusion: Residual pain in patients with psoriatic arthritis and concomitant fibromyalgia represents a challenging issue. Several studies have shown the role of anti-TNF-alpha and IL-17 in modulating neuropathic pain, suggesting a potential target for chronic pain [3, 4]. In our patients, there was also a reduction in fatigue and PDQ, demonstrating that these drugs have significant effects in improving chronic pain. Studies on a larger cohort of patients and long-term follow-up are needed to confirm the efficacy of these drugs on residual pain as well.
REFERENCES: [1] L. Gossec et al., “EULAR recommendations for the management of psoriatic arthritis with pharmacological therapies: 2019 update,” Ann Rheum Dis, vol. 79, no. 6, pp. S700–S712, Jun. 2020.
[2] C. J. Woolf, “Central sensitization: Implications for the diagnosis and treatment of pain,” Pain, vol. 152, no. 3, pp. S2–S15, Mar. 2011.
[3] A. D. Kaye et al., “Tumor Necrosis Factor and Interleukin Modulators for Pathologic Pain States: A Narrative Review,” Pain Ther, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 481–493, Jun. 2024.
[4] X. Jiang, R. Zhou, Y. Zhang, T. Zhu, Q. Li, and W. Zhang, “Interleukin-17 as a potential therapeutic target for chronic pain,” Front Immunol, vol. 13, Sep. 2022.
Table 1. Demographic characteristics of patients.
Results of FACIT FS, PD-Q and DAPSA in patient treated with anti TNF alpha and anti IL17.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (