

Background: Panniculitis is a relatively rare condition characterized primarily by inflammation of the subcutaneous fat [1-2]. Its occurrence may be associated with infections, autoimmune diseases, injuries, malignant tumors, inflammatory diseases, and other factors.When the etiology is unclear, it is referred to as primary lipedema. Currently, there is limited knowledge regarding the immunological features of primary lipedema. To evaluate the differences of lymphocyte subsets in primary panniculitis.
Objectives: To evaluate the differences of lymphocyte subsets in primary panniculitis.
Methods: We included 18 patients diagnosed with primary lipodystrophy, confirmed by pathology between January 2018 and November 2004, while excluding secondary causes such as autoimmune diseases, tumors, and infections. Additionally, we incorporated 18 healthy controls matched for gender and age. We collected general clinical characteristics and laboratory tests, and performed flow cytometry on peripheral blood to assess lymphocyte subtypes (T, B, NK, CD4 + T and CD8 + T)and CD4 + T cell subsets(Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg). The study was approved by the ethics committee of the Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University.
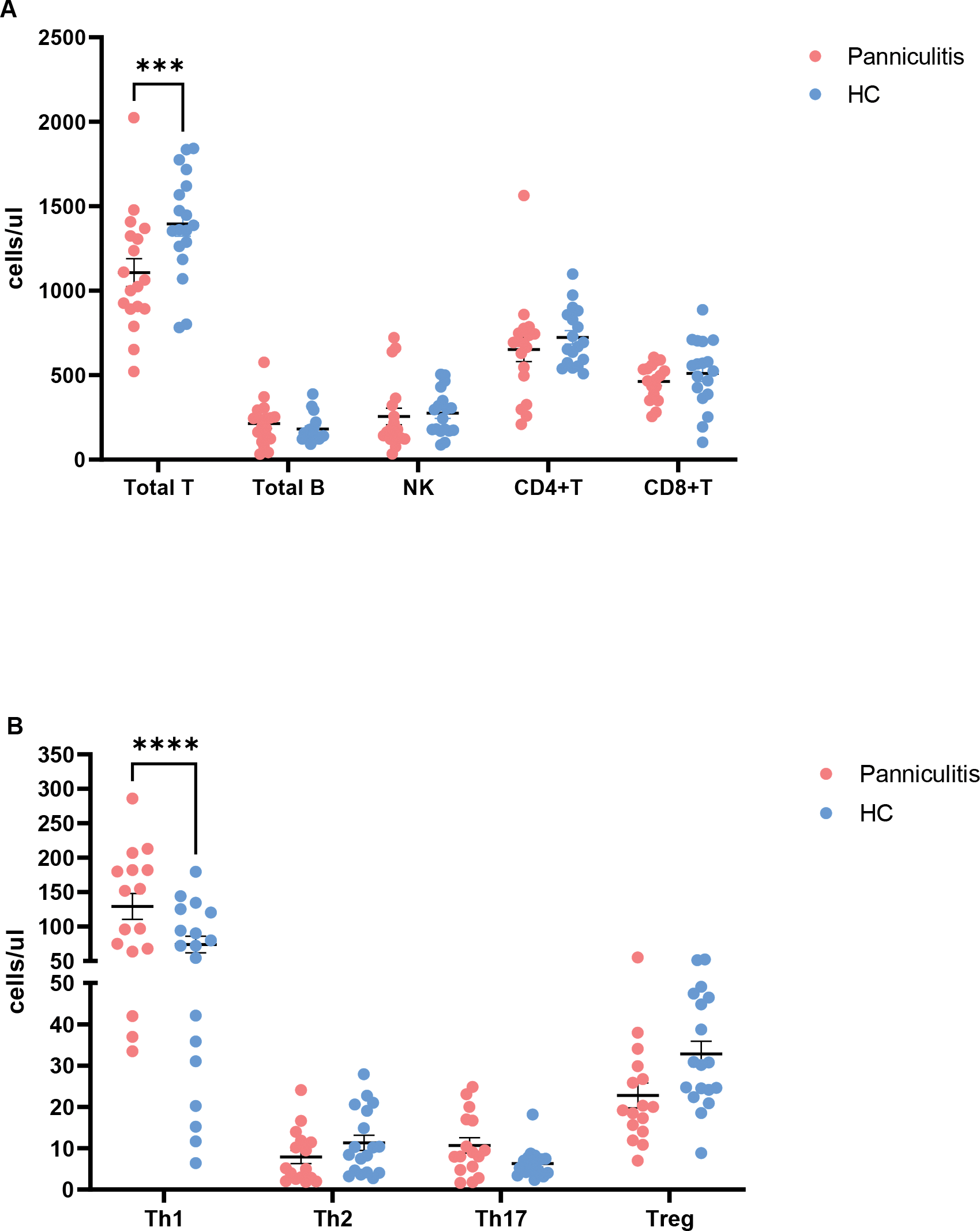
Among the 18 cases of primary lipomatosis included in our study, 12 presented with subcutaneous nodules as the initial manifestation, while 7 exhibited annular erythema as the primary symptom. Notably, 4 cases also experienced fever. The most commonly affected areas for subcutaneous nodules were the upper and lower limbs (n=10) (Figure 1A).
In the analysis of peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets, the absolute value of total T cells in the lipomatosis group was found to be lower than that of healthy controls, while there were no significant differences in the absolute value of total B cells, NK cells, and CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. About the comparsion of CD4+ T cell subsets, the Th1 cells in the lipomatosis group was significantly higher than that of healthy controls, whereas there were no differences in Th2, Th17, and Treg cells (Figure 1B).
Conclusion: The results suggest the presence of T cell-mediated immune dysregulation in primary lipomatosis, particularly characterized by a predominance of Th1-driven immune inflammation. Focusing on this immune disorder may provide directions for further therapeutic interventions.
REFERENCES: [1] Borges T, Silva S. Panniculitis: A Cardinal Sign of Autoinflammation. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2024;20(4):350-360.
[2] Wick MR. Panniculitis: A summary. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2017 May;34(3):261-272.
The immune features of primary panniculitis. A. The comparision of T,B,NK,CD4 + T and CD8 + T cells. B.The comparision of CD4 + T subsets.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.
© The Authors 2025. This abstract is an open access article published in Annals of Rheumatic Diseases under the CC BY-NC-ND license (